Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The introduction of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors in the early 1970s resulted in marked improvement in clinical outcomes of scleroderma renal crisis (SRC).Despite the undisputed improvement in outcomes of SRC since the availability of ACE inhibitors, estimates of mortality and morbidity vary considerably. The objective of this study was to systematically review the mortality and morbidity associated with SRC and to determine temporal trends.
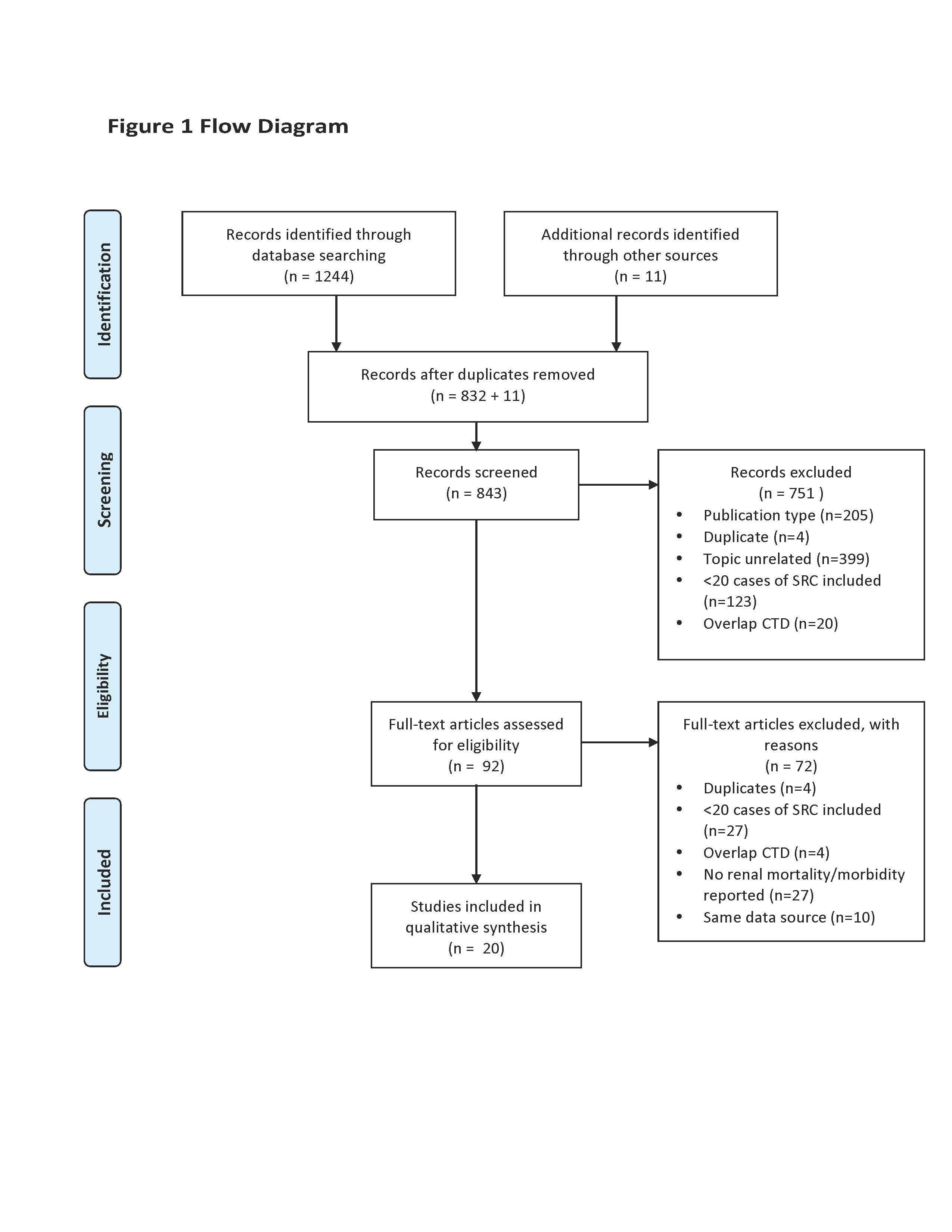
Methods: We searched Medline, EMBASE and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews from database inception to January 15, 2019. Bibliographies of selected articles were hand-searched for additional references. Data were extracted using a standardized extraction form. Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale. Results were analyzed qualitatively.
