Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes, and Raynaud's - Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics I
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
(mRSS) is the major outcome measure for skin fibrosis in clinical trials (CT)
in diffuse cutaneous scleroderma (dcSSc). Traditionally, CT in skin fibrosis included
mostly severe patients with higher mRSS. This approach is challenged by recent data
showing that patients with lower baseline skin scores are more likely to progress
during 1 year of follow-up (1). In this study, we explored baseline mRSS as a
predictor of change in skin fibrosis in patients with dcSSc.
704 patients from the EUSTAR registry. The inclusion criteria were: expert-diagnosis
of dcSSc, fulfillment of ACR1980 criteria, mRSS≥7 at baseline and
available data for mRSS at 12±2 months follow-up. Skin improvement and skin
progression were defined as a decrease/increase in mRSS of >5 points AND ≥25
% within 1 year, respectively (1). A comparison of the baseline mRSS in patients
with/without skin improvement/progression after 1 year was performed (Wilcoxon
rank sum test). Further, we explored the interdependence between different mRSS
cut-offs and progression/regression of skin fibrosis.
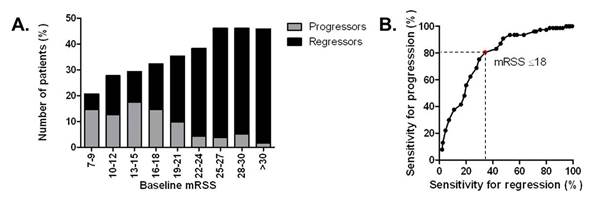
skin improvement, whereas 77/704 (11%) showed skin progression after 1 year
(Figure 1A). High baseline mRSS was strongly associated with skin improvement
(p<0.001), with the best sensitivity and specificity for prediction of skin
regression at a cut-off of 17.5 points (area under the curve 0.708). A lower
baseline mRSS was confirmed as predictor of skin progression after 1 year (p<0.001). We analysed different mRSS cut-offs
and their sensitivity for progression and regression of skin fibrosis (Figure 1B).
In this cohort, an upper baseline mRSS cut-off value of 18 points performed
best, including the highest proportion of progressors (80.5%) and the lowest
proportion of regressors (34.2%, Figure 1B). For feasibility reasons, higher
thresholds were also analyzed and, overall, a baseline mRSS between 18 and 25 allowed
the inclusion of a reasonably high rate of progressors over regressors.
and regressors per baseline mRSS range. B. Sensitivity for progression
and regression depending on different cut-off values for baseline mRSS.
paradigm shift regarding mRSS thresholds used as inclusion criteria in CT in
skin fibrosis in dcSSc. In order to preferentially include progressive patients
over those prone to improve as part of the natural history of the disease, a
lower mRSS at baseline should be considered. Further analyses on other cohorts
will add valuable data to support the choice of a specific threshold.
1. Maurer
B, Graf N, Michel BA, et al. Prediction of worsening of skin fibrosis in
patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis using the EUSTAR database.
Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(6):1124-31.
Disclosure: R. Dobrota, Pfizer Inc, 2; B. Maurer, None; N. Graf, Medac, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, Bayer, 5; S. Jordan, None; C. M. Mihai, Actelion/Geneva Romfarm, Abbvie, 5; O. Kowal-Bielecka, None; Y. Allanore, Actelion, Bayer, Biogen, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, Inventiva, Medac, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Sanofi-Aventis, Servier, 2,Actelion, Bayer, Biogen, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, Inventiva, Medac, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Sanofi-Aventis, Servier, 5; O. Distler, Actelion, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Ergonex, BMS, Sanofi-Aventis, United BioSource Corporation, Roche/Genentech, Medac, Biovitrium, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, Novartis, 4D Science, Active Biotec, Bayer-Schering, Sinoxa, Serodapharm, EpiPharm, Biogen, Inven, 5,Actelion, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Ergonex, BMS, Sanofi-Aventis, United BioSource Corporation, Roche/Genentech, Medac, Biovitrium, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, Novartis, 4D Science, Active Biotec, Bayer-Schering, Sinoxa, Serodapharm, EpiPharm, Biogen, Inven, 2.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dobrota R, Maurer B, Graf N, Jordan S, Mihai CM, Kowal-Bielecka O, Allanore Y, Distler O. Modified Rodnan Skin Score Thresholds for the Optimization of Cohort Enrichment in Clinical Trials in Skin Fibrosis in Patients with Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/modified-rodnan-skin-score-thresholds-for-the-optimization-of-cohort-enrichment-in-clinical-trials-in-skin-fibrosis-in-patients-with-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/modified-rodnan-skin-score-thresholds-for-the-optimization-of-cohort-enrichment-in-clinical-trials-in-skin-fibrosis-in-patients-with-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis/
