Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a form of inflammatory arthritis linked to psoriasis, a chronic skin and nail disease. PsA is a progressive joint disease that can severely affect mobility and hence early diagnosis and prompt treatment are needed for better disease outcomes. Methotrexate (MTX) is often the first-line of treatment for PsA patients. However, almost 31% of patients do not respond well to MTX. Identification of biomarkers which can predict response to MTX can help with treatment personalization and avoid further joint damage. MicroRNA (miRNA) are small non-coding RNA which modulate gene expression at post-transcriptional level. We hypothesize that miRNAs can help identify responders from non-responders before initiation of therapy and serve as biomarkers for MTX treatment response.
Methods: Bio-banked serum samples from PsA patients (n=70) satisfying CASPAR criteria, before initiation of treatment with MTX and after 6 months of treatment were identified. After RNA extraction, miRNA libraries were generated, and expression was evaluated using next-generation sequencing. Linear modeling with empirical Bayes moderation was used for differential expression analysis. Articular response was defined as achieving low disease activity (4 ≤ DAPSA < 14) or remission (DAPSA < 4) after treatment. Cutaneous response was defined as a reduction in PASI score by at least 50%. miRNA targets were identified through miRDIP and enriched pathways were examined by pathDIP. Differential expressed miRNAs were further validated using qRT-PCR in an independent set of patients (n=24) initiating MTX. The predictive performance of each miRNA was assessed by plotting ROC curves.
