Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
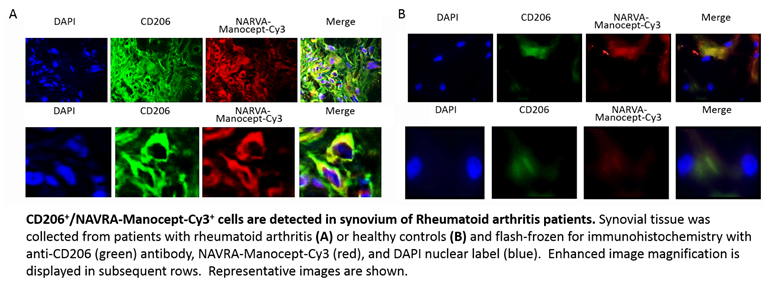
Background/Purpose: Early identification of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) would allow aggressive treatment with disease modifying rheumatic drugs and provide a system to monitor patient responses. Therefore, we developed a fluorescent agent (manocept-Cy3) that targets C-type lectin mannose receptor (CD206) to provide a diagnostic imaging tool for RA. This receptor is expressed on macrophages, which contribute to RA pathology and are strongly implicated in autoimmunity. Manocept-Cy3 follows work that was done in developing Technicium 99m Tilmanocept (Lymphoseek), which is currently used in lymph node mapping of breast cancer patients. The aim of this study was to determine if this agent could also detect these cells in synovial compartments of RA patients; thus providing the foundation to study its potential as an imaging biomarker in RA.
Methods: Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis (OA) patients, and healthy volunteers were recruited through approved institutional review board protocols. Synovial fluid was isolated and analyzed by flow cytometry. Synovial tissue was flash-frozen at the time of collection for immunohistochemical analysis and fluorescent imaging by microscopy. Tissue was incubated with DAPI nuclear stain, manocept-Cy3, and/or anti-CD206 antibody. Slides were digitally scanned for image analysis to quantitate manocept-Cy3+ staining. To demonstrate the specificity, samples were stained with an isotype-matched control antibody for CD206 or pre-incubated with 10X unlabeled (“cold”) manocept.
Results: Fluorescence microscopy showed that manocept-Cy3+/CD206+ cells were present at high levels in the synovial compartment of RA. These signals were co-localized along cellular membranes, and manocept-Cy3+ staining was statistically significant when compared to OA patients and healthy controls, as measured by digital image analysis. Flow cytometry demonstrated similar levels of CD68, CD206, and manocept-Cy3 in synovial fluid samples. No fluorescent signal was observed in RA synovial tissue incubated with CD206 isotype-matched antibody or with “cold” manocept incubation prior to manocept-Cy3 staining.
Conclusion: The identification of an imaging biomarker that is both sensitive and specific for the RA inflammatory process is critical in the diagnosis of patients with early joint symptoms and in monitoring therapeutic responses. Our results suggest that CD206-targeted manocept is a viable candidate to pursue clinically as an imaging biomarker for RA.
Disclosure:
N. A. Young,
None;
L. Schlesinger,
Navidea Biopharmaceuticals,
5;
T. J. Rosol,
Navidea Biopharmaceuticals,
5;
F. Cope,
Navidea Biopharmaceuticals,
4;
W. N. Jarjour,
Navidea Biopharmaceuticals,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/manocept-cy3-localizes-cd206-macrophages-in-synovial-tissue-and-fluid-from-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-differentially-compared-to-controls/