Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sjögren’s Disease (SjD) classification relies on the EULAR/ACR 2016 criteria: i) quantifying lymphocyte infiltration in labial salivary gland (LSG) biopsies, ii) autoantibody status and iii) objective quantification of eye and mouth dryness. Diagnosis is challenging due to heterogeneity of clinical manifestations and underlying biology, especially for seronegative patients, who comprise about 30% of the SjD population.
In a proof-of-concept study, we have demonstrated that a machine learning foundation model for histology achieved an area under the ROC curve (AUROC) of 84% in SjD diagnosis using digitalized LSG only [1]. As the main criticism towards AI are validation and mono-centricity bias, the study was extended to 6 centres. We also assessed the model’s performance in the difficult-to-diagnose seronegative population and leveraged the foundation model to identify histological biomarkers associated with SjD.
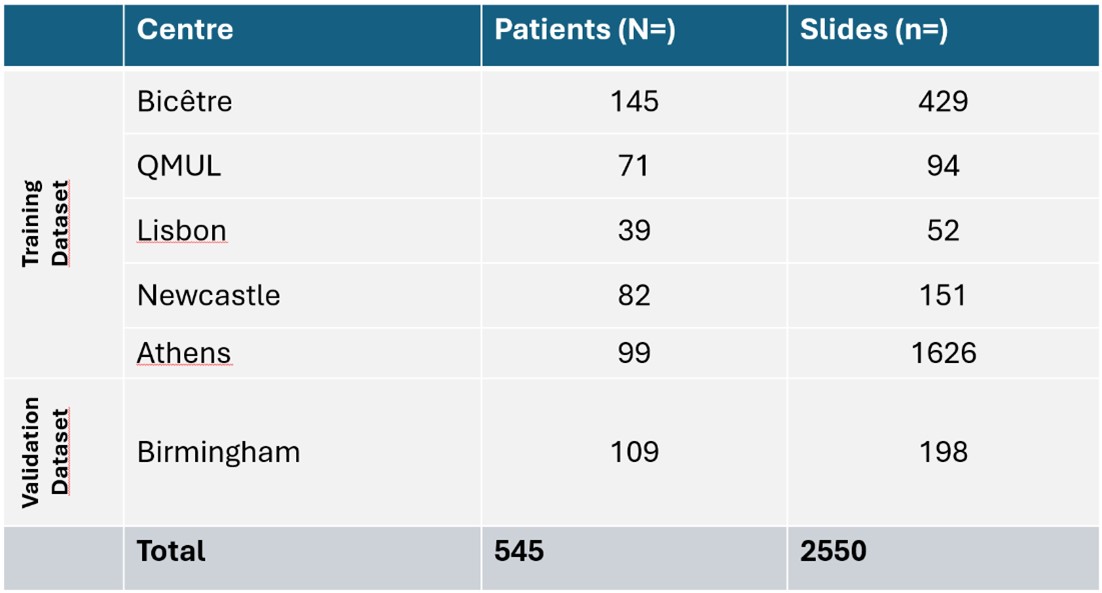
Methods: A deep learning foundation model was fine-tuned using digitalized LSG slides from 6 European expert centers of the NECESSITY consortium, a H2020 IMI2 project. Three patient groups were included: patients with sicca symptoms without autoantibodies and with FS< 1; SjD patients with FS ≥1; and SjD patients with FS< 1. All diagnoses were confirmed by expert rheumatologists and met the EULAR/ACR 2016 criteria.
The model was fine-tuned on 5 centers, the 6th center served as external validation. Algorithm performance was measured using AUROC, positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV), specificity and sensitivity. A subanalysis assessed model’s performance on SSA- patients.
A state-of-the-art machine learning technology – concept-based explainability – was used to flag histological patterns correlated to SjD diganosis.
