Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To investigate relationships between painDETECT (PDQ), neuropathic pain screening tool, and patient-reported outcomes measurement information system (PROMIS) 29 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: For rheumatoid arthritis (RA) subjects enrolled in the University of Pittsburgh Rheumatoid Arthritis Comparative Effectiveness Registry (RACER), a cross-sectional analysis was performed for all RACER patients who completed PDQ and PROMIS29 short form. Association between PDQ and PROMIS29 was evaluated by Spearman¡¯s correlation coefficient. Multiple regression models were conducted for PROMIS29 domain scores, adjusting for age, gender, race, RA disease activity measured by clinical disease activity index (CDAI). Analysis of variance and pairwise comparisons for adjusted scores were performed among PDQ classifications and standardized mean differences were calculated to assess the magnitude of effect.
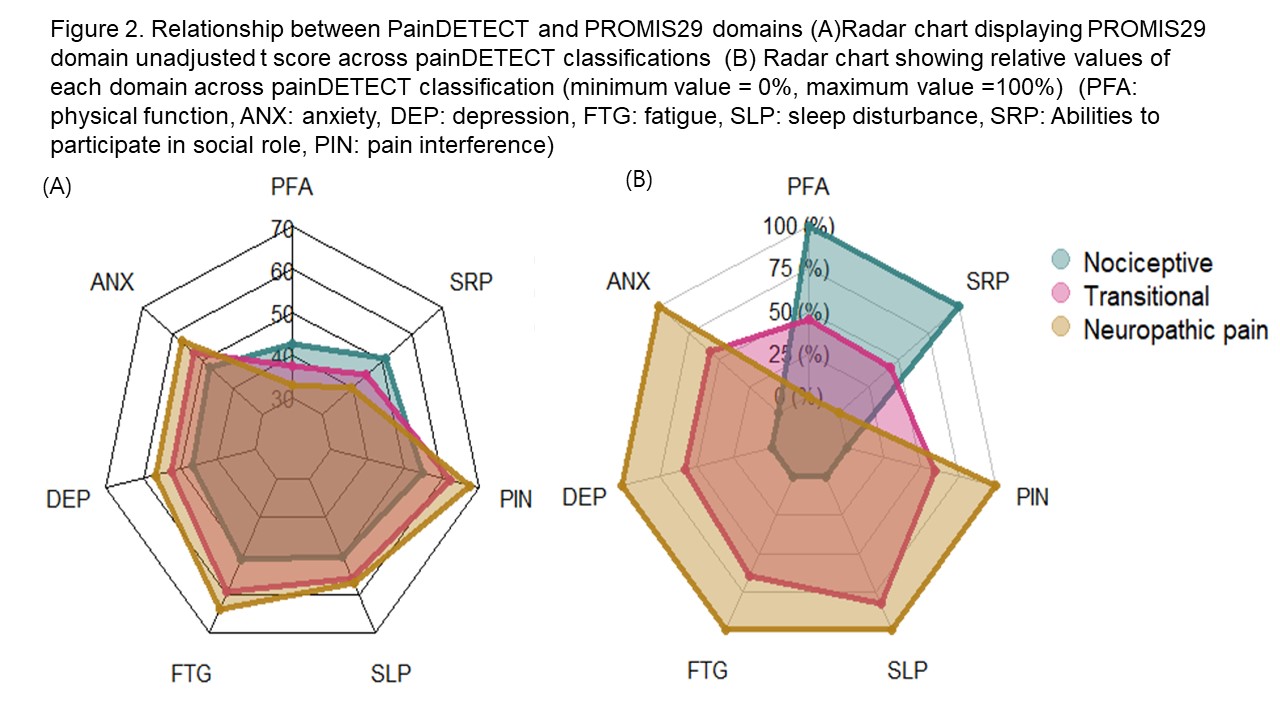
Results: For the 302 subjects analyzed, age was 63.8 +/- 12.4 (mean +/- SD) years with disease duration of 18.4 +/-11.9 years. PDQ score was moderately correlated with pain severity (current, average pain for the past week, and past month, rho =0.52, 0.60, 0.56, p <0.001, respectively). PROMIS29 scores showed poorer physical function, participation in social role and higher depression, anxiety, fatigue, and sleep disturbance across PDQ classifications from nociceptive (N=225,74.7%) to transitional (45,14.9%) to neuropathic pain group (N=31,10.3%) (Figure 1 and 2). Pairwise comparisons of PDQ classifications for adjusted PROMIS29 domain scores showed significantly worse health status for neuropathic pain group relative to both nociceptive and transitional group (Table).
