Session Information
Date: Wednesday, October 24, 2018
Title: 6W023 ACR Abstract: RA–DX, Manifestations, & Outcomes VI: Outcomes Reports (2982–2987)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose:
Mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is higher than in the general population. In most studies this becomes apparent only after more than a decade of follow up. The COBRA (COmbinatietherapie Bij Rheumatoide Artritis) trial showed long-term effectiveness of combination therapy of early RA without undue harm [1]. After 11 years of follow up, patients with COBRA treatment had numerically lower mortality compared to patients with sulphasalazine (SSZ) monotherapy [2]. We now present mortality in the COBRA trial cohort after 23 years compared to the general population and explore early predictive factors.
Methods:
In the COBRA trial, patients with early RA (median disease duration, 4 months) were treated with SSZ monotherapy (n=79) or a combination of SSZ, low-dose methotrexate and initially high, step-down prednisolone (COBRA, n=76). We investigated mortality in the COBRA cohort through the Dutch state registry for mortality (Centrum van Familiegeschiedenis). We compared the mortality in this cohort to a reference sample of the general population in the Netherlands matched for age and gender (Statistics Netherlands). The Standardized Mortality Ratio (SMR) compared the trial groups with the general population. We explored the following early predictive factors for mortality through forward stepwise Cox regression: smoking, treatment, disease duration (according to 3 definitions), disease activity score (DAS-44) and 16-week change; Health assessment questionnaire; rheumatoid factor (ACPA not available at that time); Sharp van der Heijde damage score and change at 28 and 56 weeks; HLA-DR1-4.
Results:
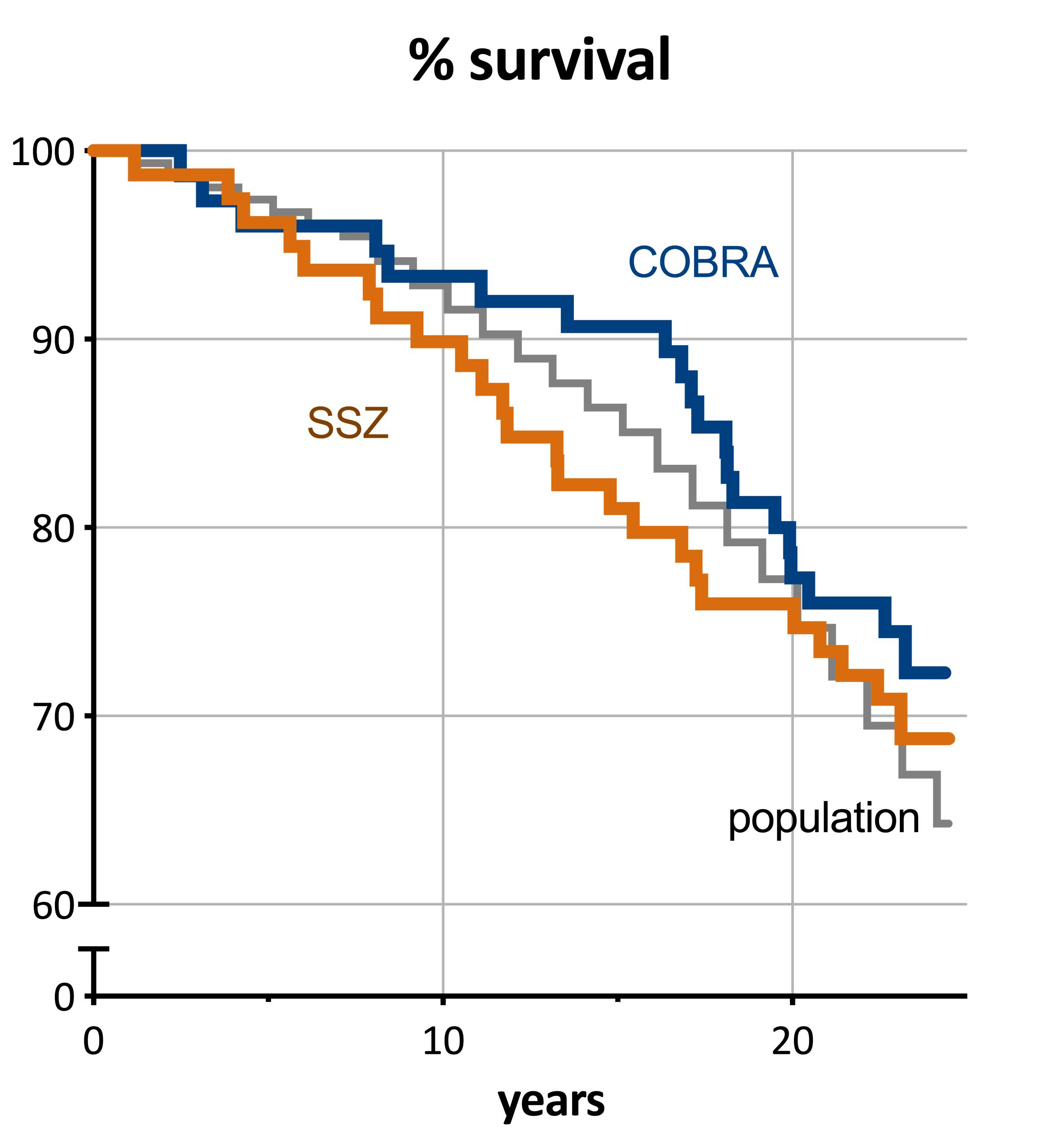
Follow up was nearly complete (154/155 patients). Duration of follow up was mean 23 (in patients alive, range 22-24) years. In total 44 patients died (28%, SMR = 0.80 [95%CI: 0.59-1.06]); 20 of 75 COBRA patients (27%, SMR 0.75; [0.47-1.14]) and 24 of 79 SSZ patients (30%, SMR 0.85 [0.56-1.25]); the difference in mortality was not significant (p=0.61). In the general population reference sample (n=154) 55 people (36%) died. The positive trend for COBRA over SSZ decreased over time (Figure). 5 factors were significantly associated with increased mortality hazard: damage progression at 28 weeks; high HAQ score; and absence of HLA-DR 2 or 3. Disease duration from start of complaints showed a nonlinear pattern.
Conclusion:
This is the first early RA (trial) cohort to show mortality similar to the general population after 23 years of follow up. In fact, mortality was numerically lower than expected. Some (but not all) predictive factors for disease severity were apparent. Our study confirms that early, intensive treatment of RA (that can include glucocorticoids) has long-term benefits, and strongly suggests these benefits include normalization of mortality.
References:
1. Boers M. Lancet 1997;350:309-18.
2. van Tuyl LH. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:807-12.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Poppelaars P, van Tuyl L, Boers M. Normal Mortality of the Cobra Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Trial Cohort after 23 Years Follow up [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/normal-mortality-of-the-cobra-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-trial-cohort-after-23-years-follow-up/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/normal-mortality-of-the-cobra-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-trial-cohort-after-23-years-follow-up/