Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical Poster III: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Uveitis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Since MTX metabolism varies depending on age and dosage, we need to know optimal MTX administration method in children. We performed multi-center prospective study to examine the relationship between MTX dosage and safety using the concentration of MTX polyglutamates in red blood cells (MTX-PG).
Methods: This study is a part of research projects for intractable diseases supported by Health and Welfare Research Expenditure in Japan. Seven hospitals participated and received approval from each ethical review board. Forty-nine JIA patients who had been undergoing the same MTX dosage for 3 months and whose consent had been obtained were included. The total and each fragment of MTX-PG were measured by previously reported methods and calculated as concentration per administration dose per weight. The factors that may influence to MTX-PG were evaluated, such as age, dose per body (mg/ m2), dose regimen (split or single), timing of the meal and combination of folic acid. In addition, we examined the presence of gastrointestinal adverse effect, and the above factors were compared in groups with and without that. The values in each group are expressed in median and 25-75% quartile. Fisher’s bilateral test and Wilcoxon rank sum test were used for statistical analysis.
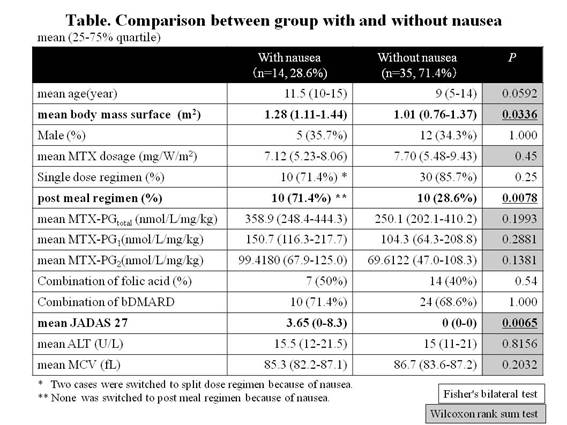
Results: The mean age was 10 (6-14) years old and the mean MTX dose was 7.24mg/ m2/W (5.48-8.62). The mean MTX- PGtotal increased linearly until MTX dose reached to 10mg/ m2/W, and became a plateau. MTX administration of 5 to 10 mg/ m2/W was required for effective and safe range (60 to 100 nmol/L) of MTX- PGtotal (y=−1.5446X2+30.989X−58.527). The mean MTX- PGtotal per administration dose per weight gradually increased as age rose, from 224.7 nmol/L/mg/kg in infants to 462.1 nmol/L/mg/kg in adolescents, and that was higher in split regimen group than in single regimen group (344.6 vs. 252.7, p=0.0216) and higher in post meal regimen group than in pre meal regimen group (384.2 vs. 230.6, p=0.0043). As for each fragment, only MTX-PG1 and MTX-PG 2 were higher in split regimen group (p=0.0102, 0.0332) and post meal regimen group (p=0.0072, 0.0092). The complaint of nausea was seen more in post meal regimen group than in pre meal regimen group (52.6% vs. 13.3%, p=0.0078). The combination of folic acid did not affect MTX- PGtotal. Compared with the group without nausea, the concentration of MTX- PGtotal and MTX-PG1-2 tended to be higher in group with nausea (there was no significant difference. see Table). The group with nausea showed significant correlation with higher body surface area, post meal regimen and higher JADAS27.
Conclusion: We recommend that children be administered 5 to 10 mg / m2/W of MTX and take it singly before meal, although it is necessary to consider reduction during puberty when the MTX-PG is prone to increase and nausea is likely to occur. The MTX-PG1-2 increases by post meal administration and may cause nausea.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Okamoto N, Shabana K, Nakagishi Y, Nishimura K, Mizuta M, Okura Y, Shimizu M, Wakiguchi H, Yasumura J, Mori M. Methotrexate Polyglutamates As an Evaluation Tool for Appropriate Dosage of Oral Methotrexate Administration in Pediatric Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/methotrexate-polyglutamates-as-an-evaluation-tool-for-appropriate-dosage-of-oral-methotrexate-administration-in-pediatric-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/methotrexate-polyglutamates-as-an-evaluation-tool-for-appropriate-dosage-of-oral-methotrexate-administration-in-pediatric-patients/