Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies (ANCA) are immunoglobulin G (IgG) autoantibodies directed against constituents of primary neutrophil granules (Davies, Moran et al. 1982). There is strong clinical, in vitro and in vivo evidence to suggest that ANCAs are pathogenic (Jennette and Falk 2014) causing pauci-immune necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis (NCGN) and systemic small vessel vasculitis. One of the major target antigens for ANCA is myeloperoxidase (MPO) (Schreiber, Xiao et al. 2006). Both MPO and the reactive oxidants it generates have been implicated as participating in tissue injury in a large number of inflammatory conditions (Nicholls and Hazen 2005). There is no available information as to activity of circulating MPO in individuals with AAV although there is limited evidence that MPO-ANCAs, extracellular MPO, and in situ immune complexes composed of MPO and anti-MPO antibodies may have an important role in the pathogenesis of glomerular capillary injury in MPO-ANCA associated vasculitis (Arimura, Kawashima et al. 2013). Additionally, MPO can stimulate Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET) formation which exacerbate inflammation contributing to the dysfunction in AAV as evidenced by NETs found on kidney biopsy specimens from patients with small vessel vasculitis (Kessenbrock, Krumbholz et al. 2009). ReAlta’s lead compound, RLS-0071, is a PEGylated peptide which has exhibits inhibition of MPO activity in animal models and ex vivo and demonstrates inhibition of MPO activity on an equimolar basis to the prototypical MPO inhibitor ABAH (4-aminobenzoic acid hydride). RLS-0071 also inhibits neutrophil mediated NETosis in vitro and in vivo (Hair, Enos et al. 2019, Enos, Hair et al. 2020).
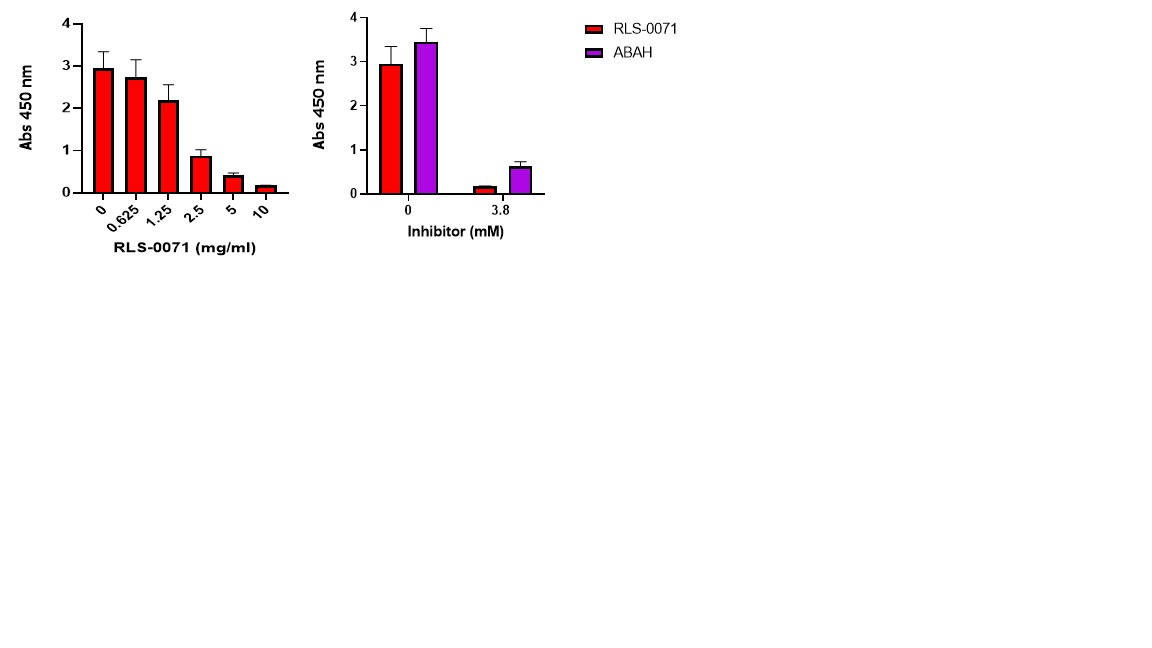
Methods: To better understand the role of MPO in ANCA associated pathophysiology, we conducted pilot analyses measuring MPO activity in plasma samples acquired commercially from individuals with known ANCA. AI (Antibody Index) units were available for each sample which represents a composite score of anti- MPO, anti- PR3 and anti- GBM antibody titers. MPO activity was measured using a TMB oxidation assay in which absorbance was measured a 450nm in a plate reader. The efficacy of RLS-0071 to inhibit MPO activity was evaluated in this assay.
Results: MPO activity as measured at 450nm absorbance ranged from 0 to 3.105. A positive correlation between MPO activity with the AI units in patient samples was observed (R2= 0.76; p=0.0046). Addition of increasing concentrations of RLS-0071 to the patient samples showed a dose dependent decrease in MPO activity to a similar level as that observed with the MPO inhibitor ABAH.
Conclusion: In this pilot study, plasma from patients with ANCA demonstrated a wide range of MPO activity with the AI units trending with plasma MPO activity. Additionally, RLS-0071 inhibited MPO activity in plasma acquired from individuals with ANCA associated pathophysiology. Future studies will focus on elucidating relationships between MPO activity, MPO quantity, free plasma DNA as a surrogate measurement of NETs and anti-MPO titers.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kumar P, Hair P, Thienel U, Cunnion K, Krishna N, Gabriel C. Myeloperoxidase Activity in Individuals with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA) Can Be Inhibited by RLS-0071 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myeloperoxidase-activity-in-individuals-with-antineutrophil-cytoplasmic-antibodies-anca-can-be-inhibited-by-rls-0071/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/myeloperoxidase-activity-in-individuals-with-antineutrophil-cytoplasmic-antibodies-anca-can-be-inhibited-by-rls-0071/