Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ), a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that inhibits both interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17F, has been demonstrated to be efficacious and well tolerated in patients (pts) with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) treated for up to 3 years in the BE AGILE study and its open-label extension (OLE).1–3 At the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020, most pts in BE AGILE had received >3 years of BKZ treatment and outcomes were stable.3 Findings from real-world studies evaluating the impact of the pandemic on disease activity and quality of life in pts with axial spondyloarthritis have been conflicting.4–6 We assess whether the COVID-19 pandemic and associated societal changes have impacted pt-reported disease activity and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among pts with active AS receiving BKZ in the ongoing OLE (NCT03355573) of a phase 2b dose-ranging study (BE AGILE; NCT02963506).
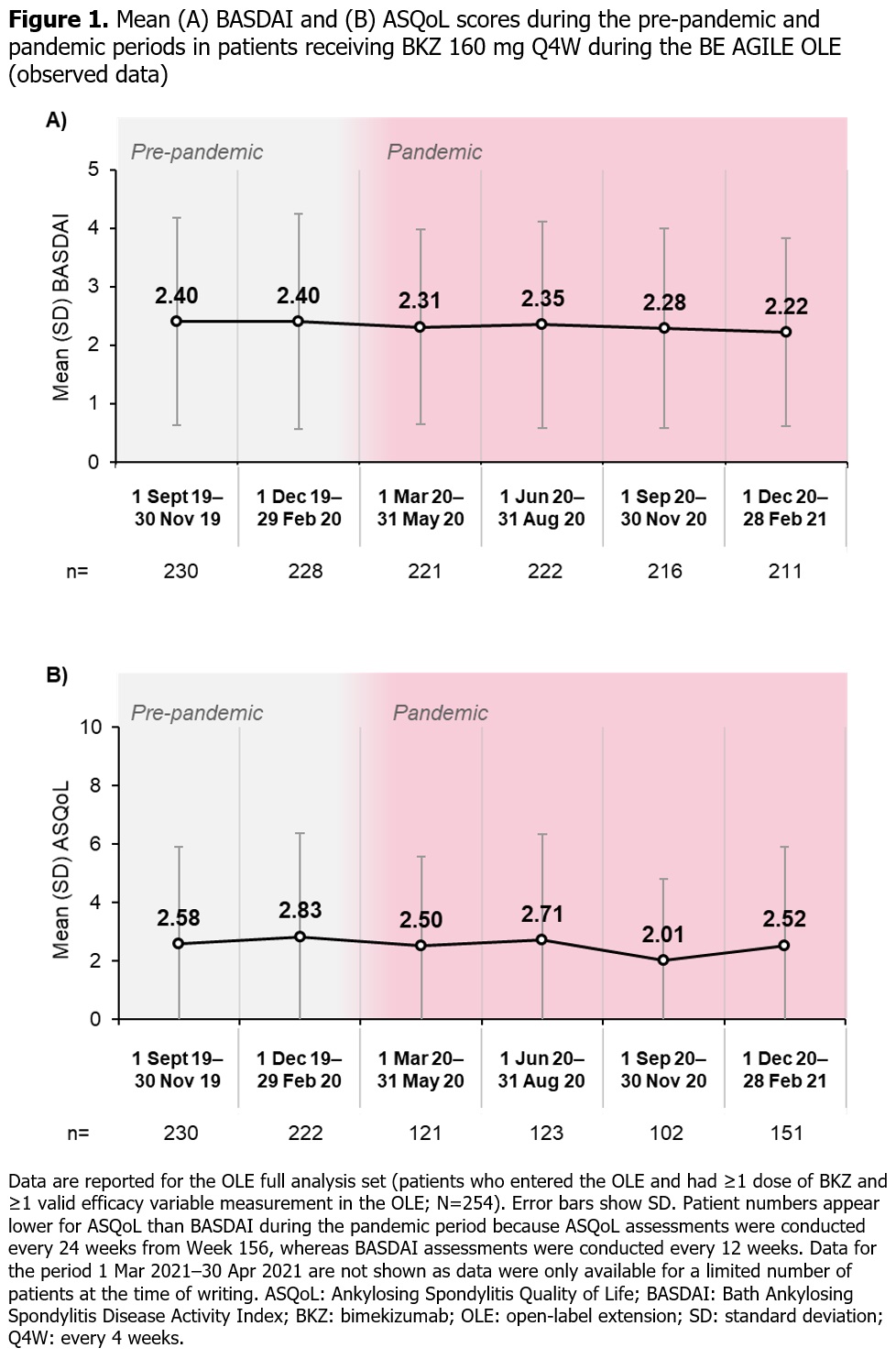
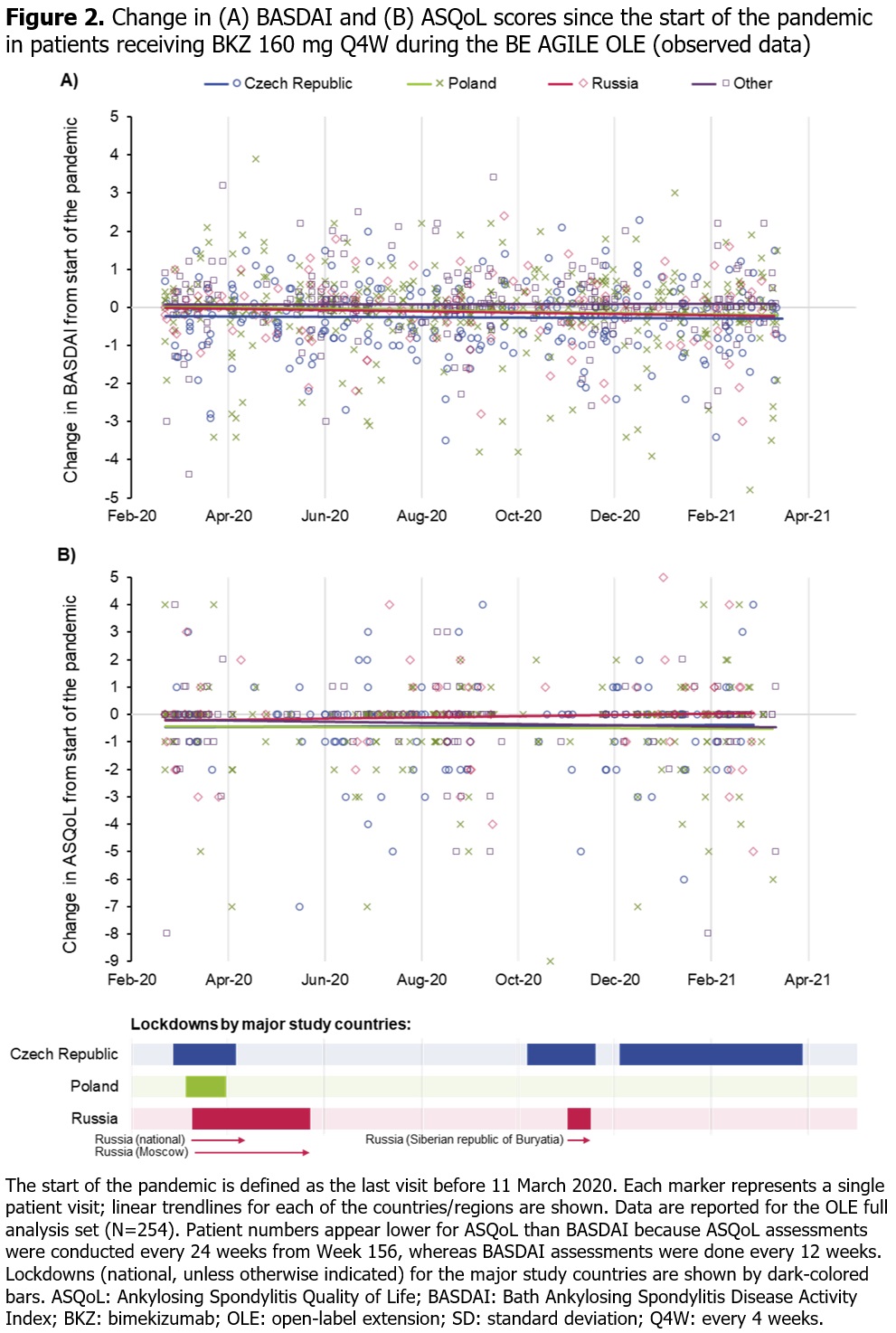
Methods: The BE AGILE study design has been described previously.1 Pts treated with BKZ 160 mg or 320 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) at Week 48 in BE AGILE were eligible for OLE entry. All OLE pts received BKZ 160 mg Q4W. For the OLE full analysis set, we report descriptive statistics for BASDAI (measured every 12 weeks) to show overall disease activity and Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life (ASQoL; measured every 12 weeks up to Week 156, then every 24 weeks) to show HRQoL for selected time periods before and during the pandemic. For this post hoc analysis, the start of the pandemic was defined as 11 March 2020, as per the World Health Organization’s declaration. Analyses included data collected between September 2019–April 2021.
