Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treat to target in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) suggests escalation of therapy in patients whose scores are high or moderate on a disease activity index such as the Clinical Disease Activity index (CDAI), although exceptions are recognized according to shared decisions. Individual RA clinical core data set measures and indices may be elevated by non-inflammatory comorbidities such as fibromyalgia (FM) and depression (DEP), independent of disease activity (ACR Open Rheum. 2022. Semin Arth Rheum. 2023;58:152151).Most studies are retrospective using various patient questionnaires to recognize DEP or FM. A Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ) contains indices to screen for FM, Fibromyalgia Assessment Screening Tool (FAST4) and DEP, MDHAQ Depression Screen (MDS2-) on a single questionnaire, in addition to RAPID3 to assess clinial status. We performed a cross sectional study to analyze the prevalence of FM and DEP in RA patients in different CDAI categories.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was performed in unselected RA patients at a routine care visit. All patients completed an MDHAQ, which includes the FAST4 and MDS2 indices.A 28 swollen joint count (SJC), 28 tender joint count (TJC), 0-10 global assessments of patient (PaGA) and physician (PhGA) were assessed to calculate a 0-76 CDAI. The proportion of patients who screened positive (+) or negative (-) for FM on FAST4 and/or DEP on MDS2 were analyzed according to CDAI remission/low (R/L) vs moderate/high (M/H) categories. Chi-square tests were used to assess statistical significance.
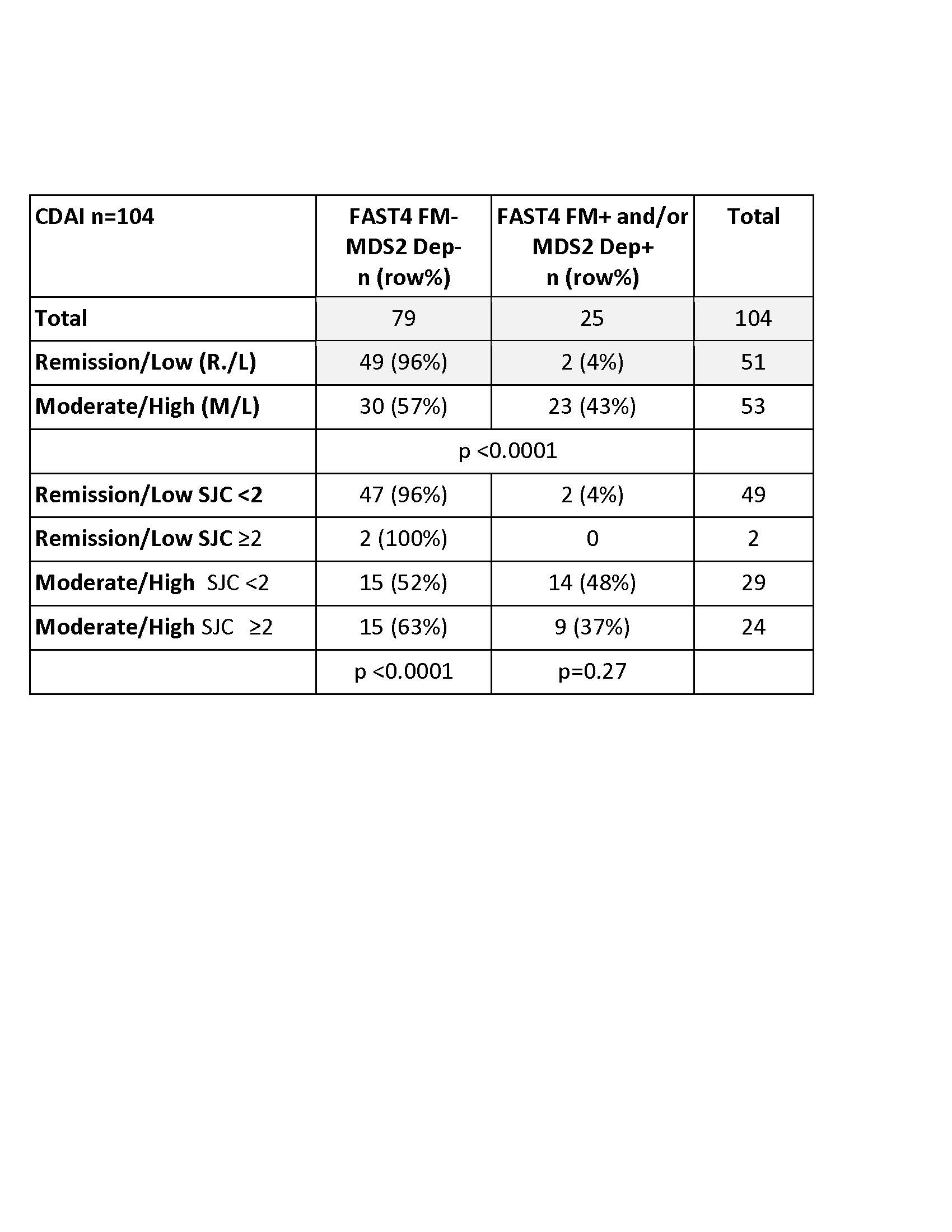
Results: The study included 104 RA patients, with median CDAI of 10.5 and interquartile range (IQR) 11.6, classified as moderate disease activity. Among the 104 patients 17 (16%) were FAST4+, 17 (16%) MDS2+, 9 (9%) were FAST4+ & MDS+ (8 each were FAST4+, MDS2- or FAST4-, MDS2+), and 79 (76%) were FAST4-,MDS2-.CDAI R/L activity was seen in 51 (49%) and M/H in 53 (51%) patients. Among the 51 in R/L, 49 (96%, 47% of all patients) were FAST4-,MDS2-, while 2 (4%, 2% of all