Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Diagnosis (0323–0356)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The universal process of aging is associated with increased risk of disease and death as a result of changing physiologic and molecular processes. In autoimmune patients, the process of aging can be exacerbated by chronic low-grade inflammation and the accumulation of biologic damage. We have previously demonstrated that Native American rheumatic disease patients present unique clinical and serological phenotypes with regards to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Because of such unique presentations of autoimmune disease, we hypothesize that Native American RA and SLE patients will exhibit an older biological age compared to chronological age relative to other racial groups.
Methods: Age matched (+/- 8 years) SLE, RA and control patients were selected across three racial groups, Native American (NA, n = 26), African American (AA, n = 25) and European American (EA, n = 26). T cells, B cells and Monocytes were isolated from PBMCs and DNA extracted. DNA was used for whole methylome analysis using the Illumina Infinium Human MethylationEpic BeadChip microarray. DNAm age, an indicator of biological age, was calculated using the Grimage algorithm leveraging differences in methylation at key CpG sites. Telomere length and mitochondrial DNA copy number were assayed using the absolute human telomere length and mitochondrial DNA copy number dual quantification qPCR (AHDQ) assay from ScienCell Research Laboratories.
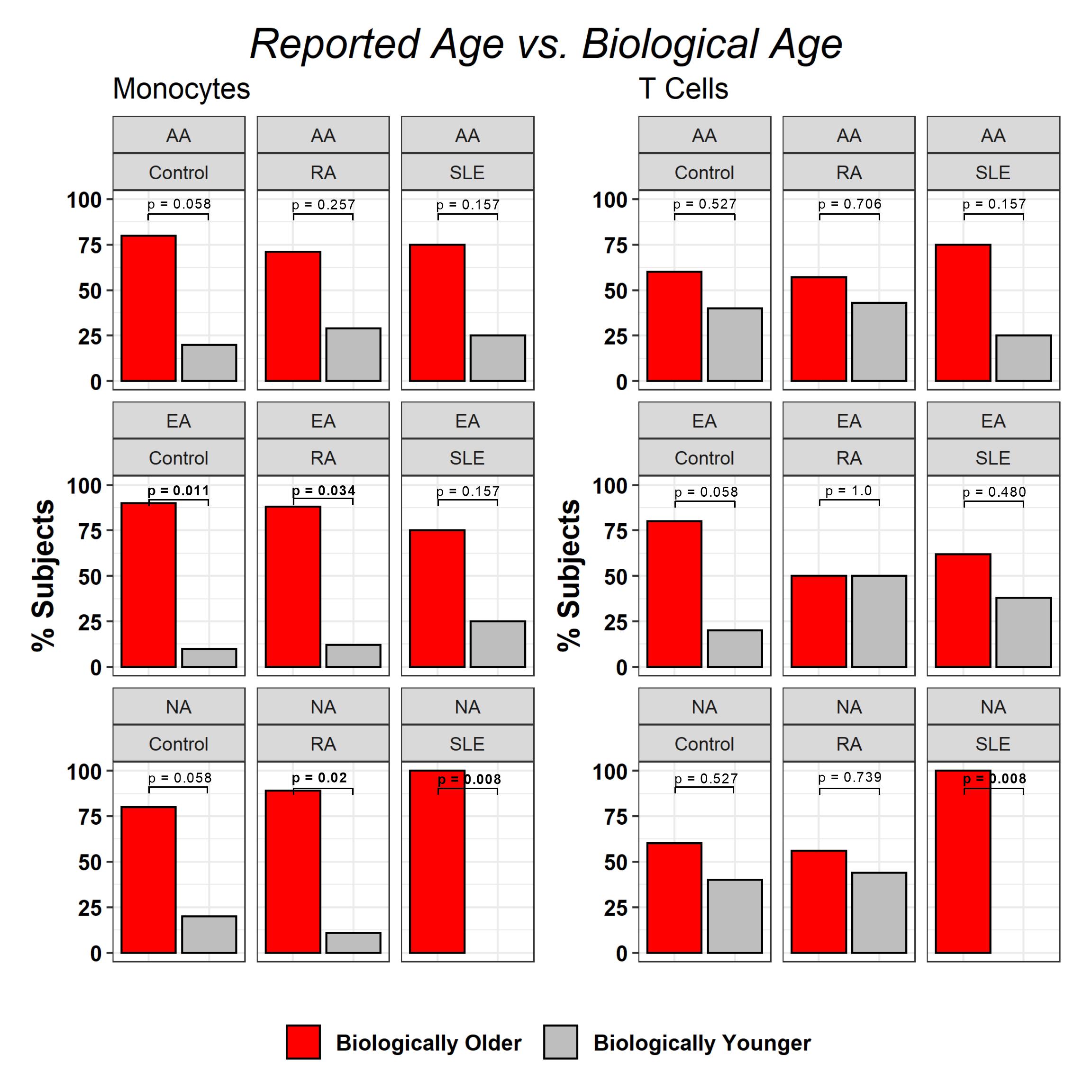
Results: All NA SLE patients (n = 7) exhibited a biologically older age for T cells and monocytes compared to reported age (p = 0.008). Although not significant, a similar trend was observer for AA (75%, n = 6) SLE patients. EA SLE patients had similar biologic and stated ages. 89% of NA RA patients (n = 8, p = 0.02) exhibited a biologically older age in monocytes but not in T cells (p = 0.739). Similarly, 88% of EA RA patients (n = 7, p = 0.034) exhibited a biologically older age in monocytes but not in T cells (p = 1.0) relative to reported age. AA RA patients had similar biologic and stated ages. The difference in biological age and reported age for NA SLE patients ranged from 1.2 years to 13 years with an average age difference of 7.1 years for monocytes and 3.5 years to 10.5 years with an average difference of 7.2 years for T cells. Interestingly, the age difference in biologically older NA RA patients ranged from 0.7 to 7.2 with an average of 3.7 years and 5.6 to 15 with an average of 7.9 years for monocytes and T Cells respectively. No statistical differences were observed in telomere length or mitochondrial DNA copy number.
Conclusion: Aging and the accumulation of low-grade chronic inflammation can lead to an increased susceptibility to disease and death. Our study demonstrated that 100% of Native American SLE patients in our cohort were biologically older than their reported age. This stark difference between biological and reported age coupled with unique clinical and laboratory phenotypes underscores the importance of further multi-omic investigation of Native American rheumatic diseases in order to elucidate causal biological pathways.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kheir J, Guthridge C, Dominguez N, DeJager W, Cooper S, Guthridge J, James J. Native American and African American Rheumatic Disease Patients Exhibit Accelerated Biological Aging Compared to European Americans [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/native-american-and-african-american-rheumatic-disease-patients-exhibit-accelerated-biological-aging-compared-to-european-americans/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/native-american-and-african-american-rheumatic-disease-patients-exhibit-accelerated-biological-aging-compared-to-european-americans/