Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Glenohumeral Osteoarthritis (GH OA) significantly impacts joint function and quality of life. Various intraarticular injectable treatments, including hyaluronic acid (HA), corticosteroids (GCs), platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and bone marrow aspirate (BMA), aim to alleviate these symptoms. This systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis aims to compare their efficacy in alleviating pain, reducing disability, improving ROM and patient reported outcomes.
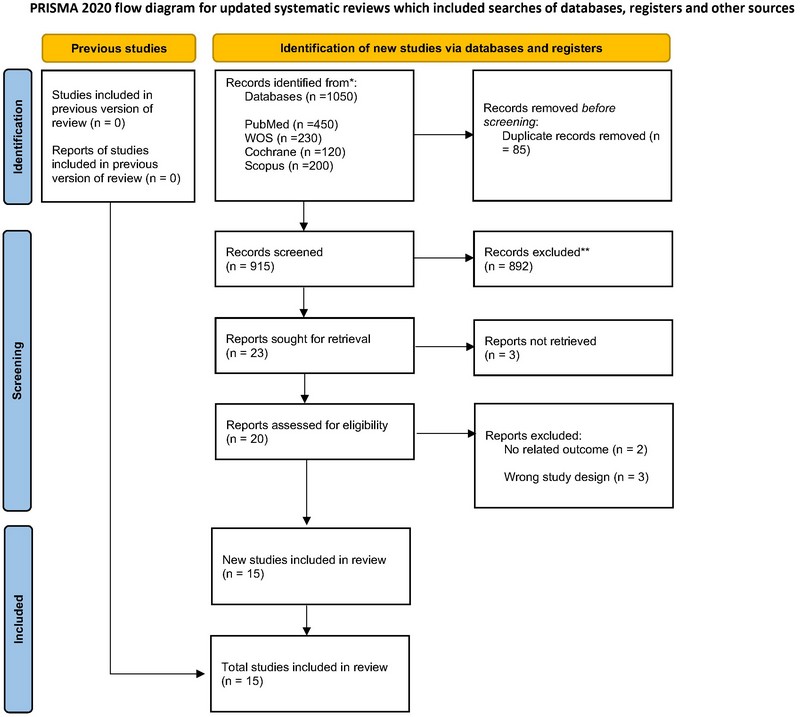
Methods: We conducted a systematic search across multiple databases, including PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Scopus from inception till April 1st, 2024. We included clinical studies evaluating the efficacy of HA, GCs, PRP, and BMA in GH OA. The outcomes were pain measured by visual analogue scale (VAS), ROM, disability by the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI), and patient reported outcomes by The Western Ontario Osteoarthritis of the Shoulder (WOOS). We used Bayesian network meta-analysis (NMA) model to compare among the included interventions. We calculated the mean difference (MD), 95% credibility interval. We used the P score to rank the interventions in order of efficacy. We used R version 4.4.0, Build 748, RStudio, Inc. to create forest and network plot for each outcome.
