Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Cardiopulmonary Aspects
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is an extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) detected in 20 to 60% of patients with RA on high-resolution computed-tomography (HRCT) chest scan and is clinically significant in near 10%. Despite a high morbi-mortality, a definite strategy for ILD screening in patients with RA remains to be determinate and the identification of markers predictive of the occurrence of ILD is needed. To date, numerous biomarkers have been reported to be associated with ILD among patients with RA but most of them requires validation in a prospective cohort. Recently, in a large international genetic association case-control study, the rs35705950 MUC5Bpromoter variant was identified as the major RA-ILD risk factor. The ESPOIR cohort included patients aged 18 to 70 years who had a definitive or probable diagnosis of RA and included a prospective follow-up. Consequently, we investigated in the ESPOIR cohort, whether the rs35705950 MUC5Bpromoter variant would improve risk stratification at baseline for ILD detection after 13 years of RA duration.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study of the French ESPOIR cohort, an ILD detection by chest HRCT scan was systematically proposed for every patient after 13 year of RA duration. Chest HRCT scans were centrally reviewed by an experienced radiologist and classified according to the presence, the extension and the pattern of ILD. All included patients were genotyped for rs35705950 MUC5Bpromoter variant. Baseline clinical and biological data were collected. A logistic model was used to identify baseline predictors for the occurrence of ILD on HRCT scans. Confidence intervals were estimated using sampling methods.
Results: Among the 170 patients who were investigated with an HRCT scan (133 women (78.2%), mean RA duration 13.7 ±1.1 years), ILD was detected in 31 patients (18.2%). ILD extension was >10% in 9 patients (5.3%), fibrotic ILD was detected in 16 patients (9.4%). Two additional patients from the ESPOIR cohort that previously died from ILD were included in the analysis. Among European Caucasian patients, MUC5Brs35705950 minor allele frequency (MAF) was 26.5% in the RA-ILD population compared to 8.9% in the RA-noILD population (OR=6.0 CI95%(2.0-17.6)). After logistic regression, baseline predictors for ILD were male sex (OR=2.6 CI95%(1.0-6.6)), age at RA onset > 49 y/o (OR=5.2 CI95%(2.0-15.1)), number of swollen joints > 9 (OR=2.9 CI95%(1.2-7.2)), migrating arthritis vs persistent arthritis (OR=3.4 CI95%(1.4-8.7)) and MUC5Brs35705950 T risk allele (OR=3.8 CI95%(1.5-10.1)). The logistic model using could predict RA-ILD occurrence after 13 years of RA duration with an AUC=0.80 CI95%(0.72-0.90).
Conclusion: In RA patients, altogether with baseline clinical data, MUC5Brs35705950 genotyping could help to improve risk stratification for ILD occurrence at 13 years of RA duration.
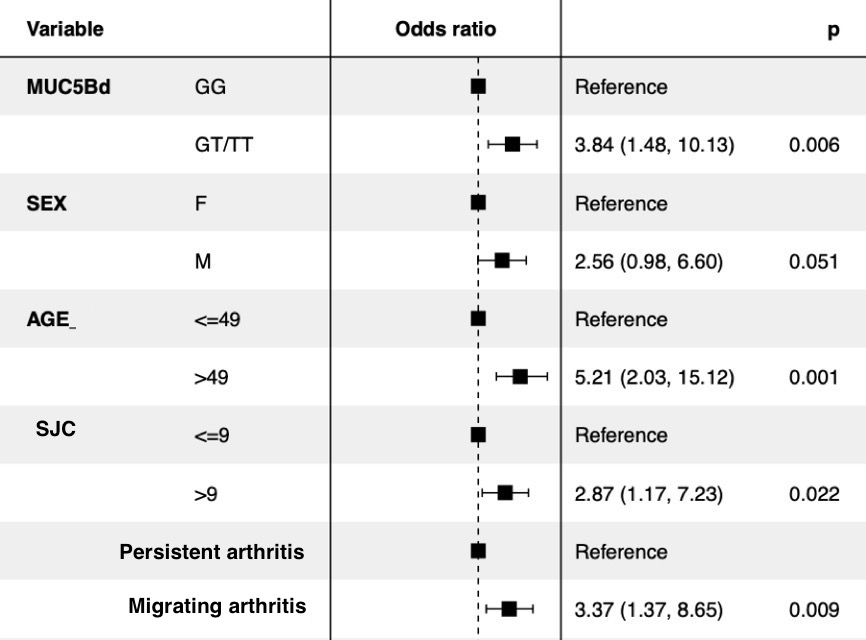 Baseline predictors of ILD occurence at 13 years of RA duration
Baseline predictors of ILD occurence at 13 years of RA duration
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Juge P, Louis-Sidney F, Granger B, Kedra J, Debray M, Ebstein E, Borie R, Constantin A, Combe B, Flipo R, Mariette X, Vittecoq O, Saraux A, Carvajal Alegria G, Sibilia J, Berenbaum F, Kannengiesser C, Crestani B, Boileau C, Fautrel B, Dieude P. MUC5B Promoter Variant rs35705950 and Risk Stratification for Rheumatoid Arthritis – Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/muc5b-promoter-variant-rs35705950-and-risk-stratification-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/muc5b-promoter-variant-rs35705950-and-risk-stratification-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease/
