Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Variable association between vasculitis activity and patient reported outcomes was reported in small groups of Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) patients in the literature so far. In this study we evaluated the utility of PROMIS (Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System) as potential indirect tool for predicting disease activity in patients with GPA.
Methods: A retrospective chart review study in GPA patients who were seen two or more times at the Cleveland Clinic vasculitis center was conducted between July 2016 and March 2019 to compare disease activity and damage measured by BVAS-WG and VDI scores with PROMIS data. BVAS-WG activity and vasculitis damage index (VDI) scores were calculated at each visit where PROMIS data was obtained. Further, glucocorticoids dose, and immunosuppressive medications were also recorded per each data set. Mixed effect models were used to calculate repeated measures correlations.
Results: 286 patients (median age at first visit 60 years, 53.8% females) with GPA were included in final analysis. Total 85 disease flares were reported (62 limited, 23 severe), median BVAS- WG score was 0 with a range (0-10).
BVAS-WG score was found to be positively correlating with fatigue (r =0.112, p < 0.001), PHQ2(r =0.142, p < 0.001) and PHQ9 (r =0.207, p-value< 0.001) respectively. However, BVAS -WG score seems to be negatively correlating with function (r = -0.081, p =0.009) and physical score (r = - 0.090, p =0.003) (Figure 1). More interestingly, patients with flares had fatigue scores > by 4.1 units (p- value =0.001), PHQ2 scores > by 0.75 units (p- value = 0.001), Function scores < by 2.2 units (p- value= 0.025), physical scores < by 3.84 units (p-value= 0.001), and mental scores < by 2.54 units (p-value = 0.013) comparing to those were in remission (Figure 2)
Not surprisingly, as VDI score increases, fatigue (r = 0.142) and PHQ2 (r =0.145) increase while function (r = -0.295) and physical scores decrease (r = – 0.213).
In comparing for different glucocorticoids dose, and immunosuppressive medications, patients who received methotrexate and cyclophosphamide had higher PHQ2 scores on average by 1.03 and 0.76 units, respectively. Furthermore, methotrexate was found to be correlating negatively with function scores (b = -2.66, p-value=0.028).
Higher doses of glucocorticoid were positively associated with fatigue (r = 0.134, p-value = 0.001), and PHQ2 (r=0.097, p- value = 0.034) while higher doses were negatively associated with function (r = -0.181, p- value < 0.001), physical score (r = -155, p- value = < 0.001), and mental score (r = -0.108, p- value = 0.009). (Figure 3)
Conclusion: PROMIS weakly correlates with disease activity as measured by BVAS-WG and may successfully differentiate between different disease statutes.
Larger studies are needed to validate our study outcomes and the use of PROMIS as indirect tool in predicting disease activity in patients with GPA.
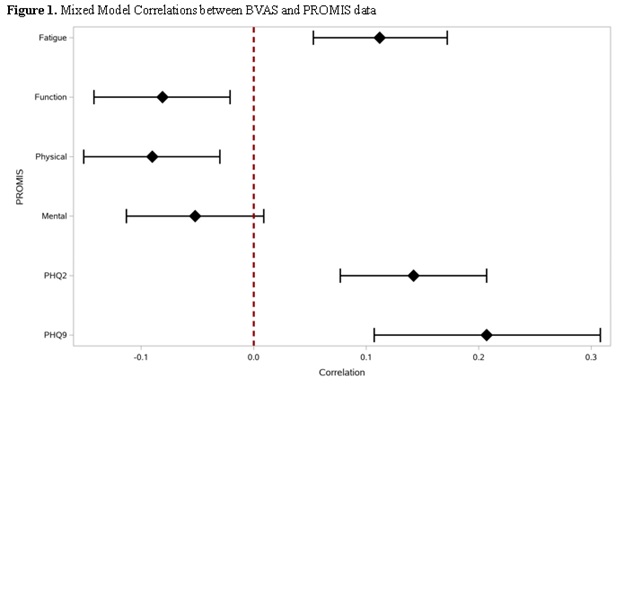 Figure 1. Mixed Model Correlation between BVAS and PROMIS data
Figure 1. Mixed Model Correlation between BVAS and PROMIS data
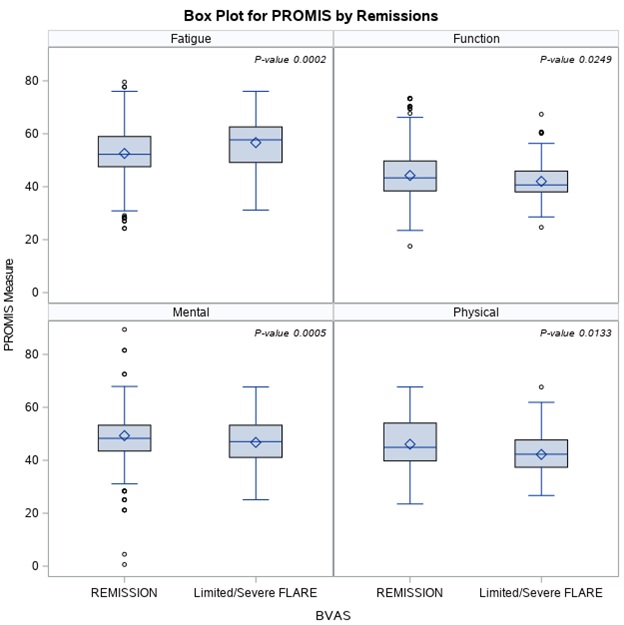 Figure 2. Box Plot for PROMIS by Remissions
Figure 2. Box Plot for PROMIS by Remissions
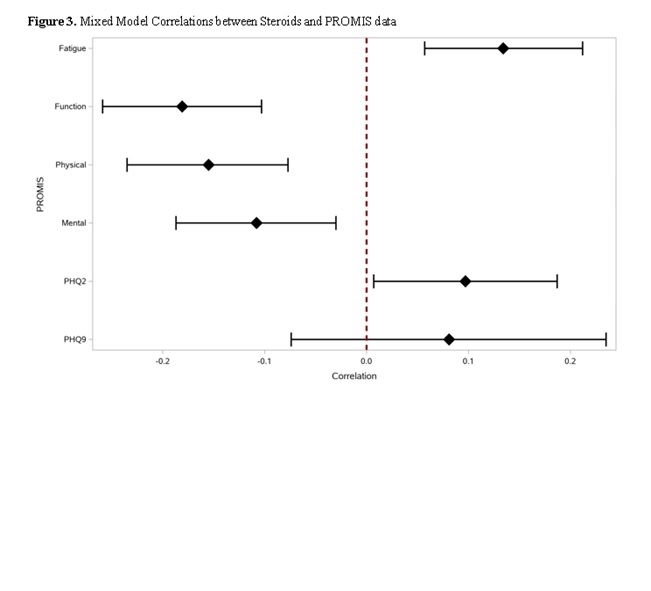 Figure 3. Mixed Model Correlation between Steriods and PROMIS data
Figure 3. Mixed Model Correlation between Steriods and PROMIS data
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yaseen K, Briskin I, Hajj-ali R. Measuring Disease Activity and Functional Status in Patients with Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener’s) (GPA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measuring-disease-activity-and-functional-status-in-patients-with-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-wegeners-gpa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measuring-disease-activity-and-functional-status-in-patients-with-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-wegeners-gpa/