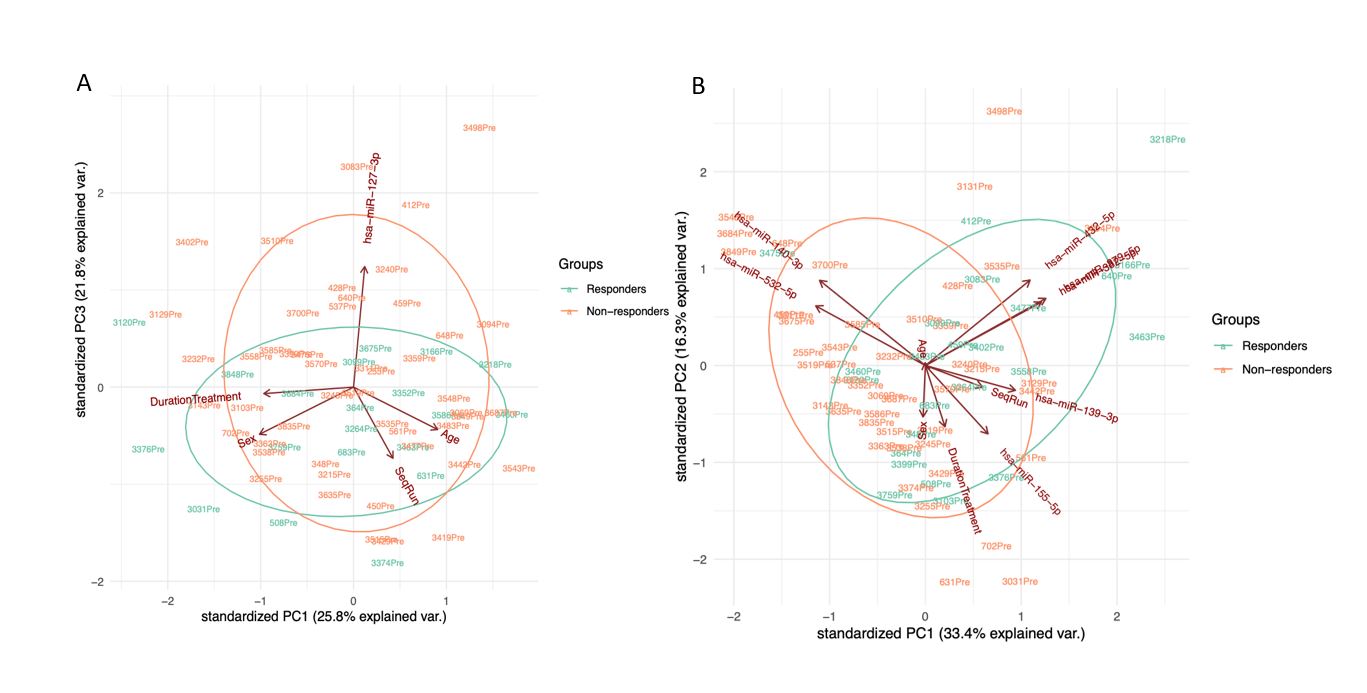
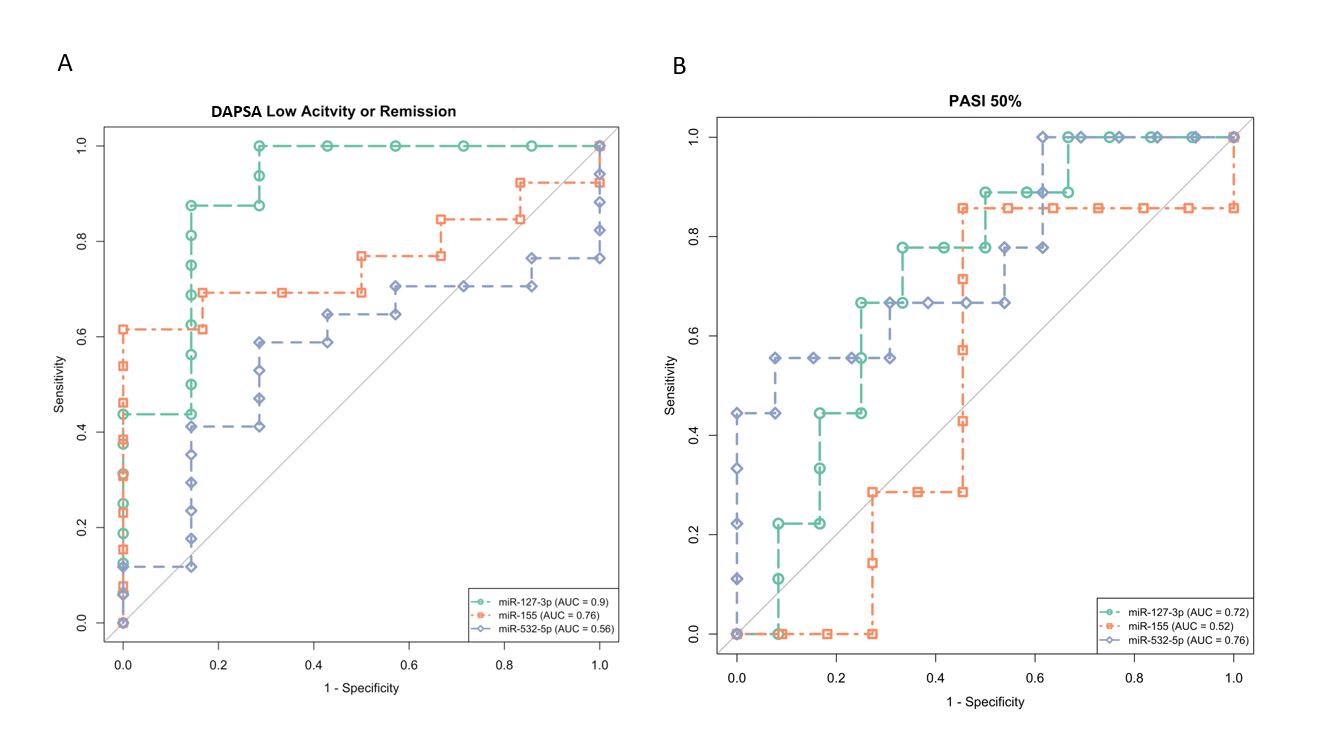
Results: In the discovery cohort, 28.57% and 34.28% of patients were responders for articular and cutaneous response, respectively. Lower pre-treatment levels of miR-127-3p were associated with articular response to MTX (p< 0.001). A set of 7 miRNAs (miR-155-5p, miR-140-3p, miR-432-5p, miR-382-5p, miR-532-5p, miR-139-3p, and miR-379-5p) were significantly associated with cutaneous response to MTX (p< 0.01) (Fig.1). In the validation cohort, 29.17 % and 70.83% of patients were responders for articular and cutaneous response, respectively. miR-155 and -532-5p had an AUC value of 0.76 for articular and cutaneous response, respectively. miR-127-3p showed a good predictive value with an AUC of 0.9 when considering the articular response and 0.72 in patients with the cutaneous response (Fig. 2). Pathway analysis revealed MAPK and WNT signaling among the top enriched pathways targeted by miR-127-3p (Fig.3).
Conclusion: We identified miR-127-3p as a biomarker of articular response, and 7 other miRNAs as biomarkers of cutaneous response to MTX treatment in PsA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ganatra D, Cruz Correa O, Garrido A, Lively S, Apurva Machhar R, Pollock R, Kapoor M, Gladman D. Micro-RNAs as Biomarkers for Methotrexate Treatment Response in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/micro-rnas-as-biomarkers-for-methotrexate-treatment-response-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/micro-rnas-as-biomarkers-for-methotrexate-treatment-response-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/