Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster II: Basic and Translational Science
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
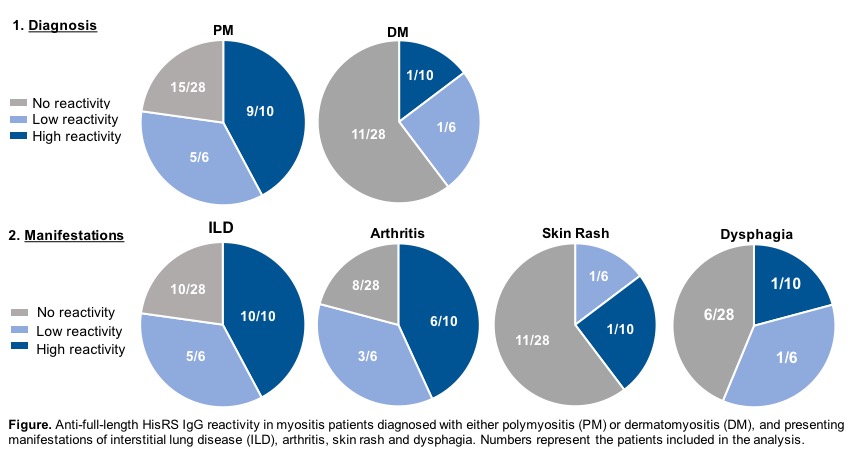
Background/Purpose: Autoimmune myositis (rheumatic muscle inflammation) associated with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and arthritis is strongly correlated with the presence of anti-histidyl tRNA synthetase (HisRS) autoantibodies. The aims of this study were to investigate: 1) myositis IgG reactivity against HisRS conformational epitopes; and 2) associations between clinical manifestations and anti–HisRS reactivity profiles.
Methods: Serum IgG was isolated using a protein G affinity column (from 25 anti-HisRS negative (-) and 19 anti-HisRS positive (+) myositis sera and 24 age/gender matched healthy controls, HC). Autoantibody reactivity was tested by in house ELISA developed against HisRS full-length protein and three HisRS conformational epitopes (WHEP domain – localized in the N-terminal; HisRS without WHEP (HisRS_WHEP); and ABD – anticodon-binding domain located in the C-terminal). Correlations between diagnosis, clinical manifestations and anti-HisRS IgG reactivity were evaluated.
Results: HisRS+ myositis IgG displayed stronger reactivity against full-length HisRS and HisRS_WHEP (median 372 ng/mL and 334 ng/mL, respectively), compared to WHEP and ABD (6.38 and 6.48 ng/mL). The strongest anti-full-length HisRS reactivity (>371 ng/mL) was detected in HisRS+ patients presenting ILD (10 of 10 of patients, figure below), arthritis (6/10) and polymyositis diagnosis (PM 9/10), in comparison to HisRS+ patients with low anti-HisRS reactivity (<23 ng/mL, ILD – 5 of 6; arthritis – 3/6; PM – 5/6) or subjects with no anti-HisRS reactivity (ILD – 10/28; Arthritis – 8/28; PM – 15/28). On the contrary, patients displaying no anti-HisRS reactivity were largely diagnosed with DM (11/28), skin rash (11/28) and dysphagia (6/28) when compared to patients with the highest anti-full-length HisRS reactivity (1 out of 10 patients was diagnosed with DM, skin rash or dysphagia). Similar associations were observed between anti-HisRS_WHEP, anti-WHEP or anti-ABD reactivity and manifestations of ILD, arthritis, skin rash or dysphagia, and DM or PM diagnosis. No anti-HisRS reactivity was detected in the HC group.
Conclusion: This study provides evidences for a possible underlying role of anti-HisRS autoantibodies in the pathogenesis of myositis with interstitial lung disease and joint involvement.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fernandes-Cerqueira C, Renard N, Notarnicola A, Wigren E, Jakobsson PJ, Graslund S, Lundberg IE. Myositis Specific Anti-Histidyl tRNA Synthetase (HisRS) Autoantibodies Display High Reactivity Against Hisrs Conformational Epitopes and Associate with Lung and Joint Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myositis-specific-anti-histidyl-trna-synthetase-hisrs-autoantibodies-display-high-reactivity-against-hisrs-conformational-epitopes-and-associate-with-lung-and-joint-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myositis-specific-anti-histidyl-trna-synthetase-hisrs-autoantibodies-display-high-reactivity-against-hisrs-conformational-epitopes-and-associate-with-lung-and-joint-involvement/