Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0593–0640) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Previous studies have shown a decline in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-related mortality rates from 1999 to 2020. This study aimed to evaluate SLE-related mortality trends in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: We analyzed SLE mortality data from 1999 to 2023 using the CDC WONDER Underlying Cause of Death database and its query system. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) were calculated by sex, race, and ethnicity for both SLE and the general population (GP). The first cases and deaths related to COVID-19 in the U.S. were reported in 04/2020. To assess the impact of COVID-19, we focused on mortality rates from 2020 onward. Trends over the study period were assessed using the NCI’s Joinpoint Regression Program to identify statistically significant changes in the slope of mortality trends and to calculate annual percentage changes (APCs).
Results: From 1999 to 2023, a total of 30,060 deaths were identified in the US with SLE listed as the underlying cause. Joinpoint trend analysis revealed one inflection point in 2021 within the SLE group. The AAMR for SLE declined between 1999-2021 (APC =–2.19; 95%CI:–2.52 to –1.51; p=0.032), followed by a more pronounced decrease from 2021 to 2023 (APC = –14.1; 95%CI:–22.5 to –3.67; p< 0.00001) (Fig 1A). In the GP, 3 joinpoints were identified (Fig 1B). Pairwise comparison testing indicated a parallel trend in AAMRs between the SLE and general population cohorts over the study period.Among female SLE patients, trend analysis identified one joinpoint. AAMR declined modestly from 1999 to 2021 (APC =–2.03; 95%CI: –2.39 to –1.6; p=0.0024), followed by a sharp decline after 2021 (APC = –18.93; 95%CI: –25.66 to –8.59; p< 0.00001) (Fig 2A). In females in the GP, 2 joinpoints were identified (Fig 2B). In the male SLE group, no joinpoints were detected, and AAMR declined consistently across the entire study period (APC = –2.32; 95%CI: –3.02 to –1.66; p< 0.00001). In contrast, 3 joinpoints were identified in males in the GP.Joinpoint analysis identified two inflection points in African American (AA) patients with SLE. The AAMR declined between 1999 and 2013 (APC=–3.14; 95%CI: –7.9 to –2.1; p=0.038), remained stable from 2013 to 2020 (APC= 0.28; 95%CI: –2.1 to 7.3; p=0.76), and then decreased significantly after 2020 (APC=–16.6; 95%CI:–27.1 to –9.9; p< 0.00001). In the White SLE group, 1 joinpoint was identified in 2021. AAMR declined gradually until 2021 (APC = –2.2; 95%CI: –2.7 to –0.6; p=0.045), followed by a more pronounced decrease thereafter (APC=–18.2; 95%CI: –29.9 to –3.0; p=0.0004) (Fig 3A).In the GP, both White and AA groups showed 3 joinpoints (Fig 3B). Hispanic and non-Hispanic SLE patients displayed similar patterns, with a notable joinpoint observed in 2021.
Conclusion: While overall SLE-related mortality continued to decline through 2023, a marked inflection point was observed during the COVID-19 pandemic across demographic subgroups. Notably, AA patients showed significant post-2021 improvements in mortality trends, suggesting potential impacts of healthcare access, disease management, or pandemic-related factors. Continued monitoring of these trends is essential to understand long-term outcomes and disparities in SLE mortality.
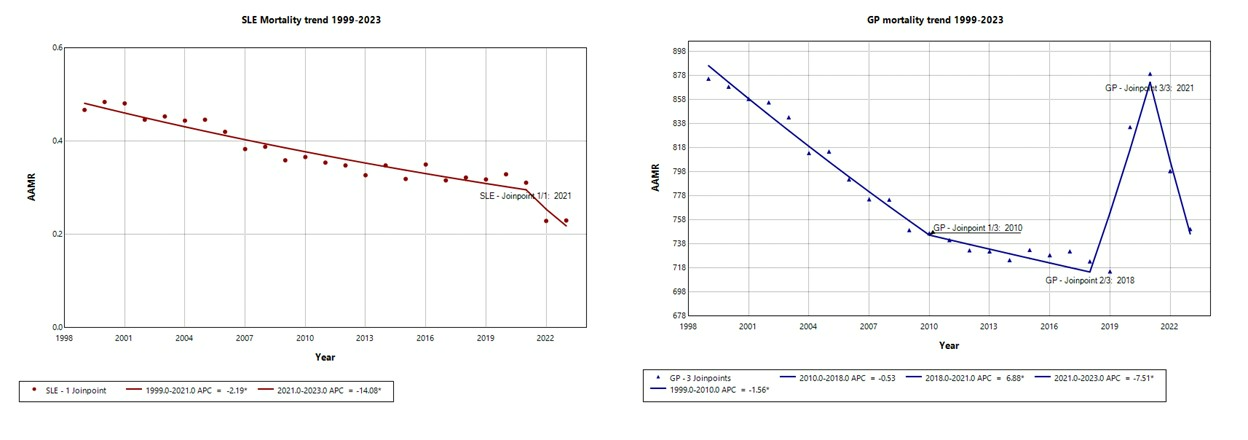 Figure 1 A. Mortality trends in SLE between 1999-2023.
Figure 1 A. Mortality trends in SLE between 1999-2023.
Figure 1B. Mortality trends in general population between 1999-2023.
.jpg) Figure 2A. Mortality trends in SLE by sex.
Figure 2A. Mortality trends in SLE by sex.
Figure 2B. Mortality trends in general population by sex.
.jpg) Figure 3A. Mortality trends in SLE by race
Figure 3A. Mortality trends in SLE by race
Figure 3B. Mortality trends in general population by race.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pamuk O, Nasuhbeyoglu A. Marked Decline in SLE Mortality Despite Rising Mortality in the General Population During the COVID-19 Pandemic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/marked-decline-in-sle-mortality-despite-rising-mortality-in-the-general-population-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/marked-decline-in-sle-mortality-despite-rising-mortality-in-the-general-population-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/
