Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In observational studies, several longitudinal methods have been proposed to impute missing data of an individual by using the available information of the same individual at other time points. An alternative approach is to apply a cross-sectional method which imputes missing values of an individual at a particular time point based on the available information from other individuals at that time point. We aimed to compare selected cross-sectional methods for imputing disease activity in longitudinal observational data of patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).
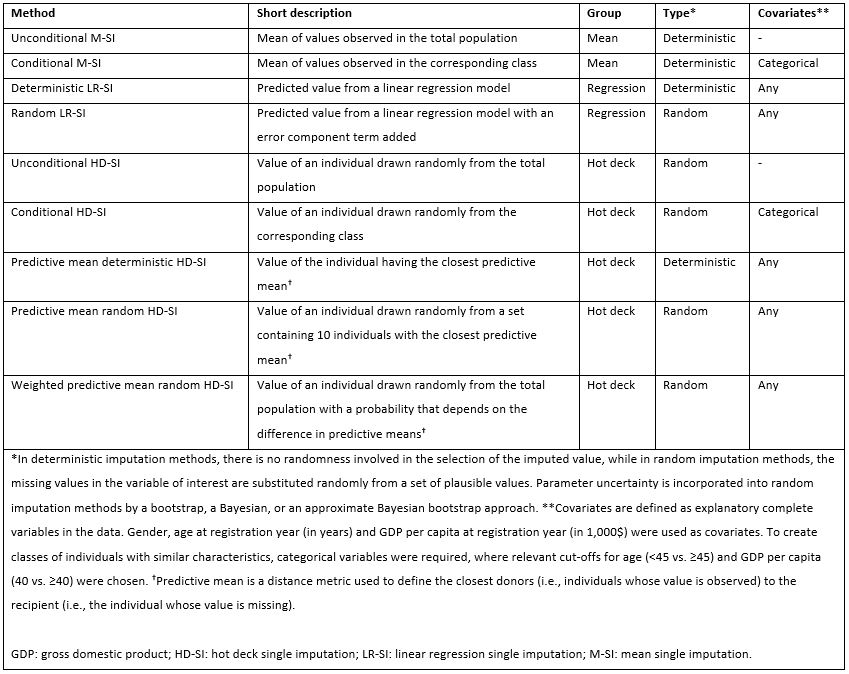
Methods: Data on patients with axSpA from 10 European registries were used to conduct a simulation study. Patients initiating a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor or an interleukin-17A inhibitor as their first biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug between 2017 and 2021 were included. Disease activity was assessed by the Axial Spondyloarthritis Disease Activity Score using C-reactive protein (ASDAS) and the achievement of low disease activity (LDA; ASDAS< 2.1) at baseline, 6 and 12 months. In a simulation setting, we applied 9 single cross-sectional imputation methods, divided into three groups: mean, regression and hot deck imputation (Table 1), while complete case analysis was applied as a comparator method to imputation. The performance of each imputation method was evaluated via relative bias, i.e., the difference between the estimated and the true value, divided by the true value, for mean ASDAS and derived proportion of patients achieving LDA. Analyses were carried out for a sample size of 1,000, where 60% of data were missing at random, and 1,000 simulated datasets were generated. Simulations were conducted separately for each of the three time points.
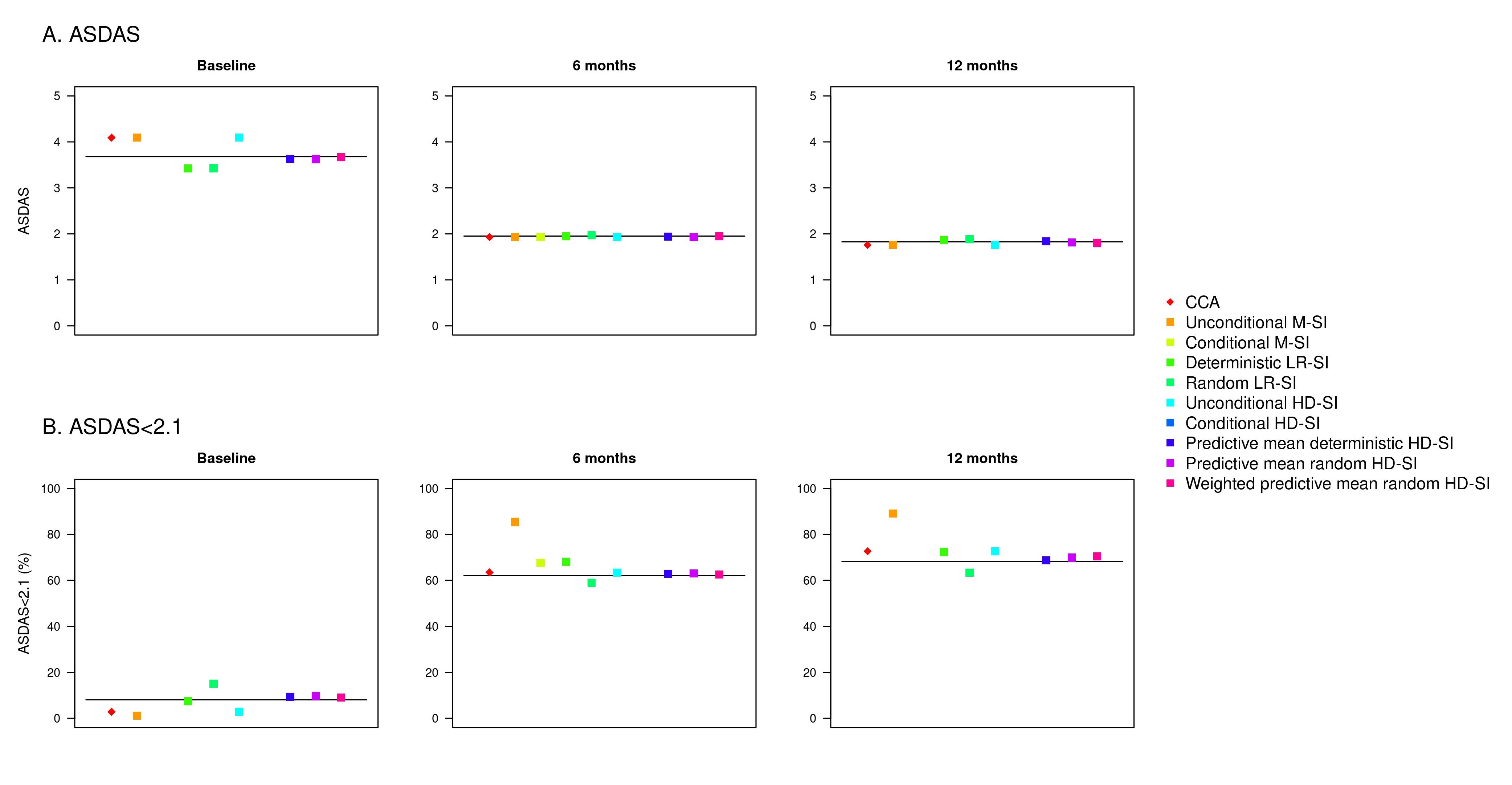