patients) were FAST4-,MDS2+. Conversely, among the 53 patients in M/H activity, 30 (57%, 29% of all patients) were FAST4-,MDS2-, while 23 (43%, 22% of all patients) were FAST4+ or MDS2+ (or both FAST4+,MDS2+) (p < 0.0001) (Table). Further stratification of patients according to CDAI category, SJC of < 2 vs ≥2, and FAST4 and MDS2 status indicated that CDAI R/L patients included 47 FAST4-,MDS2- and with SJC< 2 vs 2 with SJC ≥2, compared to 15 CDAI M/H patients each with FAST4-,MDS2- or FAST4 or MDS2+ (p < 0.0001) (Table). By contrast, no significant differences in SJC vs CDAI categories were seen in FAST4+ or MDS2+ patients (p-0.27), although numbers are small.
Conclusion: About half of unselected RA patients seen in routine care who were in M/H CDAI activity screened positive for FM, DEP or both, in contrast to only 4% of those in R/L activity.FM or DEP were screened for on MDHAQ indices FAST4 and MDS2, with minimal extra time required for the physician.Patients in M/H CDAI activity did not differ significantly for SJC < 2 vs ≥2, regardless of FM or DEP status. These findings extend prior evidence that non-inflammatory comorbidities may elevate RA index levels, with implications for treat to target and general rheumatology care.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schmukler J, Pincus T. More Than 50% of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Patients with High or Moderate CDAI (clinical Disease Activity Index) Screen Positive on MDHAQ (multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire) Indices for FAST4 (fibromyalgia Assessment Screening Tool) And/or MDS2 (MDHAQ Depression Screen) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/more-than-50-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patients-with-high-or-moderate-cdai-clinical-disease-activity-index-screen-positive-on-mdhaq-multidimensional-health-assessment-questionnaire-indices-for/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/more-than-50-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patients-with-high-or-moderate-cdai-clinical-disease-activity-index-screen-positive-on-mdhaq-multidimensional-health-assessment-questionnaire-indices-for/