Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Bone loss paradoxically coexists with bone formation in radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA). Assessing bone mineral density (BMD) in r-axSpA poses challenges, namely because of possible overestimation due to ectopic bone formation. The measurement of Computed Tomography (CT) Hounsfield Units (HU) at the individual vertebral level has been shown to correlate with BMD as measured by Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in trauma patients.1 However, its value in r-axSpA has never been studied. Whole spine low dose CT (ldCT) has been suggested as the ideal method to assess both bone formation and bone loss in r-axSpA. By using ldCT scans, we aimed to cross-sectionally describe HU measurements and their inter-reader reliability at the vertebral level from C3 to L5 in patients with r-axSpA.
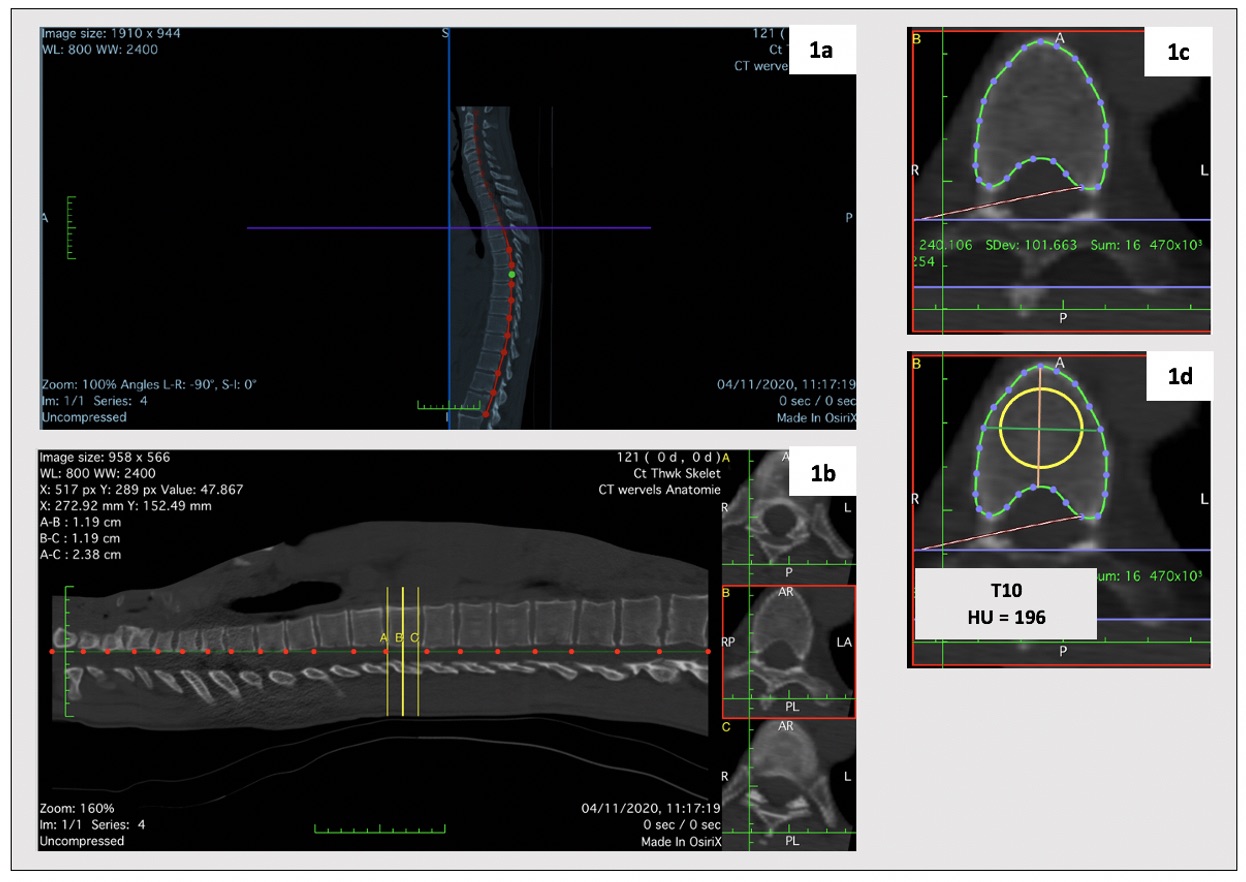
Methods: We used ldCT scans of r-axSpA patients included in the Sensitive Imaging in Ankylosing Spondylitis (SIAS) study, a multicenter (Leiden, the Netherlands and Herne, Germany) 2-year prospective cohort. A standardized protocol was applied in both centers and automatic exposure control calibration in ldCT imaging acquisition was used. For the present study, baseline ldCT scans were independently assessed by two trained readers. The HU measurement was performed as described in Figure 1 – using OsiriX software (v6.5.1). Inter-reader reliability was assessed using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) absolute agreement, applying two-way mixed effect models. Agreement was assessed using the smallest detectable difference (SDD = 1.96 x SDdifference /(√k), in which SDdifference is the standard deviation of the differences in status scores between two readers, and k=2 (number of readers) and Bland-Altman plots.
