Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Spondyloarthritis (SpA) is characterized by inflammation of the synovium. An increase in the number of Th17cells in SpA has been reported. However, it is known that Th17 cells exhibit considerable plasticity, at sites of autoimmune inflammation. Th17 cells can switch to become IL-17 and IFN-r producing ex-Th17 cells. The aim of this study was to investigate the human ex-Th17 cells in synovial fluid at the site of the inflammation in SpA.
Methods: The samples of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMC) samples were obtained from SpA patients, and age- and sex-matched Healthy controls(HCs). Cells were surface stained with anti–CD4-Pacific Blue, anti-Fixable Viability Dye-eFluor780, anti-CD45RO-PE. Cells were intracellular stained with antibodies against IFN-r (FITC) / IL-17 (APC) and analyzed. Intracellular cytokine staining, samples were pre-stimulated with 100 ng/ml PMA and 1UM ionomycin in the presence of Golgi-plug for 4 h. For STAT3 Phosflow, Cells were harvested, fixed, and permeabilized using appropriate buffers (Cytofix Fixation Buffer and Phosflow Perm Buffer III) at the time points indicated. The anti-phospho-STAT3 Tyr705-PE Abs were used. The Levels of cytokines in the serum or synovial fluid were assessed using Magnetic Luminex Assay. Statistical analysis was performed using Prism 5.0 Software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, USA). A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
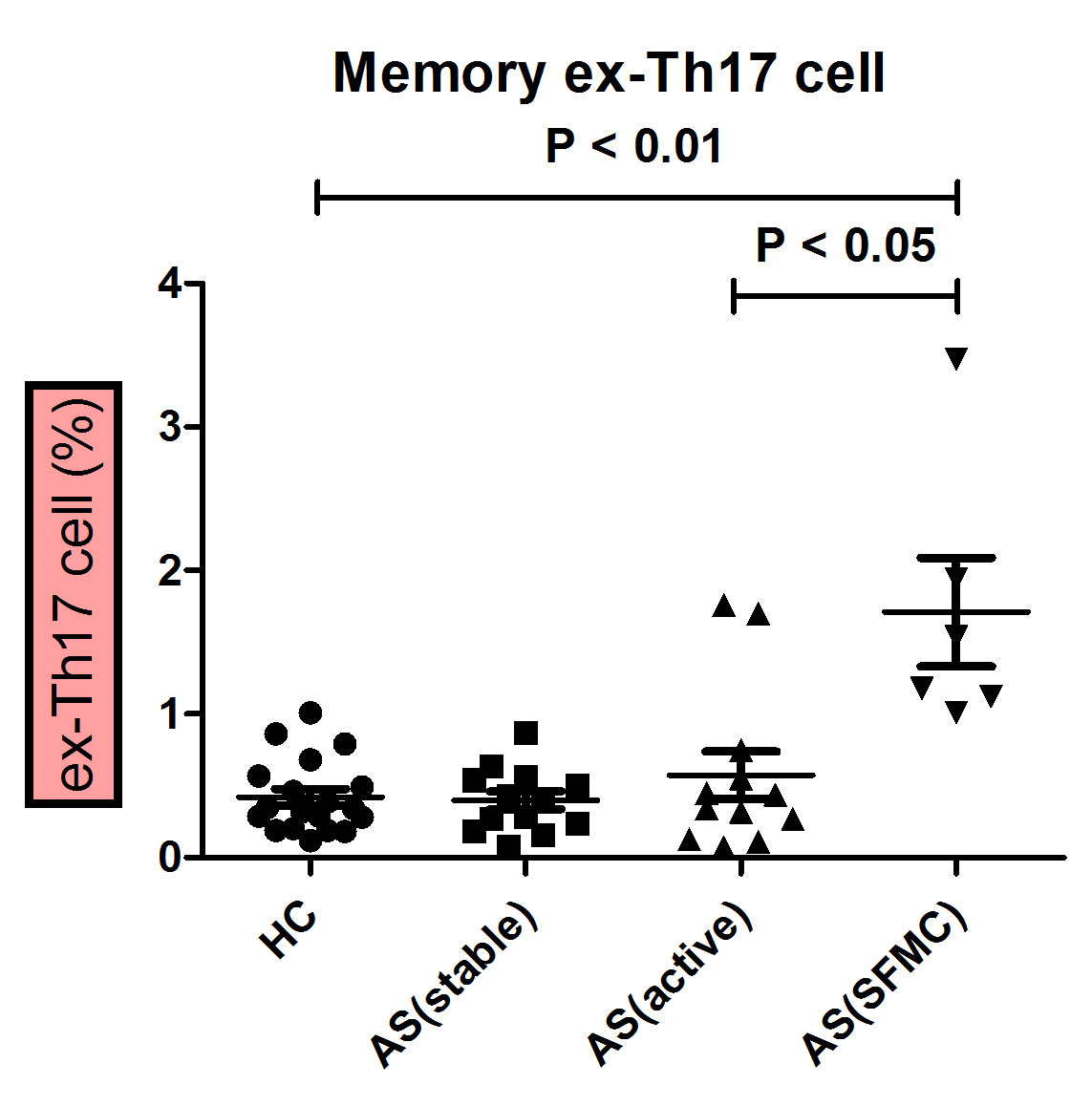
Results: Memory CD4 T cells present in the PBMC and SFMC of patients with SpA, as well as in the PBMC of HCs, were analyzed for the production of IFN-r and IL-17A. We observed a increase of ex-Th17 cells in the synovium from patients with SpA compared to the PBMC from HCs. The proportion of memory ex-Th17 was higher in SpA arthritis patients (mean±SD, 1.70±0.92 %) than in healthy controls (0.42±0.25 %) (P< 0.01) (Figure 1). Because the cytokine milieu regulates the immune cells function, we measured the inflammatory cytokines in the synovial fluid. Among the cytokines, synovial IL-6 levels were significantly higher in SpA patients(13357±4984 pg/ml) than those in Osteoarthritis (207±146 pg/ml) or serum in HCs (37.87±56.11 pg/ml) (P < 0.001).
We next evaluated IL-6 and pSTAT3 expression. Significantly higher levels of IL-6 and pSTAT3 transcripts were detected in arthritis patients when compared with SpA without arthritis, or normal controls. PBMC from AS patients were cultured in the presence of different concentrations of IL-6 (10, 20, 50, 100, or 500ng/ml), in the absence of exogenous IL-23 and TGF. IL-6 was sufficiently inducing significant ex-Th17 expansion. Ex vivo targeting of ex-Th17 cells with the IL-6 inhibitor significantly decreased the production of IL-17 as well as IFN-r cytokines in synovial cells.
Conclusion: We showed that pathogenic ex-Th17 cells accumulated in the joints of SpA patients. Ex-Th17 cell is dependent on the cytokine milieu with IL-6. They may play a pathogenic role at sites of inflammation, suggesting that the IL-6/STAT-3 axis is functioning in arthritis patients with SpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
JIN S, PARK P, KANG J, PARK D, KIM T. Memory ex-Th17 Cells Contribute to Synovial Inflammation in Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/memory-ex-th17-cells-contribute-to-synovial-inflammation-in-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/memory-ex-th17-cells-contribute-to-synovial-inflammation-in-spondyloarthritis/