Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose:
Patient no-show and cancellation rates are long-standing problems in the healthcare system, affecting patient outcomes, revenue, system efficiency, and resource utilization. At the Hoxworth Rheumatology Clinic, which sees over 180 patients monthly (approximately 2,000 annually), no-show rates have persisted despite automated reminders. These unused slots are non-reimbursable, leading to financial losses. These rates, ranging from 12% to 80% in various settings, led to unreimbursed slots and financial losses.
This study aimed to integrate live telephone call reminders to reduce the median benchmark for no-shows and late cancellations from 23.8% by 5% between September 1, 2023, and May 31, 2024. Internal research indicated that the optimal time for reminder calls was 5-6 days before the appointment, allowing for barrier identification.
Methods: The study, conducted from September 1, 2023, to May 31, 2024, involved making live telephone calls to patients 5-6 days before their scheduled appointments. A refined patient waitlist was also utilized to manage cancellations effectively. From January 1, 2024, to February 28, 2024, patients who no showed were contacted to investigate the barriers contributing to their absence despite reminder calls. The study aimed to understand the reasons behind no-shows and develop strategies to address them.
Results: Live telephone calls significantly increased pre-appointment cancellations but markedly decreased no-show rates.
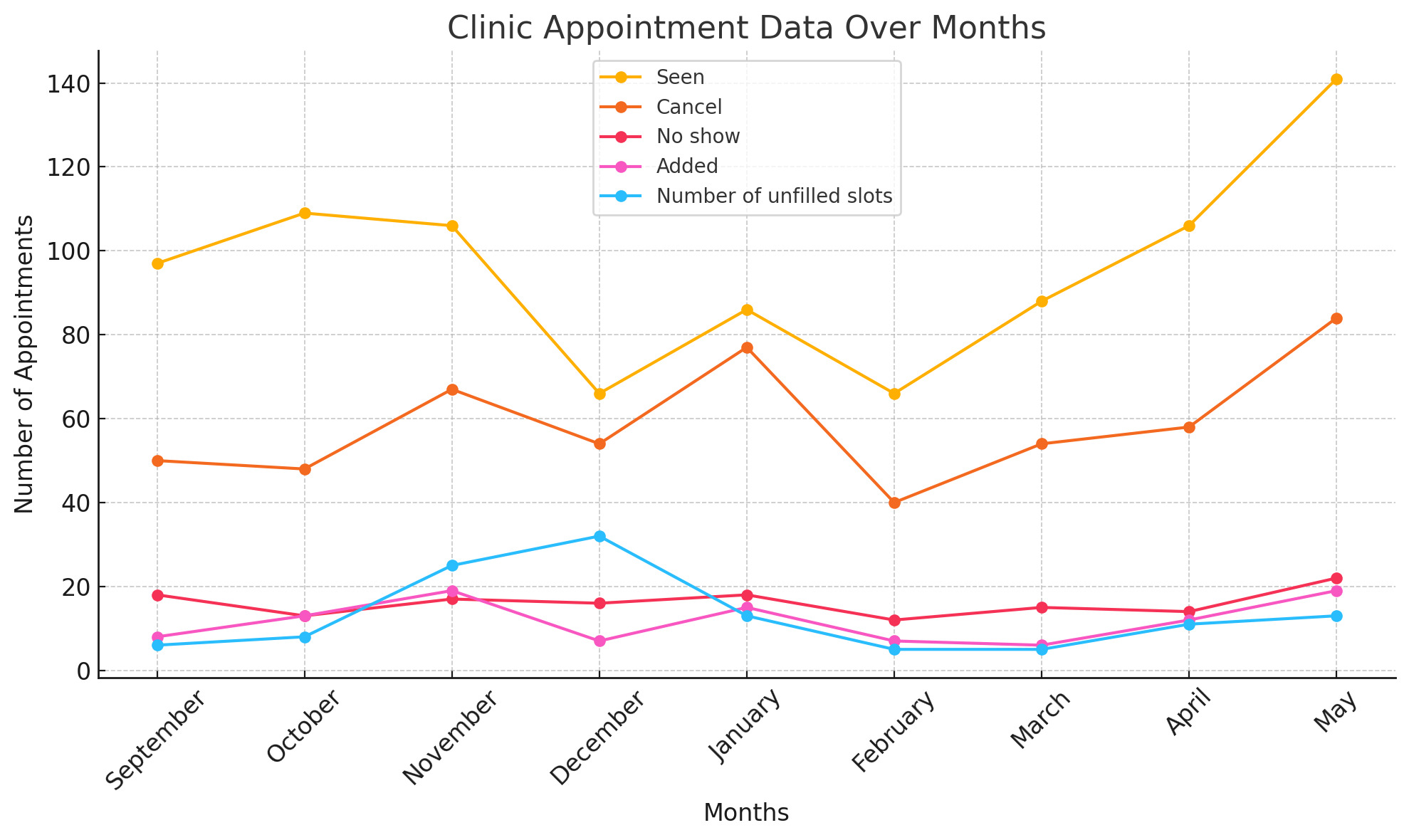
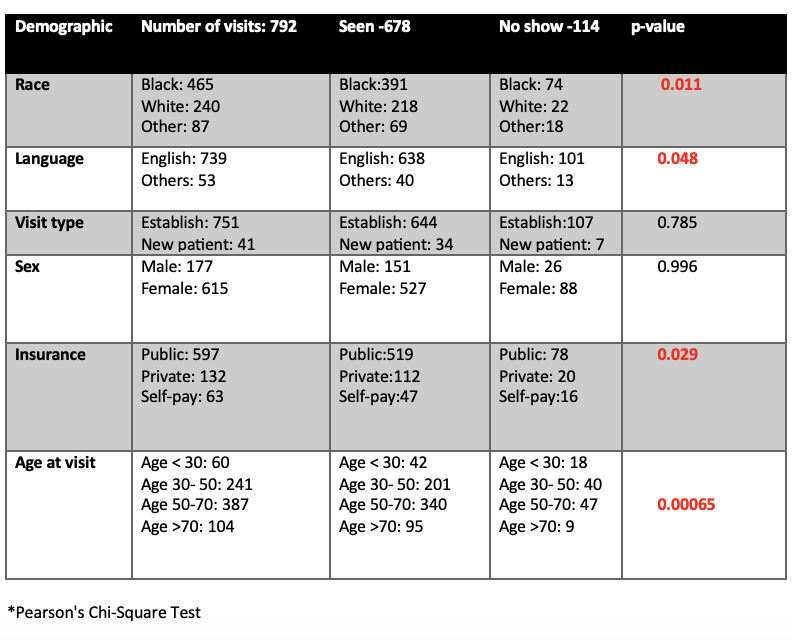
