Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Metabolomics, the study of global alterations in small metabolites is a useful tool to look for novel biomarkers. Recently, we reported a reprogramming of the serum metabolomic profile on nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR) spectroscopy following treatment in Lupus Nephritis (LN).(1)We explored urinary parameters using NMR Spectroscopy in patients with biopsy proven proliferative lupus nephritis. Change in parameters after 6 months Cyclophosphamide induction treatment and its correlation with disease activity was assessed.
Methods: Urine obtained from Lupus Nephritis (n=18, F=16,M=2) at diagnosis and following induction therapy with cyclophosphamide, and healthy controls (n=18, median age 35,all females) were stored at -80 °C. Metabolomic profiling was done using high resolution 800 MHz 1D 1H NMR spectroscopy. Urinary ratio of metabolites was calculated- (Metabolitex1000)/Creatinine. Disease activity was measured using SLEDAI. Metabolomic profiles were compared between groups and correlated with clinical parameters using SPSS
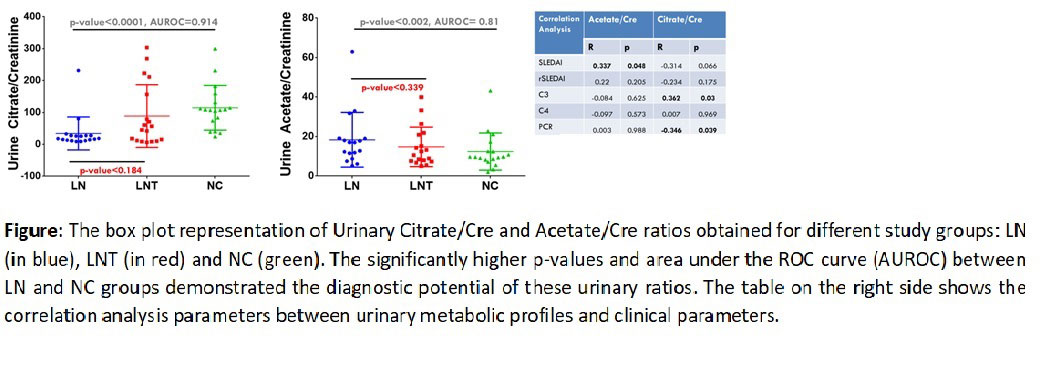
Results: Urinary metabolomic fingerprint of LN patients differed from healthy controls by having significantly raised urinary acetate/creatinine(LN=41.84±100.6, HC=12.36±9.40, p=< 0.002) and reduced urinary citrate/creatinine.(LN=34.22±54.8, HC=114.5±70.09, p=< 0.0001). Urinary citrate (88.68±98.33) increased after 6 months of Cyclophosphamide, while urinary acetate showed a trend towards decrease(14.77±9.98). AUC for urinary citrate/creatinine and acetate/creatinine were 0.9136 and 0.8086. The urinary acetate levels correlated with SLEDAI (r=0.337,p=0.048). Urinary citrate levels correlated with C3 (r=0.362,p=0.03) and negatively correlated with uPCR (r=0.346, p=0.039).
Conclusion: The decreased urinary citrate mirrors the finding seen in serum of the patients done earlier which reflects dampened aerobic glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation.(1) Raised urinary acetate levels possibly reflects renal tubular injury and decreased entry into TCA cycle. Urinary metabolomics parameters are potential noninvasive biomarkers for diagnosis and monitoring treatment response in LN.
References
- Guleria A et al. NMR based serum metabolomics reveals reprogramming of lipid dysregulation following Cyclophosphamide based induction therapy in lupus nephritis. J ProteomeRes. 2018, 17 (7), 2440–2448.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ganguly S, Kumar U, Guleria A, Majumder S, Phatak S, Chaurasia S, Gupta N, Kumar S, Aggarwal A, Kumar D, Misra R. NMR Spectroscopy Reveals Alterations of Urinary Acetate and Citrate Levels Following Cyclophosphamide Therapy in Patients with Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nmr-spectroscopy-reveals-alterations-of-urinary-acetate-and-citrate-levels-following-cyclophosphamide-therapy-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nmr-spectroscopy-reveals-alterations-of-urinary-acetate-and-citrate-levels-following-cyclophosphamide-therapy-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/