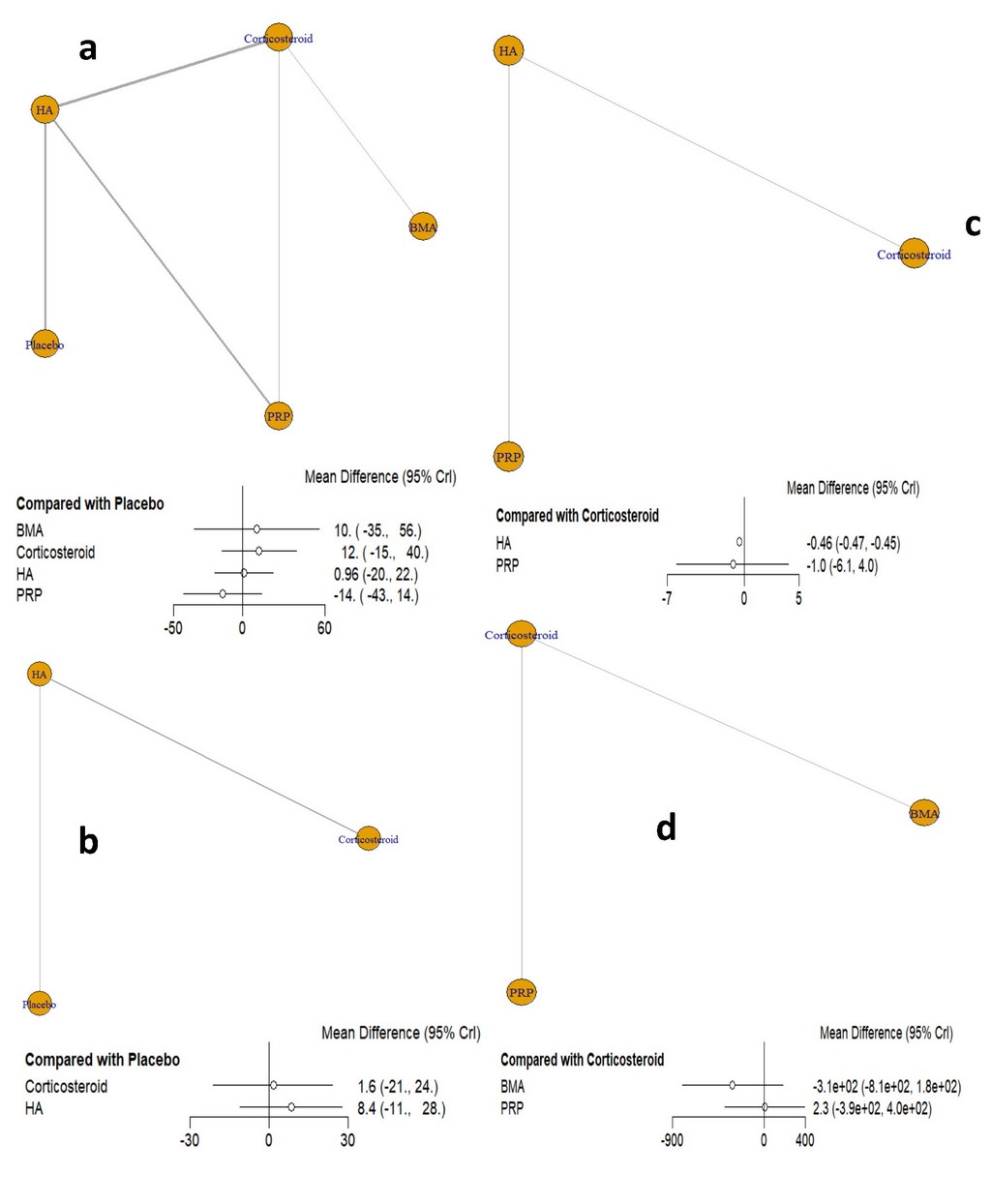
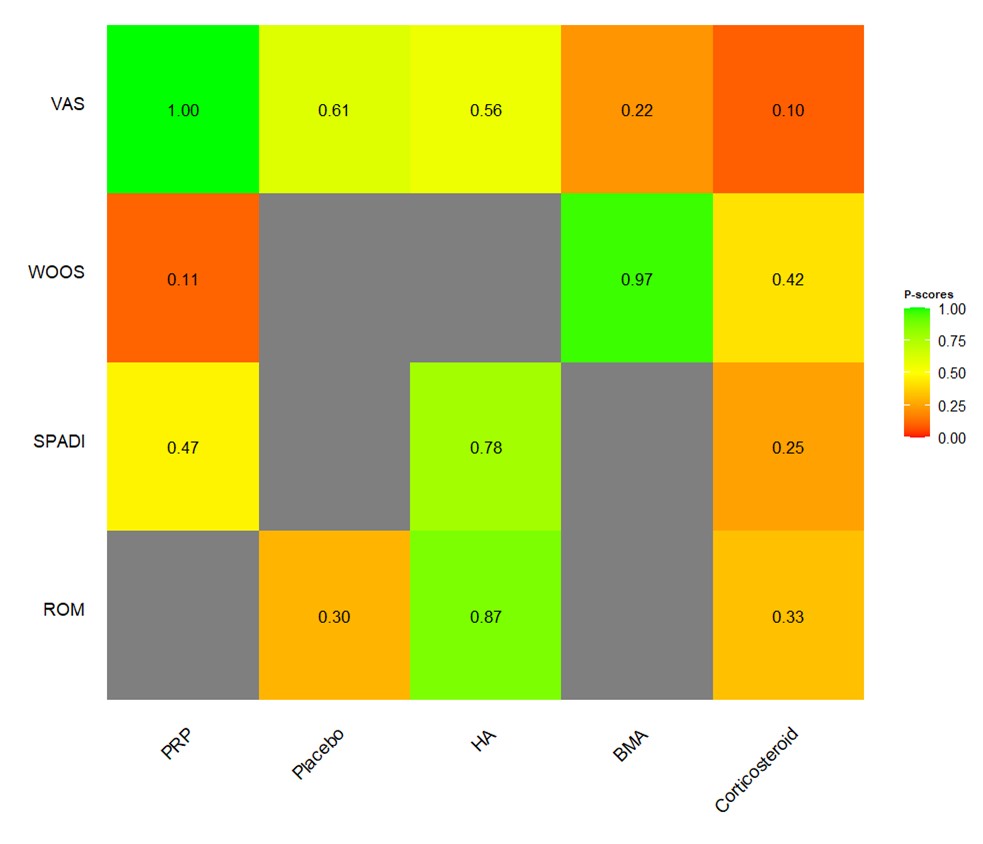
Results: This systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis incorporates data from 15 studies, encompassing a total of 1.968 patients diagnosed with GH OA. For pain relief (VAS) served as the primary endpoint, the comparisons between HA, GCs, BMA, PRP, and Placebo, GCs injections appear to have the highest mean difference compared to placebo, but it is not statistically significant. GCs injections: Mean Difference (MD) = 12, 95% Credible Interval (CrI) = -15 to 40 (Figure 2). As for ROM, HA is the highest (HA: MD = 8.4, 95% CrI = -11 to 28) but similar to the VAS results, neither HA nor GCs intraarticular injections show a statistically significant improvement in ROM compared to placebo. In SPADI, HA (HA: MD = -0.46, 95% CrI = -0.47 to -0.45.) shows a statistically significant improvement over GCs and PRP. Regarding WOOS, no treatment shows significant improvement, but PRP (MD = 2.3, 95% CrI = -3.9 to 4.0.) has a higher mean difference compared to GCs and BMA numerically.
Conclusion: Intra-articular HA injections improve pain and disability in GH OA. However, all the intra-articular injection treatments did not show significant differences in improving ROM or patient reported outcomes. Further research and larger, randomized controlled trials are warranted to validate these findings.