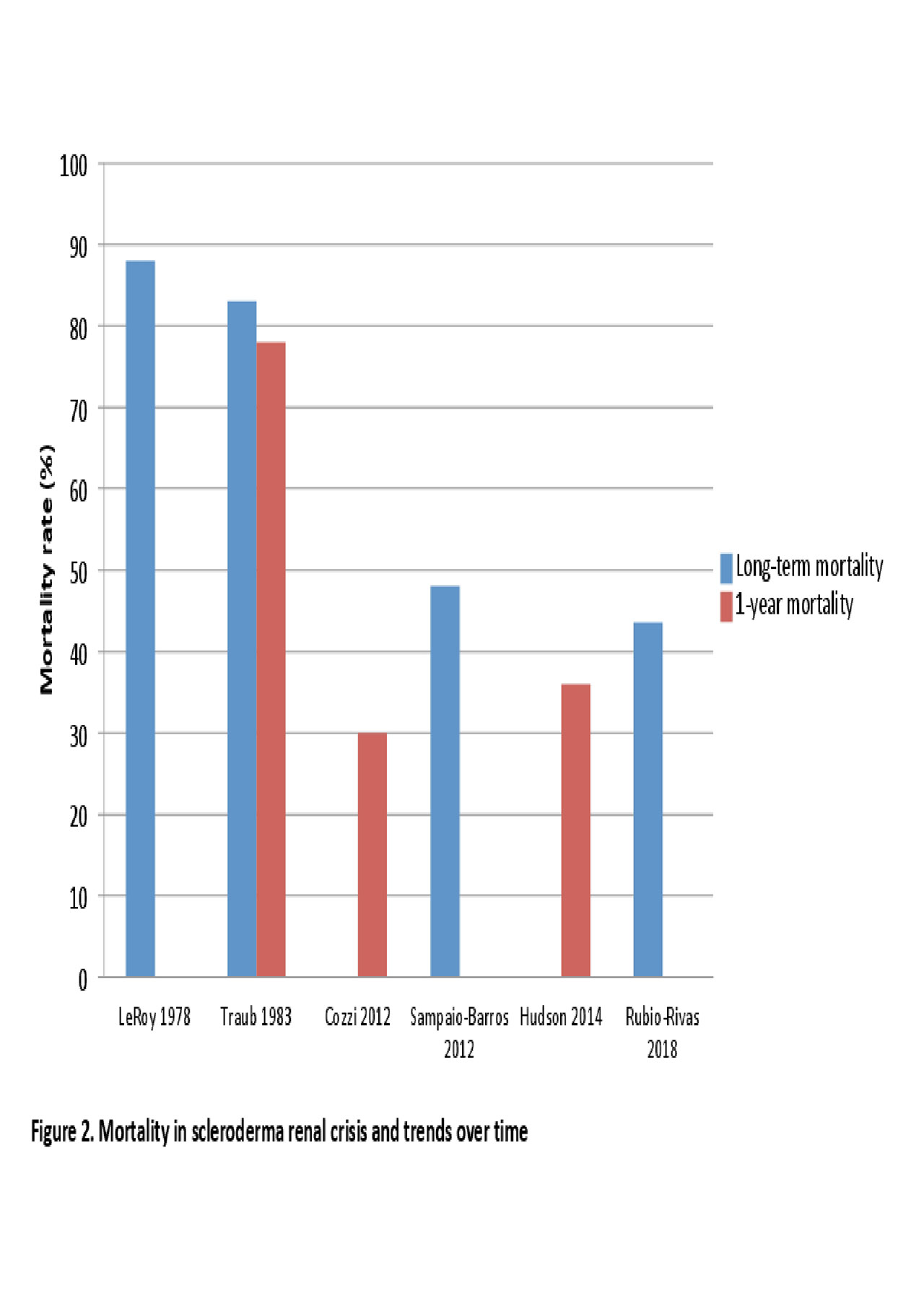
Results: Twenty studies with 14,059 SSc subjects, of which 854 had SRC and 4095 had SSc-associated end stage renal disease (SSc-ESRD), met inclusion criteria. Study quality was generally moderate. Cumulative mortality in the post-angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor era was approximately 20% at 6 months, 30-36% at 1 year, 19%-40% at 3 years and almost 50% at 10 years from SRC onset. Although the introduction of ACE inhibitors in the early 1970s resulted in a 50% improvement in SRC mortality, there was no further improvement thereafter. SRC mortality rates were proportionally higher than mortality rates associated with other SSc organ involvement. The rate of permanent dialysis after SRC in the post-ACE inhibitor era ranged from 19-40%. Three to 17% of SSc patients underwent renal transplant. Survival was better in patients post-renal transplant (54-91%) compared to those on dialysis (31-56%). Graft survival improved over time and appeared similar to that of patients with other types of ESRD.
Conclusion: SRC mortality and morbidity remain high. Novel treatments are required to improve outcomes of SRC.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim H, Lefebvre F, Hoa S, Hudson M. Mortality and Morbidity in Scleroderma Renal Crisis: A Systematic Literature Review [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mortality-and-morbidity-in-scleroderma-renal-crisis-a-systematic-literature-review/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mortality-and-morbidity-in-scleroderma-renal-crisis-a-systematic-literature-review/