Conclusion: Mapping the relationships between PDQ and PROMIS29 domains showed classifications by PDQ of nociceptive, transitional and neuropathic pain are characterized by overall decremental health status measured by PROMIS29. These data support the PDQ score as a possible treatment outcome measure and its use in RA management.
|
Table. Pairwise comparison of PROMIS29 domain scores across painDETECT classifications (Noci: Nociceptive, Tr: Transitional, NeP: Neuropathic, SMD: standardized mean difference, PFA: physical function, ANX: anxiety, DEP: depression, FTG: fatigue, SLP: sleep disturbance, SRP: Abilities to participate in social role, PIN: pain interference) |
||||||||
|
PROMIS Domain |
PainDETECT classification |
Comparison |
SMD |
|||||
|
Nociceptive |
Transitional |
Neuropathic |
Group |
difference |
p value |
Raw score |
Adjusted score |
|
|
PFA |
43.13 |
37.18 |
32.79 |
NeP -Noci |
-10.34 |
<0.001 |
1.46 |
2.45 |
|
NeP – Tr |
-4.39 |
<0.001 |
0.70 |
1.14 |
||||
|
Tr – Noci |
-5.95 |
<0.001 |
0.77 |
1.63 |
||||
|
ANX |
47.36 |
53.40 |
57.31 |
NeP -Noci |
9.94 |
<0.001 |
0.80 |
4.09 |
|
NeP – Tr |
3.90 |
<0.001 |
0.28 |
1.93 |
||||
|
Tr – Noci |
6.04 |
<0.001 |
0.57 |
2.83 |
||||
|
DEP |
46.92 |
52.19 |
55.58 |
NeP -Noci |
8.66 |
<0.001 |
1.02 |
3.72 |
|
NeP – Tr |
3.39 |
<0.001 |
0.30 |
1.70 |
||||
|
Tr – Noci |
5.27 |
<0.001 |
0.67 |
2.51 |
||||
|
FTG |
50.59 |
58.84 |
64.23 |
NeP -Noci |
13.64 |
<0.001 |
1.45 |
3.56 |
|
NeP – Tr |
5.39 |
<0.001 |
0.41 |
1.53 |
||||
|
Tr – Noci |
8.25 |
<0.001 |
1.08 |
2.31 |
||||
|
SLP |
49.75 |
54.72 |
57.43 |
NeP -Noci |
7.68 |
<0.001 |
0.72 |
3.08 |
|
NeP – Tr |
2.71 |
<0.001 |
0.02 |
1.27 |
||||
|
Tr – Noci |
4.97 |
<0.001 |
0.78 |
2.17 |
||||
|
SRP |
51.27 |
44.77 |
40.33 |
NeP -Noci |
-10.94 |
<0.001 |
1.43 |
3.67 |
|
NeP – Tr |
-4.43 |
<0.001 |
0.54 |
1.67 |
||||
|
Tr – Noci |
-6.50 |
<0.001 |
0.88 |
2.40 |
||||
|
PIN |
54.22 |
62.17 |
67.85 |
NeP -Noci |
13.63 |
<0.001 |
1.83 |
3.14 |
|
NeP – Tr |
5.68 |
<0.001 |
0.66 |
1.39 |
||||
|
Tr – Noci |
7.94 |
<0.001 |
1.07 |
2.01 |
||||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hwang YG, Zhu L, Wasan A, Moreland LW. Mapping Paindetect, a Neuropathic Pain Screening Tool, to Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) 29 in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Developing a Neuropathic Pain Scale As a Measure of Treatment Outcome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mapping-paindetect-a-neuropathic-pain-screening-tool-to-patient-reported-outcomes-measurement-information-system-promis-29-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-developing-a-neuropathic-pain-scal/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mapping-paindetect-a-neuropathic-pain-screening-tool-to-patient-reported-outcomes-measurement-information-system-promis-29-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-developing-a-neuropathic-pain-scal/