Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA) it has been hypothesized that inflammation-driven bone loss triggers bone repair but at anatomically distinct sites of the same vertebra (i.e. bone loss occurring in the trabecular bone and bone repair in the periosteum)1. However, the possible association between bone loss and new bone formation at the same individual vertebra has never been studied. The purpose of this study was to investigate if in r-axSpA low vertebral bone mineral density (BMD) is associated with development of new syndesmophytes at the same vertebral level.
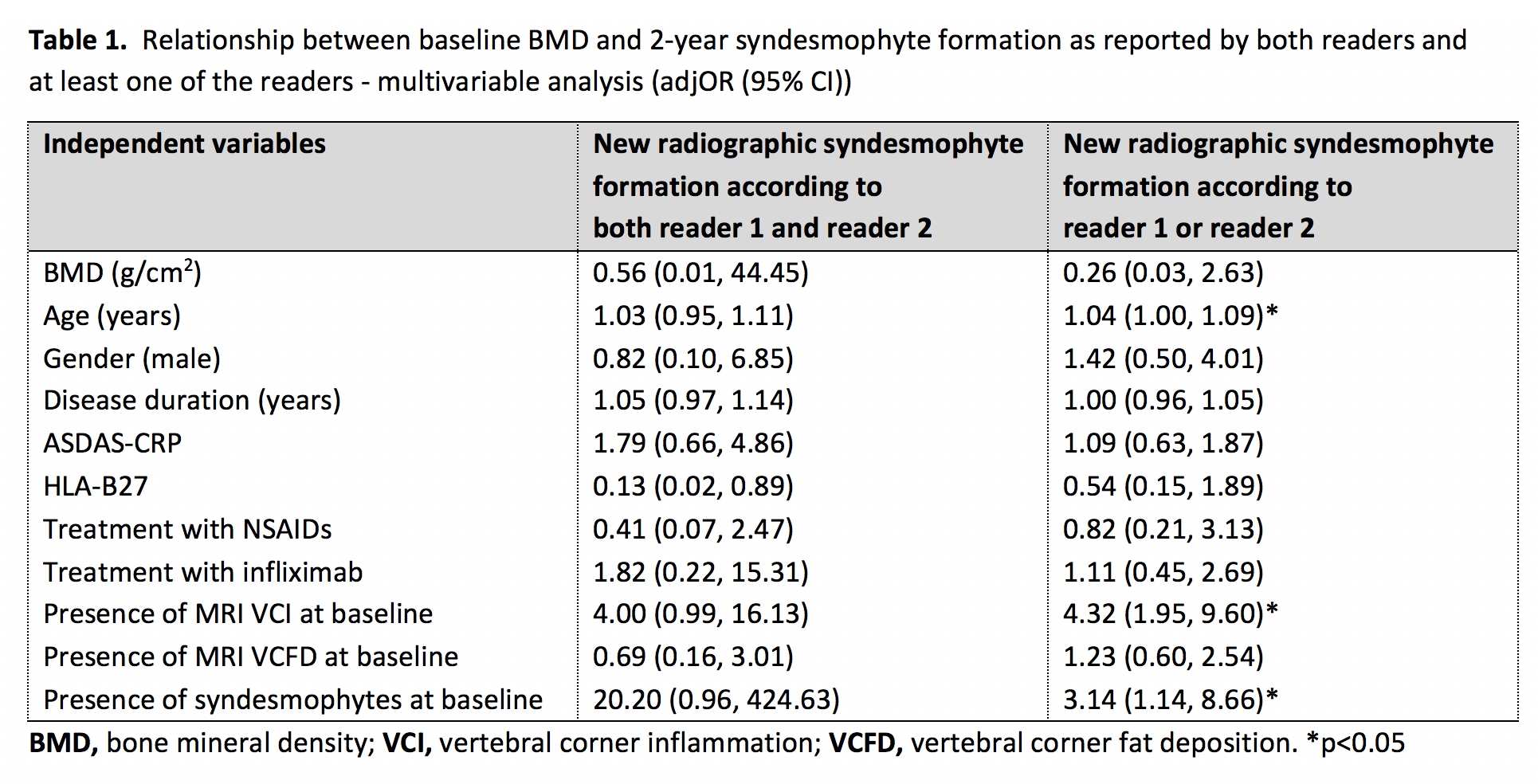
Methods: In a post-hoc analysis from the ASSERT trial (infliximab vs placebo) dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry was used to measure baseline BMD (g/cm2) of the lumbar spine L1 to L4. Syndesmophyte formation was assessed in the same vertebrae on conventional radiographs defined as an increase in modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score from 0 or 1 to 2 or 3 after 2 years. Radiographs were scored by two readers. Generalized estimating equations (GEE) adjusted for within-patient correlation across multiple vertebrae, taking potential confounders into account (Table 1).
Results: We analyzed 599 vertebrae in 165 r-axSpA patients (78% male, mean (SD) age 38 (10) years, 67% with at least one syndesmophyte anywhere in the spine). In total, 24 to 74 new syndesmophytes developed in 9 (5%) to 30 (18%) patients and 13 (2%) to 39 (7%) vertebrae, if either a syndesmophyte was seen by both or only one of the readers (i.e. specific and sensitive definitions) respectively. Analyses with both definitions, and both uni- and multivariable, showed no significant association between baseline local vertebral BMD and new syndesmophyte formation after two years in the same vertebra (multivariable analysis adjOR (95%CI): 0.56 (0.01, 44.45) (specific definition) and 0.26 (0.03, 2.63) (sensitive definition)) (Table 1).
Conclusion: In patients with active and established r-axSpA, with an observed low incidence of lumbar spine syndesmophyte formation over two years, no relationship was found between baseline BMD and new radiographic syndesmophyte formation in the same vertebra.
1 Lories RJ. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Jun;32(3):331–41.
This study, carried out under YODA Project #2018-2761, used data obtained from the Yale University Open Data Access Project, which has an agreement with JANSSEN RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT, L.L.C.. The interpretation and reporting of research using this data are solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Yale University Open Data Access Project or JANSSEN RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT, L.L.C..
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marques M, Ramiro S, Machado P, van der Heijde D, van Gaalen F. No Relationship Between Lumbar Bone Mineral Density and Syndesmophyte Formation at the Same Level – A Multilevel Analysis in Patients with Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/no-relationship-between-lumbar-bone-mineral-density-and-syndesmophyte-formation-at-the-same-level-a-multilevel-analysis-in-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/no-relationship-between-lumbar-bone-mineral-density-and-syndesmophyte-formation-at-the-same-level-a-multilevel-analysis-in-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/