Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The significance of antibodies directed against activated Factor (FXa) and thrombin (Thr) found in ~40% of patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and/or Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) has not been determined. FXa and Thr are both co-regulated by antithrombin (AT)III and increasingly implicated in alternative pathways of complement activation. Therefore, we studied the ability of anti-(a)FXa and/or anti-(a)Thr IgG to modulate complement activation in SLE and APS.
Methods: Patients with SLE +/- APS and known aThr and/or aFXa IgG positivity had serial measurements of complement C3 at clinic appointments at University College London Hospital from 2015-19. Affinity purification of aFXa and aThr IgG were performed by passage through heparin/FXa or heparin/Thr and then protein G column. The effect of this IgG upon FXa and Thr mediated C3 and C5 activation was measured by Western Blot. Structural analysis of FXa and Thr was performed by Scalable Molecular Dynamics (NAMD) , Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD) and Discotope (v1.1). Predicted sites were modelled onto high resolution crystal structures of the ATIII-FXa and ATIII-Thr complexes and compared with the in-vitro ability of ATIII to regulate aFXa-FXa and aThr-Thr mediated C3/C5 activation.
Results: Longitudinal analysis of 66 patients with SLE (n=5 with APS) from an average of 8.2 (range 1 to 10) visits across 5 years found that patients positive for anti(a)FXa alone (n=16) or in combination with anti(a)Thr IgG (n=26) had lower C3 levels than patients with aThr IgG alone (n=24) (Figure1). We affinity purified IgG from 15 of these patients. aThr IgG increased Thr mediated activation of C3 (x 1.8 fold) and C5 (x3 fold), whilst aFXa IgG increased (x 1.3 fold) C3 activation only. Using in silico epitope mapping we identified potential epitopes for binding of aFXa to FXa and aThr to Thr. These studies predicted steric hindrance of binding to ATIII at 2 of 4 potential aFXa IgG epitopes on FXa compared with only 1 of 6 aThr IgG epitopes on Thr. This increased likelihood of steric hinderance of aFXa compared to aThr was confirmed by in-vitro studies whereby ATIII inhibition of Thr-mediated C3 and C5 activation was not affected by aThr IgG, whilst ATIII inhibition of FXa-mediated C3 and C5 activation was abrogated by aFXa IgG.
Conclusion: We propose a novel method of complement regulation in SLE and APS patients whereby aFXa and aThr IgG increase complement activation. Furthermore, we demonstrate that natural inhibition by ATIII is less efficient on FXa-FXa IgG-mediated complement activation compared with the one mediated by Thr-aThr IgG due to proximity of the IgG epitope to the ATIII binding site in FXa but not Thr.
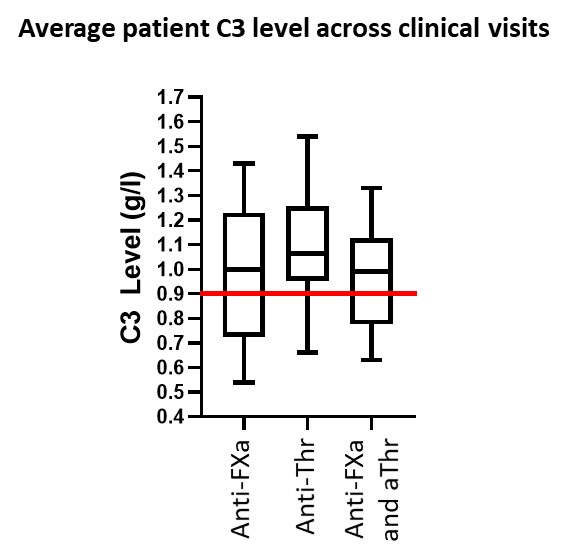 Figure 1: The average C3 level from SLE and APS patients (n=66) across their visits to clinic (2015_2019) demonstrate lower levels of C3 on average for FXa positive patients and double positive (aFXa and aThr) patients compared to aThr alone. The red line indicates clinical cutoff for low C3 levels. This implies the presence of aFXa antibodies may influence the C3 levels of SLE and APS patients.
Figure 1: The average C3 level from SLE and APS patients (n=66) across their visits to clinic (2015_2019) demonstrate lower levels of C3 on average for FXa positive patients and double positive (aFXa and aThr) patients compared to aThr alone. The red line indicates clinical cutoff for low C3 levels. This implies the presence of aFXa antibodies may influence the C3 levels of SLE and APS patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McDonnell T, Amarnani R, Spiteri V, Spicer C, Pericleous C, Artim-Esen B, Mackie I, Botto M, Rahman A, Giles I. Molecular Modelling Predicts Inhibition of Functional Effects of Anti-thrombin III on Factor Xa Mediated Complement Activation by Anti- Factor Xa IgG in SLE and APS [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/molecular-modelling-predicts-inhibition-of-functional-effects-of-anti-thrombin-iii-on-factor-xa-mediated-complement-activation-by-anti-factor-xa-igg-in-sle-and-aps/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/molecular-modelling-predicts-inhibition-of-functional-effects-of-anti-thrombin-iii-on-factor-xa-mediated-complement-activation-by-anti-factor-xa-igg-in-sle-and-aps/
