Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a potentially life-threatening autoimmune disease. Childhood-onset SLE (cSLE) patients have younger disease onset and more severe disease than adults, and thus may have a larger genetic burden. Our current understanding of the genetic architecture of cSLE is limited. Examining the polygenic risk score (PRS) allows us to capture both the number of common SLE risk variants and the magnitude of influence of each genetic variant on SLE predisposition. Prior studies have described rare variants in genes linked to risk for monogenic SLE. We aimed to assess the burden of common and rare variants in an ancestrally diverse cSLE cohort. We characterized type I interferon (IFN) gene expression scores along with genomic data.
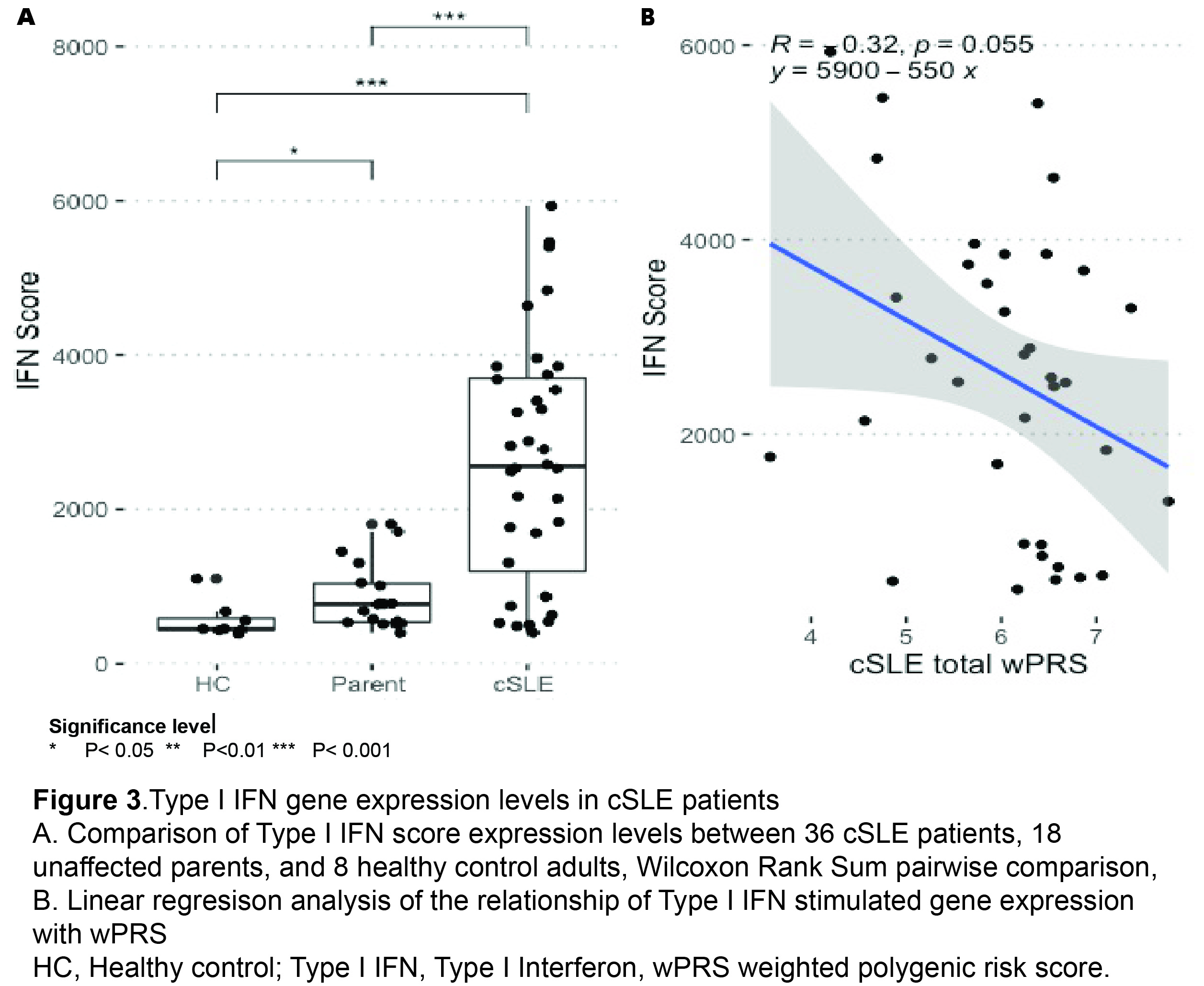
Methods: All cSLE patients met at least 4 of the 11 American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for SLE prior to age 18 years. Samples collected from 83 SLE patients and 109 unaffected parents were sequenced via whole genome sequencing using Illumina HiSeq X Ten, with mean depth coverage of 36x. We assessed 32 non-HLA and 7 HLA SLE risk single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) tagging independent previously published SLE genetic susceptibility loci. A weighted PRS was calculated for each subject based on the sum of the product of the natural logarithm of the odds ratio for each association and the number of alleles present in each individual at each risk locus. Cumulative scores were calculated for each subject. Each SLE patient was assessed for rare, exonic variants in monogenic SLE genes. Total RNA was isolated from PAXgene tubes using Qiagen kits and checked for quality standards. Type I interferon (IFN) regulated genes were measured from RNA via NanoString assay. A type I IFN score (based on 37 IFN regulated genes) was measured on a subset of patients (n=36), parents (n=18) and healthy controls (n=8). We calculated the geometric mean of the 37 gene score and compared geomeans between groups using Wilcoxon rank sum pairwise comparison. We investigated the relationship between cSLE, genomic profile, and type I IFN signatures in this cohort.
