Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. Tofacitinib +/- background MTX has been shown to be an effective treatment for reducing RA disease activity by many validated patient-reported outcomes (PROs),1,2 including the Short Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36). However, the impact of MTX withdrawal in patients (pts) with RA who achieve low disease activity (LDA) or remission with tofacitinib in combination with MTX is unclear.
Methods: ORAL Shift (NCT02831855) was a global Phase 3b/4 study in pts aged ≥ 18 years with moderate to severe RA and an inadequate response to MTX. Pts received open-label (OL) tofacitinib modified-release (MR) 11 mg once daily (QD) + MTX (tofacitinib + MTX) for 24 weeks. Pts achieving LDA (Clinical Disease Activity Index ≤ 10) at Week (W)24 entered the 24-week double-blind (DB) MTX withdrawal phase and were randomized 1:1 to receive tofacitinib MR 11 mg QD + placebo (tofacitinib monotherapy; ie blinded MTX withdrawal) or continue tofacitinib + MTX. The SF-36 includes Physical and Mental Component Summary (PCS and MCS, respectively) and 8 individual domain scores, and was administered to pts during the OL and DB phases. We report the following SF-36 data (norm-based scores) in pts who achieved LDA and were treated in the DB phase: mean scores at baseline (BL), W12 and W24 (OL phase; post hoc); mean changes from BL to W24 (OL phase; post hoc); least squares mean (LSM) changes from W24 to W36 and W48 (DB phase; pre-defined secondary endpoint); and mean scores at W48 (DB phase; post hoc). SF-36 mean scores at W48 were re-expressed on the 0–100 scale, along with BL values combined in a single group, for comparison with SF-36 values of a 1998 US age and gender matched normative population (A/G norms).
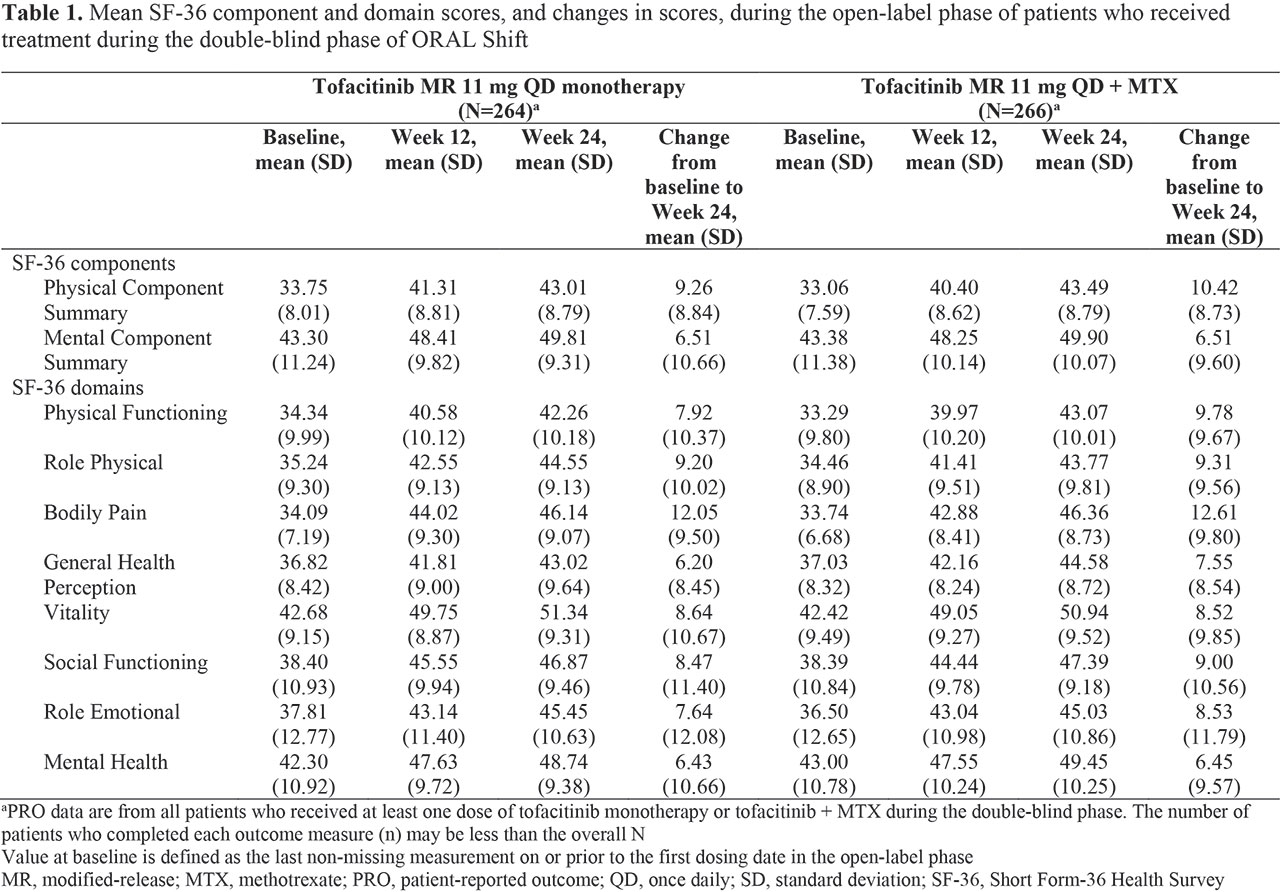