High cancellation rates led to an increased number of unfilled slots, as depicted in Figure 1, which compares patients seen, canceled, no-show, added from the waitlist, and unfilled slots. Elevated cancellation rates, primarily 1-2 days before appointments, posed challenges in filling these slots on short notice. However, the patient waitlist enabled the clinic to start accepting new patients within two months of the study’s initiation, reversing the previous decision to stop accepting new patients. Analysis revealed that the most common reasons for cancellations were forgetfulness followed by hospitalization, lack of transportation, lack of time off work, seeing another provider, death, and insurance issues. For no-shows, the primary reasons were forgetfulness followed by lack of transportation, illness, insurance problems, and fear of medication side effects. The no-show rate decreased from 23.8% to 16.7%. Statistical analysis revealed a significant association between show and no-show visit with race, language, insurance and age at visit, as shown in Figure 2.
Conclusion: Implementing live phone call reminders effectively reduced the no-show rate but increased last-minute cancellations, leading to unfilled slots. Addressing specific barriers such as transportation and scheduling flexibility is crucial. Understanding the demographics associated with no-shows can guide targeted interventions to further improve attendance rates.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jackson N, Nguyen k, Nguyen T, James M, Ware A. No Show QI at Hoxworth Rheumatology Clinic: Evaluating the Impact of Live Telephone Calls Combined with Automated Reminders [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/no-show-qi-at-hoxworth-rheumatology-clinic-evaluating-the-impact-of-live-telephone-calls-combined-with-automated-reminders/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/no-show-qi-at-hoxworth-rheumatology-clinic-evaluating-the-impact-of-live-telephone-calls-combined-with-automated-reminders/