Results: Of the 255 pts (safety set) who entered the OLE and received BKZ 160 mg, 229 (89.8%) were based in Eastern Europe (most were from Poland [n=89; 34.9%], the Czech Republic [n=72; 28.2%] or Russia [n=32; 12.5%]), 18 (7.1%) in Western Europe and 8 (3.1%) in North America. Study discontinuation rate was low, with 224/255 (87.8%) pts remaining in the study at Week 156; very few BKZ doses and study visits were missed for any reason. Across 3-monthly periods before and during the pandemic, BASDAI or ASQoL scores appeared to be stable (Figure 1). During the pandemic period between March 2020 and April 2021, there were no notable changes in these outcomes since the last pre-pandemic visit (last visit before 11 March 2020; Figure 2).
Conclusion: In pts with AS receiving BKZ in this OLE study, disease activity (BASDAI) and HRQoL (ASQoL) remained stable during the pandemic; there was no indication that the pandemic had a detrimental impact on these outcomes. Our findings, which differ from some recent real-world studies evaluating the impact of the pandemic on pts with rheumatic disease,4–6 may partly reflect the clinical trial setting of this study.
References: 1. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:595–604; 2. Baraliakos X. Arthritis Rheumatol 2020;72 (suppl 10):1364; 3. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80 (suppl 1):332–3; 4. Liew JW. ACR Open Rheumatol 2020;2:533–9; 5. Ciurea A. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:238–41; 6. Garrido-Cumbrera M. RMD Open 2021;7:e001546.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Robinson P, Machado P, Haroon N, Gensler L, Reveille J, Taieb V, Vaux T, Fleurinck C, Oortgiesen M, de Peyrecave N, Deodhar A. Minimal Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Patient-Reported Disease Activity and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis Receiving Bimekizumab: Post Hoc Analyses from a Phase 2b Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/minimal-impact-of-the-covid-19-pandemic-on-patient-reported-disease-activity-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-receiving-bimekizumab-post-hoc-analyses-from-a/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/minimal-impact-of-the-covid-19-pandemic-on-patient-reported-disease-activity-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-receiving-bimekizumab-post-hoc-analyses-from-a/