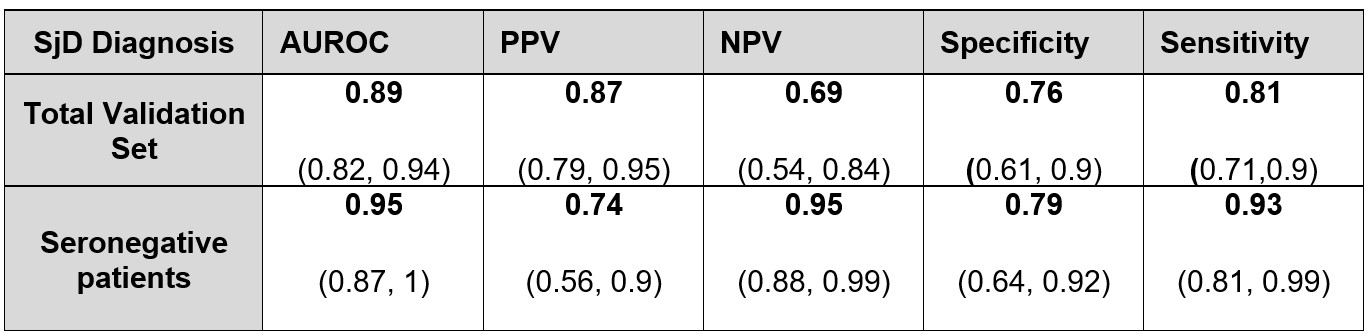
Results: We included 545 patients – 436 patients in the training set and 109 in the validation, see Table 1. In the validation set, the model achieved an AUROC of 0.89 (95% CI 0.82 to 0.94) for SjD diagnosis – compared to 0.84 (95% CI 0.83 to 0.86) in the 2023 study with 3 centers. Notably, for the seronegative population, the model achieved an AUROC of 0.95 (95% CI 0.87 to 1) – this result is particularly interesting as seronegative patients are the hardest to diagnose. The performances are presented in Table 2.
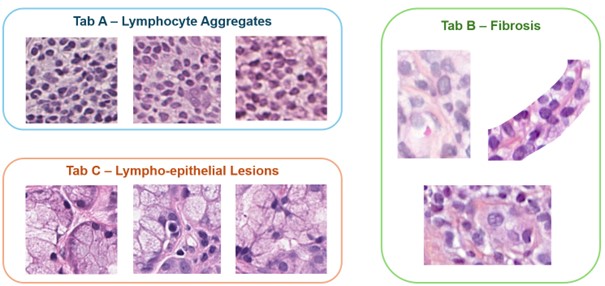
In addition, histological patterns most associated with SjD were identified (Figure 1). As expected, lymphocyte aggregates were correlated with SjD (Tab A). Interestingly, the model also identified fibrosis (Tab B) and lympho-epithelial lesions (Tab C) as SjD markers. These histological patterns serve as potential histological biomarkers for stratifying SjD in homogeneous patient subgroups, supporting precision approaches in drug development and therapeutic approach.
Conclusion: This study is a large multicentric validation of a machine-learning foundation model for SjD diagnosis. Potential histological biomarkers were identified and could serve for SjD stratification, supporting precision therapeutic approaches.
1. Basseto L, et al. Deep Learning Accurately Predicts Focus Score and Diagnosis of Primary Sjögren Syndrome Using Labial Salivary Gland Biopsies. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Duquesne J, Claye C, Basseto L, Barnes M, Pontarini E, Syed A, Bombardieri M, Fisher B, NAYAR S, Goules A, Tzioufas A, chatzis L, Ng W, Scane B, Bandeira M, C. Romão V, Lazure T, Adam C, Mariette X, Bitoun S, Bouget V. Multicenter Validation of a Machine Learning Foundation Model to Diagnose Sjögren’s Disease and Identify Histological Biomarkers for Disease Stratification [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multicenter-validation-of-a-machine-learning-foundation-model-to-diagnose-sjogrens-disease-and-identify-histological-biomarkers-for-disease-stratification/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multicenter-validation-of-a-machine-learning-foundation-model-to-diagnose-sjogrens-disease-and-identify-histological-biomarkers-for-disease-stratification/