Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Vasculitis Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Thrombosis occurs in
around 20% of Behçet’s Syndrome (BS) patients and
causes substantial morbidity. There is a clear need for better biomarkers
of thrombotic risk in BS to inform treatment decisions. MPs are released from
cells undergoing activation and/or apoptosis and express phosphatidylserine
(PS) on their surface. MP that also express Tissue Factor (TF) provide a
stimulus for blood coagulation, whereas Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI)
expressed by MP may be protective. We tested the hypothesis that
imbalance between TF+ and TFPI+ MPs provides a biomarker for thrombotic risk in
BS.
Methods: MPs were prepared from peripheral
blood from 88 BS patients (who fulfilled International Study Group diagnostic
criteria), and 72 age- and sex- matched healthy controls. The BS group
was composed of 21 patients with a history of thrombosis (Th+)
and 67 patients with no history of thrombosis (Th-).
MPs were identified using flow cytometry by size (<1µm) and binding to
Annexin V (to PS). MP were further characterized by
binding of monoclonal antibodies to CD14 (a monocyte marker), TF and TFPI.
Results: Total numbers of plasma MPs and
also CD14+, TF+ and CD14+TF+ MPs were increased in BS compared to HC (all p
< 0.0001), and also in Th+ compared to Th– BS patients (p ≤ 0.0002). TFPI+ MPs were
higher in BS patients than HC (medians: 3.60 x 104/ml vs.
2.15 x 103/ml, p < 0.0001), but not between Th+
and Th– BS patients (medians: 3.09 x 104/ml
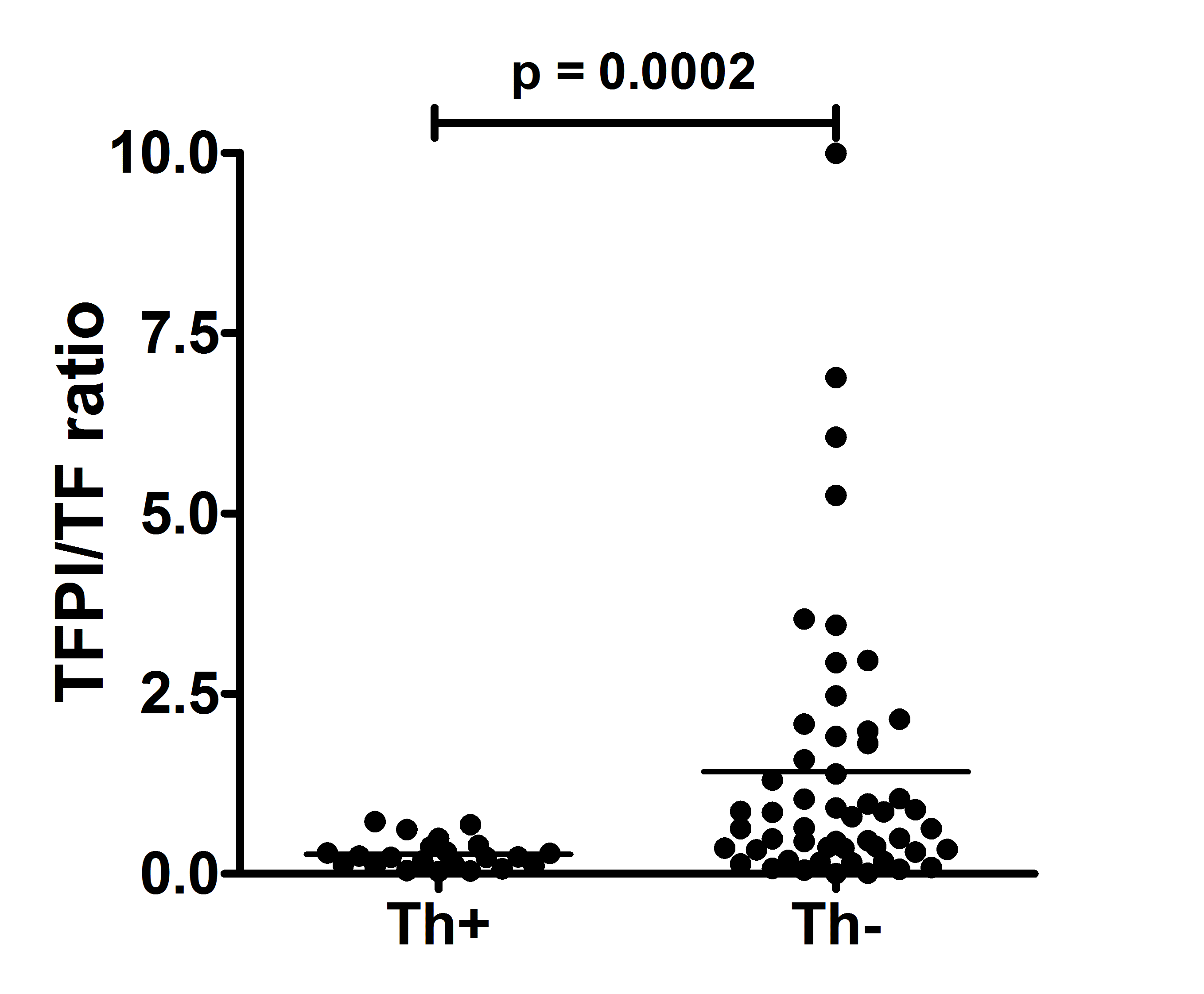
vs. 3.74 x 104/ml, p = 0.6660). The TFPI/TF ratio was
higher in BS patients than HCs (medians: 0.49 vs. 0.20, p < 0.0001) and in Th– compared to Th+
patients (medians: 0.85 vs. 0.23, p =
0.0002). Strikingly, a TFPI/TF ratio > 0.7 conferred freedom from thrombosis
(Figure).
Conclusion: Monocyte-derived MP
expressing TF were increased in BS patients and more so in those with a history
of thrombosis. Discrimination between BS patients with and without a
history of thrombosis was improved by also measuring TFPI+ MPs and generating a
TFPI/TF ratio. The data suggest that the balance between TF+ and TFPI+ MPs is
important for thrombotic risk in BS and raise the possibility that the TFPI /TF
MP ratio may allow the identification and appropriate treatment of BS patients
with a low risk of thrombosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khan E, Ambrose N, Stanford M, Laffan MA, Haskard DO. Microparticles (MPs) Derived from Cell Plasma Membranes Are Increased in Behcet’s Syndrome (BS) and a Low Ratio of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor Positive Mps to Tissue Factor Positive Mps (TFPI/TF) Is Associated with Thrombosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microparticles-mps-derived-from-cell-plasma-membranes-are-increased-in-behcets-syndrome-bs-and-a-low-ratio-of-tissue-factor-pathway-inhibitor-positive-mps-to-tissue-factor-positive-mps-tfpitf/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microparticles-mps-derived-from-cell-plasma-membranes-are-increased-in-behcets-syndrome-bs-and-a-low-ratio-of-tissue-factor-pathway-inhibitor-positive-mps-to-tissue-factor-positive-mps-tfpitf/