Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The recent CARES trial findings have contributed to the controversy around the development of cardiovascular (CV) events in gouty patients using febuxostat (FBX). In those with prior CV disease, FBX showed an increased CV mortality risk over allopurinol (ALLO), leading to the issue of an FDA warning. Whether this also applies to individuals without prior established CV disease is unknown. We aimed to assess the risk of new CV events in gout patients after the prescription of xanthine-oxidase inhibitors (XOI) in clinical practice.
Methods: Inception cohort (Jan’14-Dec’17), enrolling patients with crystal-proven gout in whom XOI (ALLO or FBX) were initiated and had at least 6 months of follow-up. The primary outcome were new CV events [CV death; coronary heart disease (CHD); congestive heart failure (CHF); stroke; peripheral artery disease (PAP)] after XOI initiation. Comparison between ALLO and FBX was performed using Kaplan-Meier plots and log-rank test. To adjust for confounders, Cox regression models were built, for the whole sample and stratified by the pre-existence CV disease. Covariates were selected if associated with the outcome or if they showed a different distribution between XOI groups.
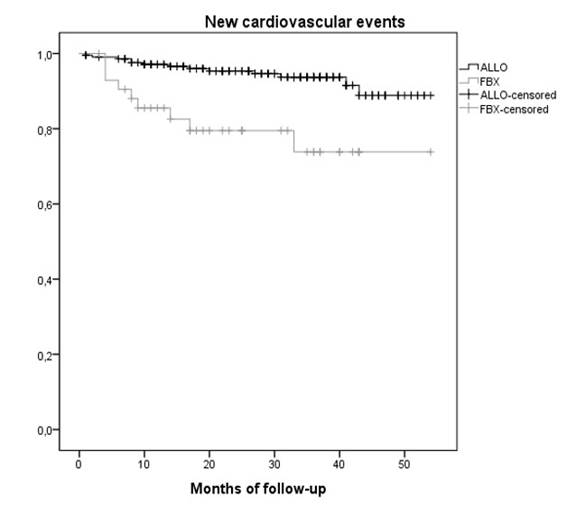
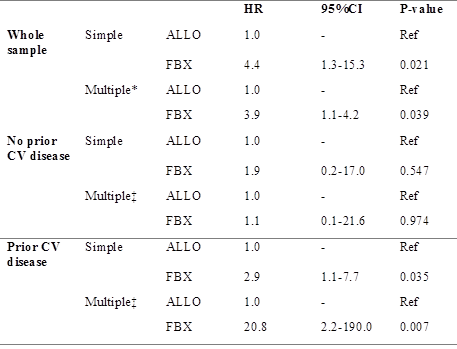
Results: 256 patients were analyzed, 213 treated with ALLO and 43 with FBX. 69 cases (27.0%) had established CV disease. 22 new CV events occurred in a median of 9.5 months (IQR 4.5-19.3): 13 CHF cases, 5 CHD, 2 strokes, and 2 PAP, leading to 7 CV deaths. 16 events occurred in patients with a prior CV (23.2%), six in those with no prior CV events (3.2%). Regarding XOI treatment, 13 events happened with ALLO (6.1%) and 9 with FBX (20.9%). Use of colchicine at the time of the event was comparable. A higher incidence of new CV events in those treated with FBX was seen (p<0.001, Kaplan-Meier plot). The simple Cox regression model confirmed a higher risk with FBX compared to ALLO (table), which persisted after adjustment. After stratification by prior CV disease, a significant CV risk with FBX was only detected in those with prior CV disease.
Conclusion: After adjustment for confounders, an excess risk of CV events is confirmed in patients with gout and prior CV disease treated with FBX. Whether this phenomenon relates to FBX itself needs further clarification.
*covariates: age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, smoking, established CV disease, baseline GFR, overweight, baseline SU, tophi, oligo/polyarthritis at presentation.
‡covariates: age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, smoking, baseline GFR, overweight, baseline SU, tophi, oligo/polyarthritis at presentation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Quilis N, Ranieri L, Sanchez-Paya J, Andrés M. New Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Gout Treated with Xanthine-Oxidase Inhibitors: An Inception Cohort Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/new-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-gout-treated-with-xanthine-oxidase-inhibitors-an-inception-cohort-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/new-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-gout-treated-with-xanthine-oxidase-inhibitors-an-inception-cohort-analysis/