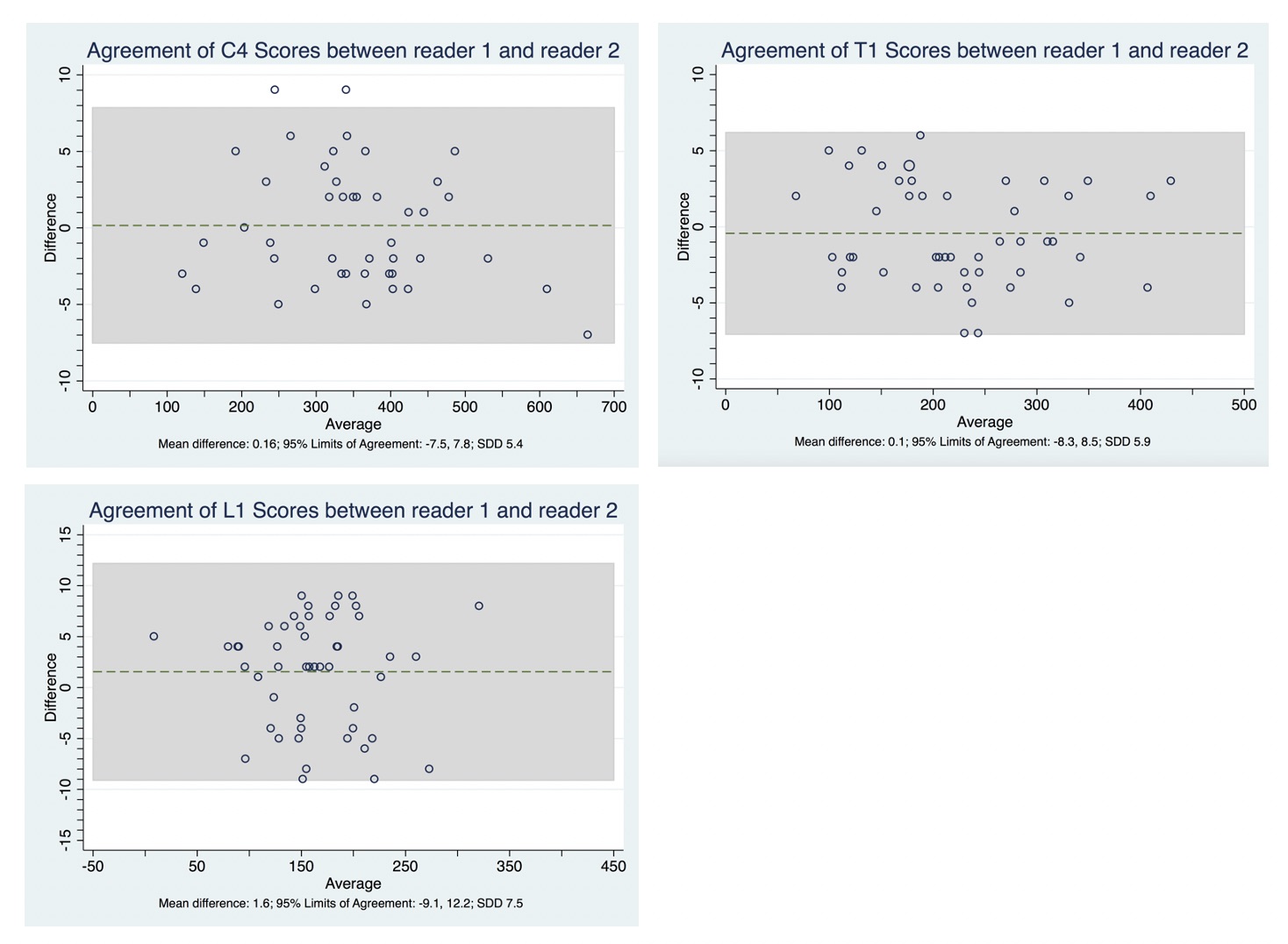
Results: Whole spine ldCT scans from 50 r-axSpA patients (mean (SD) age of 49 (10) years; 43 (86%) male and 42 (84%) HLA-B27 positive) were included. In total, 220 cervical, 588 thoracic and 245 lumbar vertebrae were assessed by both readers. The HU values decreased from the cervical to the lumbar spine – Table 1. For both readers, the highest mean (SD) value for HU was obtained at C3 (354 (106) and 355(108), for reader 1 and 2 respectively), and the lowest at L3 (153 (65) and 150 (65), for reader 1 and 2 respectively). Inter-reader reliability was shown to be excellent (cervical spine ICC: 0.90 to 1.00; thoracic spine ICC: 0.97 to 1.00; lumbar spine ICC: 0.89 to 0.91). SDD varied from 4 to 8. A small degree of systematic error was observed between the two readers, i.e., for the majority of vertebrae, reader 1 scored somewhat higher than reader 2 (mean difference of scores ranging from -0.6 HU to 2.9 HU). Bland-Altman plots show homoscedasticity throughout the whole spine. Representative examples from vertebrae of each segment of the spine are presented in Figure 2.
Conclusion: Low dose CT measurement of HU is a reliable method to assess BMD at each vertebra from C3 to L5. This methodology can aid the future study of bone loss in r-axSpA, a disease affecting the whole spine. Further validation and longitudinal assessment of reliability are warranted in future studies.
1Shaun P. Patel, et al. J Clin Exp Orthop. 2016;2(1:14):1–7.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marques M, Pereira da Silva N, van der Heijde D, van Gaalen F, Ramiro S. Measurement of Vertebral Hounsfield Units in Low Dose Computed Tomography – a Reliable Methodology for Assessing Bone Mineral Density at the Vertebral Level in Patients with Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measurement-of-vertebral-hounsfield-units-in-low-dose-computed-tomography-a-reliable-methodology-for-assessing-bone-mineral-density-at-the-vertebral-level-in-patients-with-radiographic-axial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measurement-of-vertebral-hounsfield-units-in-low-dose-computed-tomography-a-reliable-methodology-for-assessing-bone-mineral-density-at-the-vertebral-level-in-patients-with-radiographic-axial/