Results:
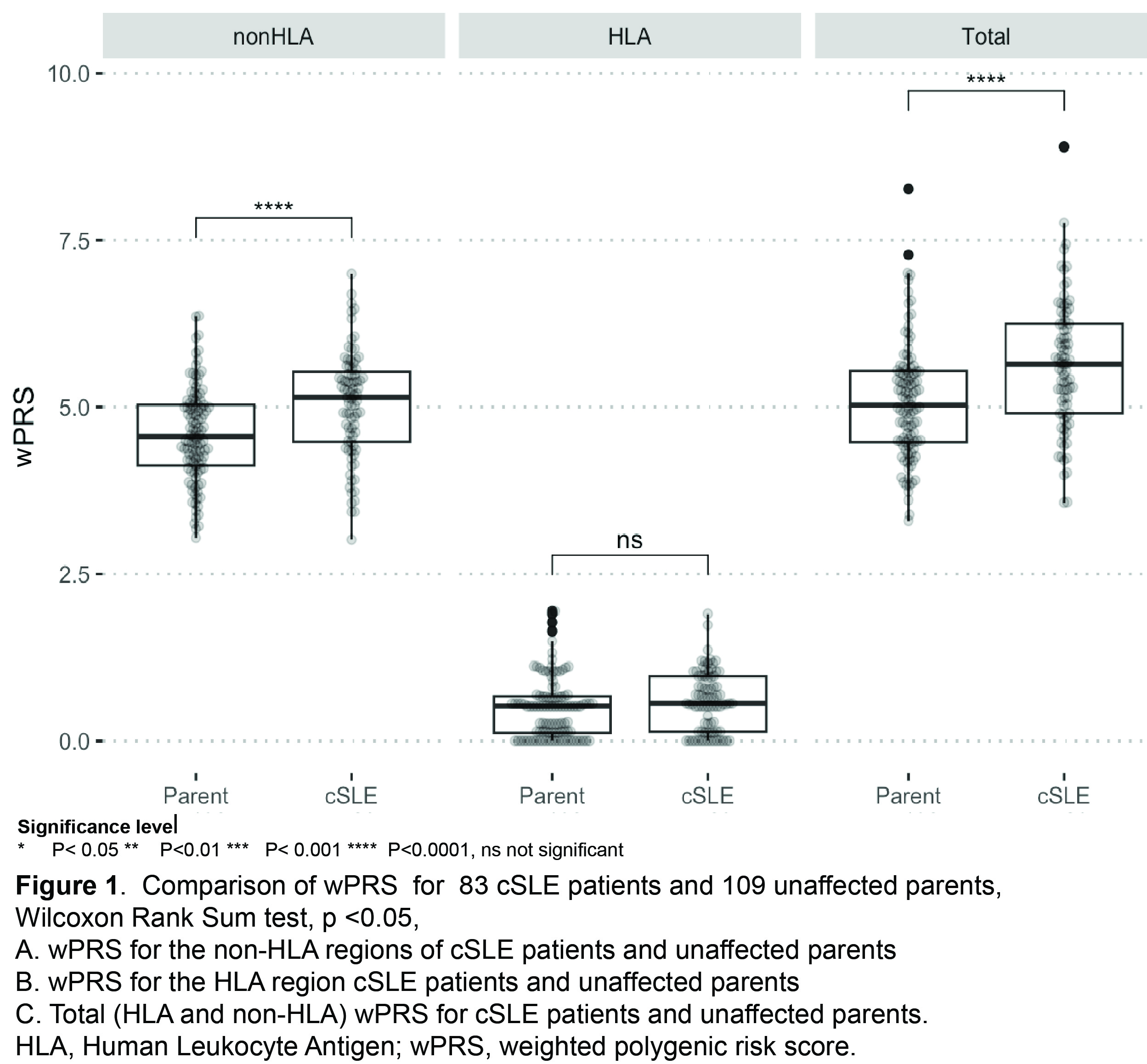
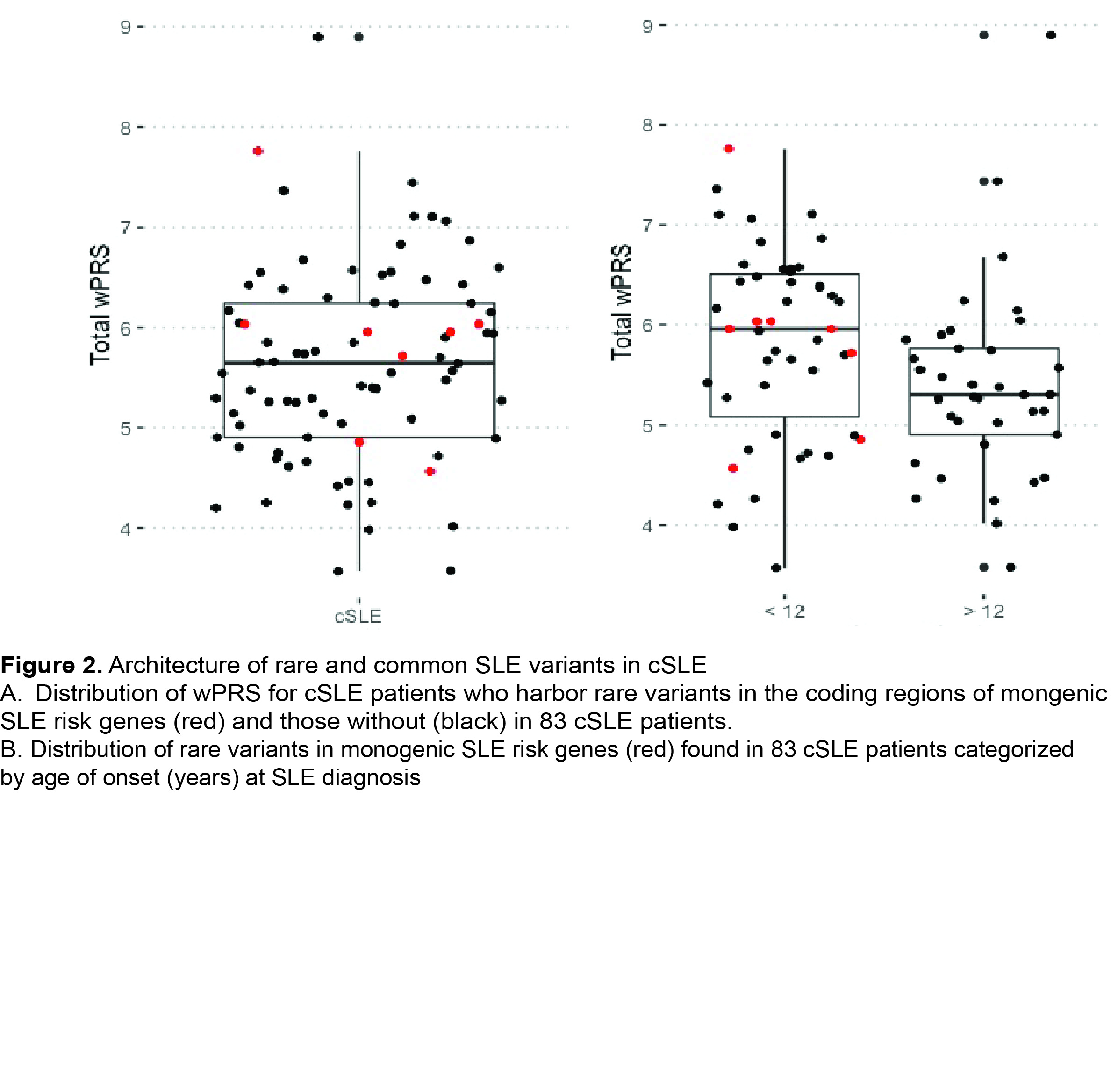
cSLE patients from a diverse cohort are enriched for common SLE risk variants compared to unaffected parents (Figure 1A-C). We identified rare SLE risk variants in 11% of individuals with cSLE. We observed rare SLE risk variants in cSLE patients across a range of PRS (Figure 2A). All cSLE patients with rare variants had earlier onset of disease (< 12 years) than those without (Figure 2B). cSLE patients had an elevated type I IFN score compared to unaffected parents and controls. (Figure 3A). The type I IFN score did not correlate with cSLE wPRS (Figure 3B).
cSLE patients from this diverse cohort are enriched in common cSLE risk variants compared to controls, and 11% carried a rare variant in known monogenic SLE risk genes. The type I IFN score had no correlation with cSLE wPRS, suggesting scores are not driven by common variant mechanisms. The relationship between rare and common risk variant burden is more complex than previously hypothesized. Our findings indicate that studying cSLE patients will be important for understanding genetic contributions to SLE pathogenesis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lewandowski L, Hiraki L, Scott C, Barrera-Vargas A, Gómez-Martin D, Ombrello M, Aksentijevich I, deng Z, Musolf A, Paul S, Hupalo D, Dalgard C, Hasni S, Silverman E, Kaplan M. Next Generation Sequencing Analysis Reveals Complex Genetic Architecture of Childhood-onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/next-generation-sequencing-analysis-reveals-complex-genetic-architecture-of-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/next-generation-sequencing-analysis-reveals-complex-genetic-architecture-of-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/