Results: Data from 8,583 patients who had at least one available ASDAS registration at any time point were included in the simulations. Mean (standard deviation) ASDAS at baseline, 6 months and 12 months were 3.7 (1.1), 2.0 (1.0) and 1.8 (0.9), respectively. Overall, the simulation results showed that performance of the imputation methods was better for missing follow-up data than for missing baseline data, and higher bias was observed when assessing achievement of ASDAS LDA than for mean ASDAS (Figure 1). When estimating the mean ASDAS, all predictive mean hot deck methods had a relative bias < 2% for baseline data, while mean and regression methods resulted in a bias >5%. For missing values at both follow-up time points, all imputation methods had a bias < 5%. The lowest bias was observed for linear regression and predictive mean hot deck methods (< 1%) at 6 months, and for predictive mean hot deck (< 2%) at 12 months. Regarding performance for estimating ASDAS LDA, all imputation methods resulted in bias > 5% at baseline, while predictive mean hot deck methods consistently resulted in a bias < 5% at both follow-up time points.
Conclusion: This study adds knowledge regarding possible methods for handling missing data in observational research. Of the 9 cross-sectional imputation methods, the three hot deck single imputation methods using predictive mean matching showed the highest robustness and thus constitute the suggested approaches.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Georgiadis S, Pons M, Rasmussen S, Hetland M, Linde L, DiGuiseppe D, Michelsen B, Karlsson Wallman J, Olofsson T, Pavelka K, Závada J, Glintborg B, Loft A, Codreanu C, Melim D, Esperança Almeida D, Kvien T, Rantalaiho V, Peltomaa R, Gudbjornsson B, Palsson O, Rotariu O, MacDonald R, Rotar Z, Perdan-Pikmajer K, Laas K, Iannone F, Ciurea A, Ostergaard M, Oernbjerg L. Missing Data in Observational Studies: Investigating Cross-sectional Single Imputation Methods for Assessing Disease Activity in Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/missing-data-in-observational-studies-investigating-cross-sectional-single-imputation-methods-for-assessing-disease-activity-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/missing-data-in-observational-studies-investigating-cross-sectional-single-imputation-methods-for-assessing-disease-activity-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/