Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Methods: Bayesian NMA were conducted using randomized controlled trials identified from a systematic literature review. The analysis included only trials assessing a treatment combined with one cDMARD. Studies reporting ACR20 response and change from baseline in disease activity score 28 (DAS28) based on the C-reactive protein (CRP) at 24±4 weeks were included. A Bayesian network meta-regression adjusted for baseline risk (ie, the estimated baseline effect of the common comparator arm in each trial) was conducted for the ACR20 analysis. The baseline risk is used as a proxy to adjust for differences in patients’ characteristics that lead to variations across common comparator arms. Evidence networks included treatment and dose-specific nodes except for cDMARDs. Non-informative prior distributions were used. Selection of fixed versus random effects was based on the Deviance Information Criterion (DIC).
Results: The review identified 24 studies reporting results at 24 weeks for abatacept, adalimumab, baricitinib, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, golimumab, rituximab, sarilumab, tocilizumab and tofacitinib, all combined with a cDMARD. ACR20 response rates in the cDMARD arms varied greatly across trials (9% to 46%). The meta-regression adjusting for baseline risk suggested a strong interaction between baseline risk and treatment effect. Based on the DIC, a random effects model was selected for the ACR20 analysis. All bDMARDs (including sirukumab) and tsDMARDS achieved better ACR20 response compared with cDMARDs (Figure 1a). Most biologics’ credible intervals show significant overlap, suggesting a similar level of efficacy in achieving ACR20. For DAS 28, a fixed effect model was used, and with a small network of available studies. The 4 biologics included in this evidence network performed better than cDMARDs. Sirukumab and abatacept appear to demonstrate improvement over the other agents in the network on this measure (Figure 1b).
Conclusion: The NMA suggests that sirukumab has similar ACR20 response, and similar or slightly higher DAS28-CRP improvement, compared with most bDMARDs and tsDMARDs. 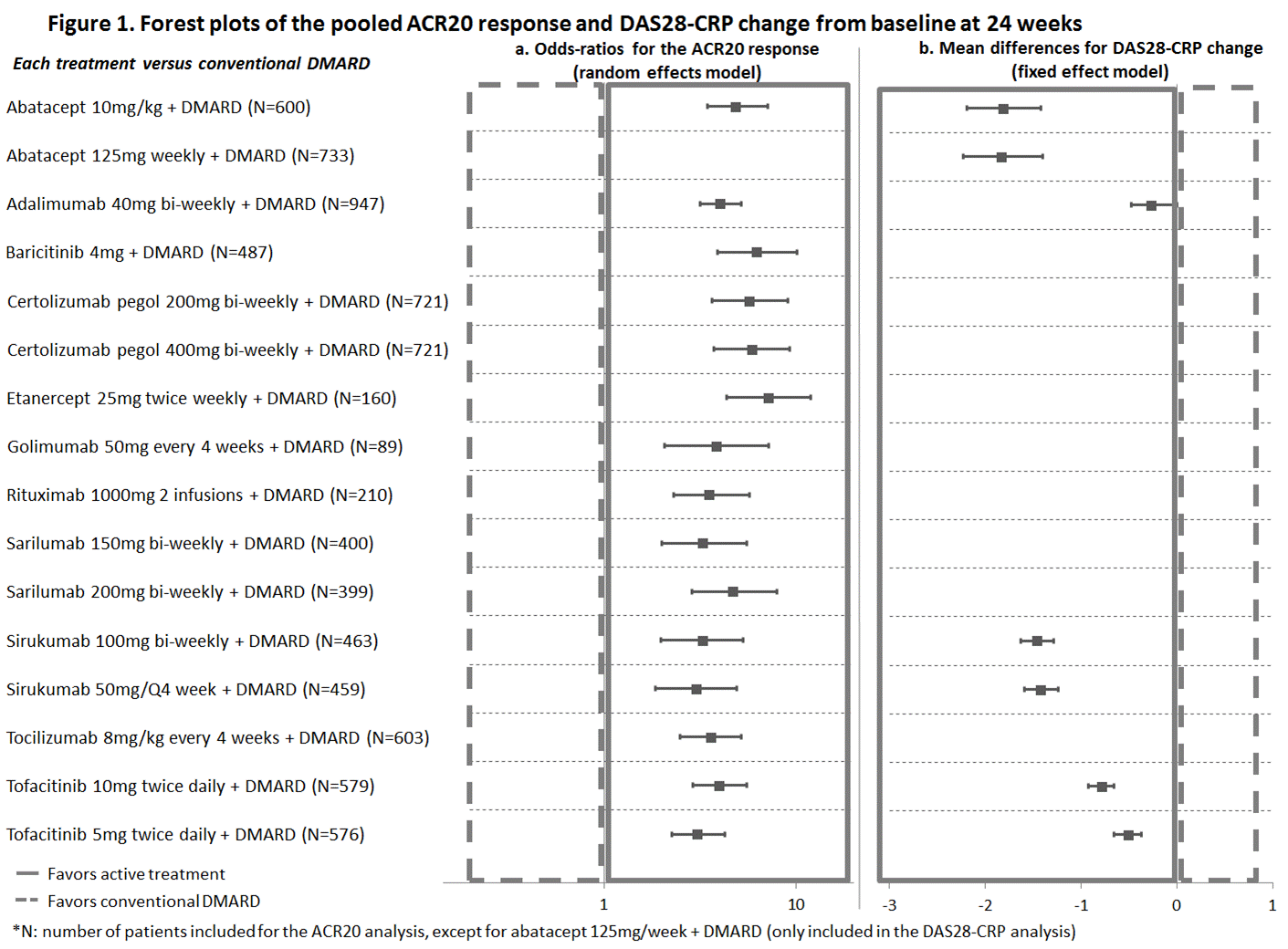
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Peterson S, Pacou M, Belhadi D, Van Sanden S, Webb T, Ganguly R, Kurrasch R, Rao R, Hsu B, Fei K, Kielar D, Alfonso R. Network Meta-Analysis to Assess the Relative Efficacy of Sirukumab, an Anti–IL-6 Cytokine Monoclonal Antibody, in Combination Therapy for Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Conventional Dmards [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/network-meta-analysis-to-assess-the-relative-efficacy-of-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-in-combination-therapy-for-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-despite-conv/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/network-meta-analysis-to-assess-the-relative-efficacy-of-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-in-combination-therapy-for-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-despite-conv/
