Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The ASAS-EULAR recommendations for management of axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA) includes that patients should be encouraged to exercise. There is no validated instrument for measuring physical activity in axSpA. Our previous study recommends to adapt the Short QUestionnaire to Assess Health-enhancing physical activity (SQUASH) to improve the validity in axSpA patients. Our goal was to mak an AxSpA-disease specific adaptation of the physical activity questionnaire SQUASH to improve content validity and measurement properties.
Methods: This study was conducted according to the OMERACT-filter within the Groningen Leeuwarden AxSpA (GLAS) cohort and was performed in two parts. Part 1: adaptation and evaluation of content validity using a qualitative stepwise approach with in-depth interviews with different healthcare professionals (n=9) and patients (n=8), field testing in patients (n=10), and consensus meeting for final adaptations. Thereafter, content validity (n=45) was tested by filling out axSpA-SQUASH and SQUASH in random order two weeks apart. Part 2: measurement properties were tested using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) as comparator. Criterion validity (n=40): Spearman’s correlation with accelerometer as golden standard and classification accuracy of intensity. Construct validity (n=106): Spearman’s correlation with disease activity, physical functioning and quality of life as clinical outcome with expected fair to moderated associations. Test-retest reliability (n=45): intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) after 2 weeks. Responsiveness (n=47): standardized response mean (SRM) after 3 months stratified by Ancor method.
Results: In total 156 patients were included: mean age 48±13 years, 56% males, 72% HLA-B27 positive, symptom duration 21±13.3 years and ASDAS 2.0±1.0. Part 1: main adaptations were better explanation of intensities, adding answer option “not applicable”, examples were modernized, physiotherapy and activity “shopping” were added. Compared to the original SQUASH, the adapted axSpA-SQUASH measured a systematically higher activity count and had less missing values (8% vs. 32%). Part 2: criterion validity: axSpA-SQUASH correlated better with accelerometer compared to IPAQ (ρ=0.51 vs. ρ=0.35). Classification accuracy: accelerometer defined most activity as light (97%), whereas axSpA-SQUASH and IPAQ defined most activity as moderate intensity (55% and 62% resp.). Construct validity: correlations were low to moderate and strongest for axSpA-SQUASH compared to IPAQ. Construct validity: correlations were low to moderate and stronger for axSpA-SQUASH compared to IPAQ (BASDAI -0.27 vs -0.15, BASDAI –0.27 vs. -0.15, ASDAS -0.24 vs -0.09, BASFI -0.39vs. -0.21, ASQoL -0.39 vs. -0.35). Test-retest reliability: ICC axSpA-SQUASH: 0.80. Responsiveness: axSpA-SQUASH changed over time in the corresponding direction (Table 1). Feasibility: considered comprehensible and average completion time was 7 minutes.
Conclusion: The new axSpA-SQUASH resulted in improved content validity and measurement properties. It seems the most appropriate questionnaire and can be used to assess daily physical activity in patients with axSpA.
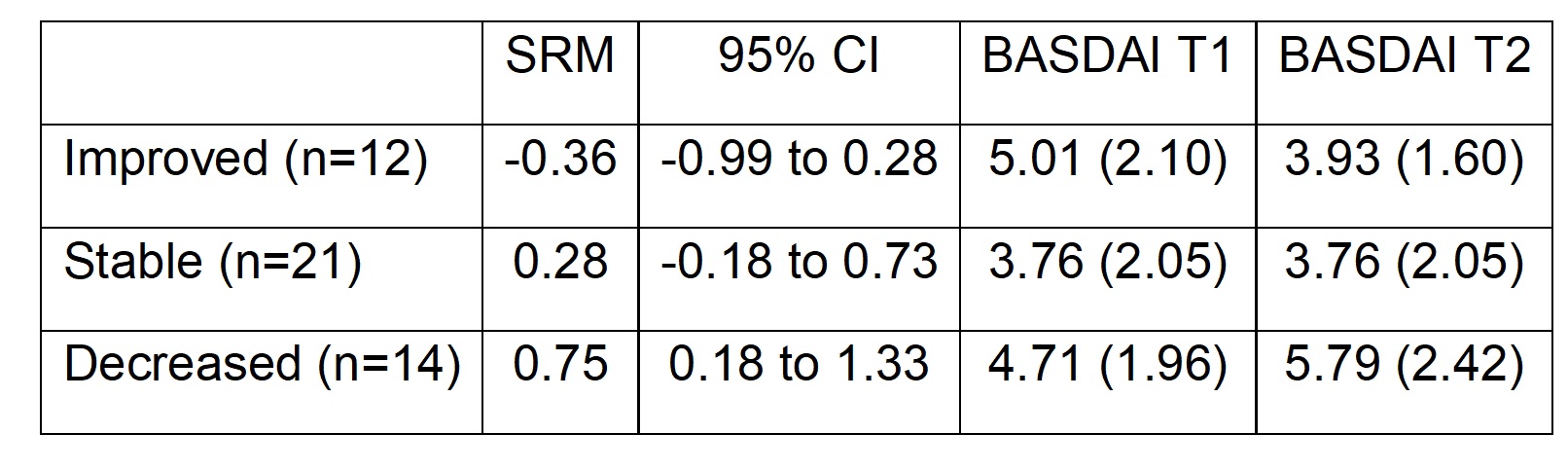 Table 1. Responsiveness of the axSpA-SQUASH versus change in BASDAI
Table 1. Responsiveness of the axSpA-SQUASH versus change in BASDAI
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Carbo M, Paap D, Maas F, Siderius M, Bootsma H, Wink F, Arends S, Spoorenberg A. Measuring Physical Activity in AxSpA:Content Validity and Measurement Properties of the New AxSpA-SQUASH [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measuring-physical-activity-in-axspacontent-validity-and-measurement-properties-of-the-new-axspa-squash/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measuring-physical-activity-in-axspacontent-validity-and-measurement-properties-of-the-new-axspa-squash/