(c) The Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI). Network Plot: comparisons between HA, GCs, and PRP. Forest Plot: HA vs. Corticosteroid: MD = -0.46, 95% CrI = -0.47 to -0.45. PRP vs. Corticosteroid: MD = _1.0, 95% CrI = -6.1 to 4.0. significance: HA shows a statistically significant improvement over corticosteroid as indicated by the CrI that does not include zero. PRP does not show a significant difference compared to corticosteroid. Highest Ranked: HA is the highest-ranked treatment for improving SPADI.
(d) The Western Ontario Osteoarthritis of the Shoulder (WOOS). Network Plot: comparisons between BMA, GCs, and PRP. Forest Plot: BMA vs. Corticosteroid: MD = _3.1e+02, 95% CrI = -8.1e+02 to 1.8e+02. PRP vs. Corticosteroid: MD = 2.3, 95% CrI = _3.9e+02 to 4.0e+02. Significance: Neither BMA nor PRP show statistically significant improvements compared to corticosteroid, as all CrIs include zero. Highest Ranked: The results do not favor any treatment as statistically significant, but numerically, PRP has a higher mean difference compared to corticosteroid.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abdelsalam M, Sajed M, Alsaeed A, Abdelrahman H, Rafat r, Tarek M, al-Najjar A. My Shoulder Hurts, What Should I Do? A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-analysis of Different Injectables in Glenohumeral Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/my-shoulder-hurts-what-should-i-do-a-systematic-review-and-bayesian-network-meta-analysis-of-different-injectables-in-glenohumeral-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/my-shoulder-hurts-what-should-i-do-a-systematic-review-and-bayesian-network-meta-analysis-of-different-injectables-in-glenohumeral-osteoarthritis/