Results: In all, 694 pts received tofacitinib + MTX in the OL phase; 530 achieved LDA at W24 and were treated in the DB phase (tofacitinib monotherapy: n=264; tofacitinib + MTX: n=266). Demographics and pt characteristics at OL phase BL were similar between treatment arms. Mean changes from BL to W24 showed improvements in SF-36 PCS, MCS, and all domain scores (Table 1). LSM changes from W24 to W36 and W48 in SF-36 PCS, MCS, and all domain scores (except Role Physical and Bodily Pain at W36) were similar in both treatment arms (Table 2). By W48, Vitality scores exceeded and Mental Health scores were comparable with A/G norms in both treatment arms (Figure 1).
Conclusion: In the OL phase, pts receiving tofacitinib MR 11 mg QD + MTX reported improvements in health-related quality of life by SF-36 PCS, MCS, and domains. In pts who achieved LDA, MTX withdrawal during the DB phase resulted in similar SF-36 scores, compared with patients continuing combination therapy. These findings are consistent with those from ORAL Shift disease activity measures and PROs (primary and secondary efficacy endpoints; reported elsewhere),3 and reinforce that pts receiving tofacitinib MR 11 mg QD + MTX who achieve LDA, may withdraw MTX up to W48 without significant worsening of PROs.
- Strand et al. Rheum 2016; 55: 1031-41.
- Strand et al. Arth Res Ther 2015; 17: 307.
- Cohen et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2019; 78: A260.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Jennifer Arnold of CMC Connect and funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Pope J, Woolcott J, Rivas J, Diehl A, Liu S, Gruben D, Cohen S. MTX Withdrawal in Patients with RA Who Achieve Low Disease Activity with Tofacitinib Modified-Release 11 Mg Once Daily + MTX: An Assessment of the Impact on the Short Form-36 Patient-Reported Outcome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mtx-withdrawal-in-patients-with-ra-who-achieve-low-disease-activity-with-tofacitinib-modified-release-11-mg-once-daily-mtx-an-assessment-of-the-impact-on-the-short-form-36-patient-reported-outcome/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mtx-withdrawal-in-patients-with-ra-who-achieve-low-disease-activity-with-tofacitinib-modified-release-11-mg-once-daily-mtx-an-assessment-of-the-impact-on-the-short-form-36-patient-reported-outcome/