Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Psoriatic Arthritis Quality of Life (PsAQol), Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life (ASQoL), and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) are tools that assess different aspects of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in psoriatic arthritis (PsA). We aimed to determine if each of the three tools capture HRQL domains relevant to both skin and joints.
Methods:
Patients with PsA (physician diagnosed) completed PsAQoL, ASQoL, and DLQI in a 15-country longitudinal study [1] designed to develop new composite measure for PsA. We used Rasch analysis to determine the reliability and validity, including how well the tools targeted the skin and joint aspects of HRQoL.
We assessed the following: (i) fit to the Rasch model to determine different aspects of validity in PsA, (ii) person- separation index to determine internal consistency, (iii) differential item functioning (DIF) across five regions (Asia, Europe, N. America, S. America and the UK) to determine cross-cultural validity, and (iv) person-item threshold location maps to determine targeting of the tools to skin and joint aspects of HRQoL.
Results:
The sample comprised 503 patients (male/female = 286/217) with mean (SD) age, 50.8 (13.1), and PSA duration, 9.8 (9.9) years.
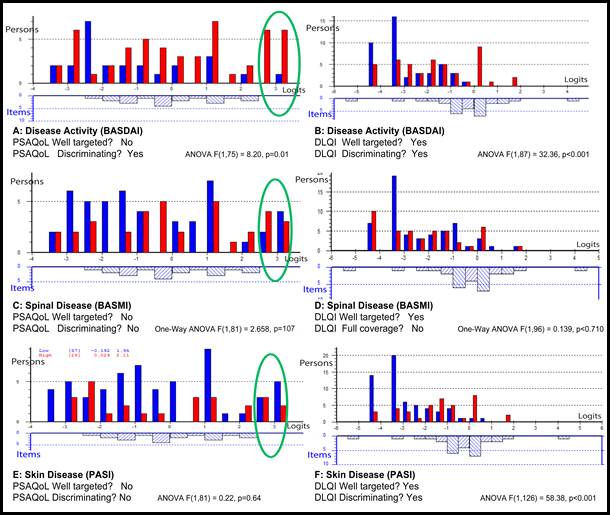
Expectations of the Rasch model were satisfied only in N America PsAQoL, UK ASQoL and both UK & N America DLQI datasets. Reliability was adequate and the measures were invariant to age and gender. There were not enough data in each country to reliably determine cross-cultural invariance, therefore targeting and discrimination properties of the tools were based on N. American dataset (Figure 1).
DLQI targeted better (than PsAQoL) articular and skin aspects of HRQoL. DLQI discriminated better HRQoL related to skin involvement (fig 1B and 1F) but not spinal involvement (fig 1D), where ASQoL was better at discriminating this aspect (F(1,66) = 13.76, p<0.001).
Figure
1. Targeting and discriminating properties of the tools
Figure legends: The left side of the plots represents low PSAQoL or QLQI scores (good HRQoL). The right side represents high scores (impaired HRQoL). The blue plots represent people with low/mild disease while the red plots those with severe disease. Significant ANOVA p-values suggest ability of the tool to discriminate
between persons with low/high disease. Green circles mark persons with severe HRQoL not targeted by PsAQoL
items.
Conclusion:
The data suggest that PsAQoL does not cover the full spectrum of HRQoL in psoriasis. Conversely, DLQI does not cover the full spectrum of HRQoL of articular disease in PsA. PsAQoL, (or ASQoL) and DLQI complement each other in capturing both joint and skin aspects of HRQoL. Confirmation of these findings is needed using larger datasets.
References:
1. Helliwell PS, et al. The development of candidate composite disease activity and responder indices for psoriatic arthritis (GRACE project). Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72(6)986-91
Disclosure: M. Ndosi, None; M. A. Hsu, Pfizer Inc, 3,Pfizer Inc, 1; J. Cappelleri, Pfizer Inc, 1; A. Chhabra, Pfizer Inc, 3; H. Jones, Pfizer, Inc, 3,Pfizer, Inc, 1; P. S. Helliwell, None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ndosi M, Hsu MA, Cappelleri J, Chhabra A, Jones H, Helliwell PS. Measures of Health-Related Quality of Life in Psoriatic Arthritis: Are They Sensitive to Both Joint and Skin Aspects? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measures-of-health-related-quality-of-life-in-psoriatic-arthritis-are-they-sensitive-to-both-joint-and-skin-aspects/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measures-of-health-related-quality-of-life-in-psoriatic-arthritis-are-they-sensitive-to-both-joint-and-skin-aspects/