Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:15PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: ORAL Surveillance (NCT02092467) was a post-authorization safety study to assess the relative risk of tofacitinib vs TNF inhibitors (TNFi), based on observed increases in lipids and malignancies in patients (pts) with RA following tofacitinib treatment in the Phase 3 development program. Here, we characterized malignancies in ORAL Surveillance.
Methods: ORAL Surveillance was a long-term, randomized, open-label, non-inferiority, Phase 3b/4 safety study of tofacitinib vs TNFi in pts with RA aged ≥ 50 yrs, with ≥ 1 additional cardiovascular risk factor and an inadequate response to MTX. Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to receive open-label tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily (BID) or a TNFi (adalimumab 40 mg every two weeks [North America; NA] or etanercept 50 mg once weekly [rest of world; RoW]) while on stable background MTX doses. Incidence rates (IRs; pts with events/100 pt-yrs [PY]) of all malignancies excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC), NMSC, and cancer subtypes of interest were determined for each treatment arm. Number Needed to Harm (NNH; PY of treatment exposure needed for 1 more pt to report an event vs reference) was evaluated post hoc for all malignancies excluding NMSC. Potential risk factors for all malignancies excluding NMSC were analyzed via univariate/multivariate Cox models (post hoc). IRs of all malignancies excluding NMSC were analyzed post hoc by baseline (BL) characteristics (eg age, smoking status, and geographic region [proxy for TNFi use]).
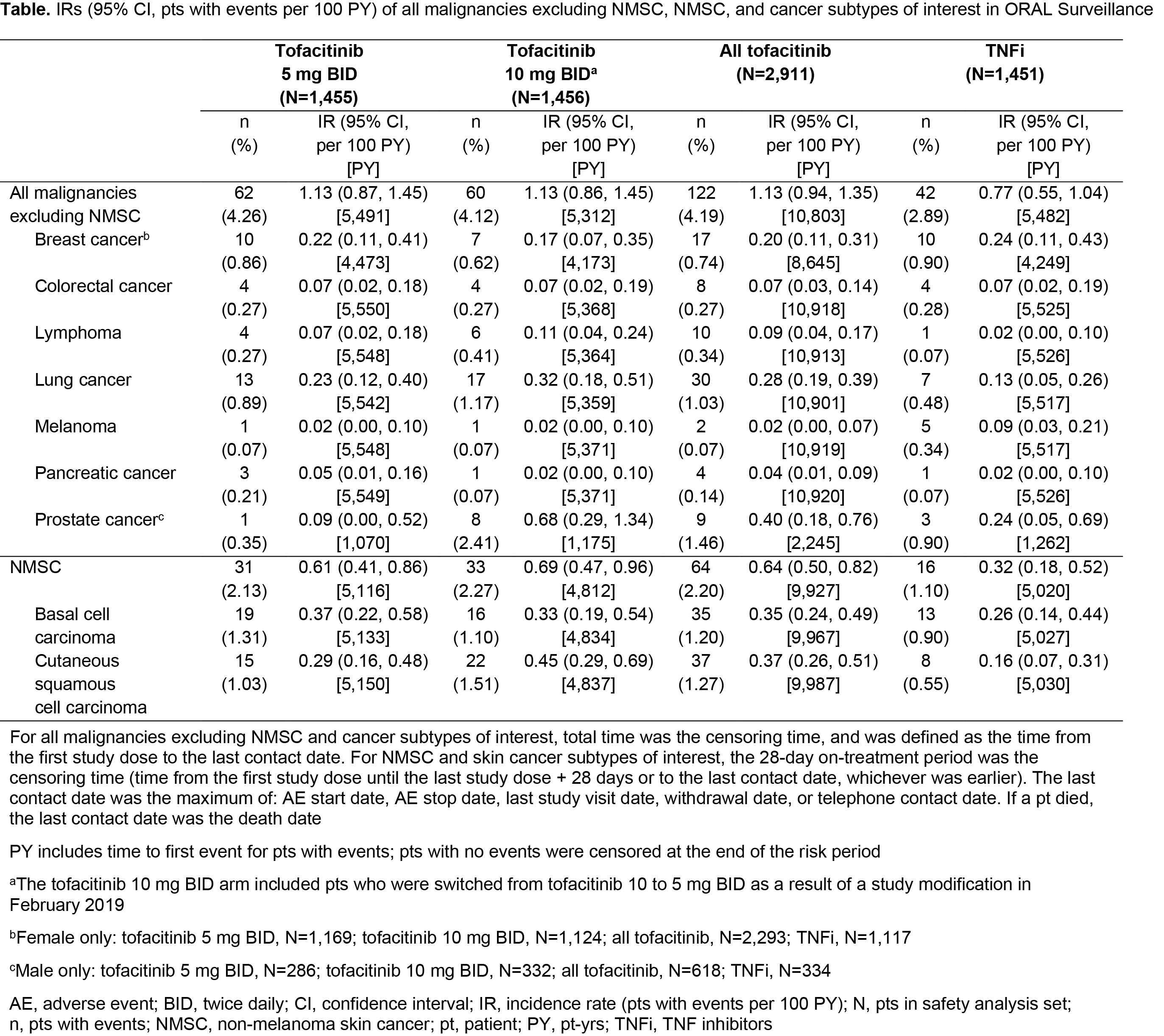
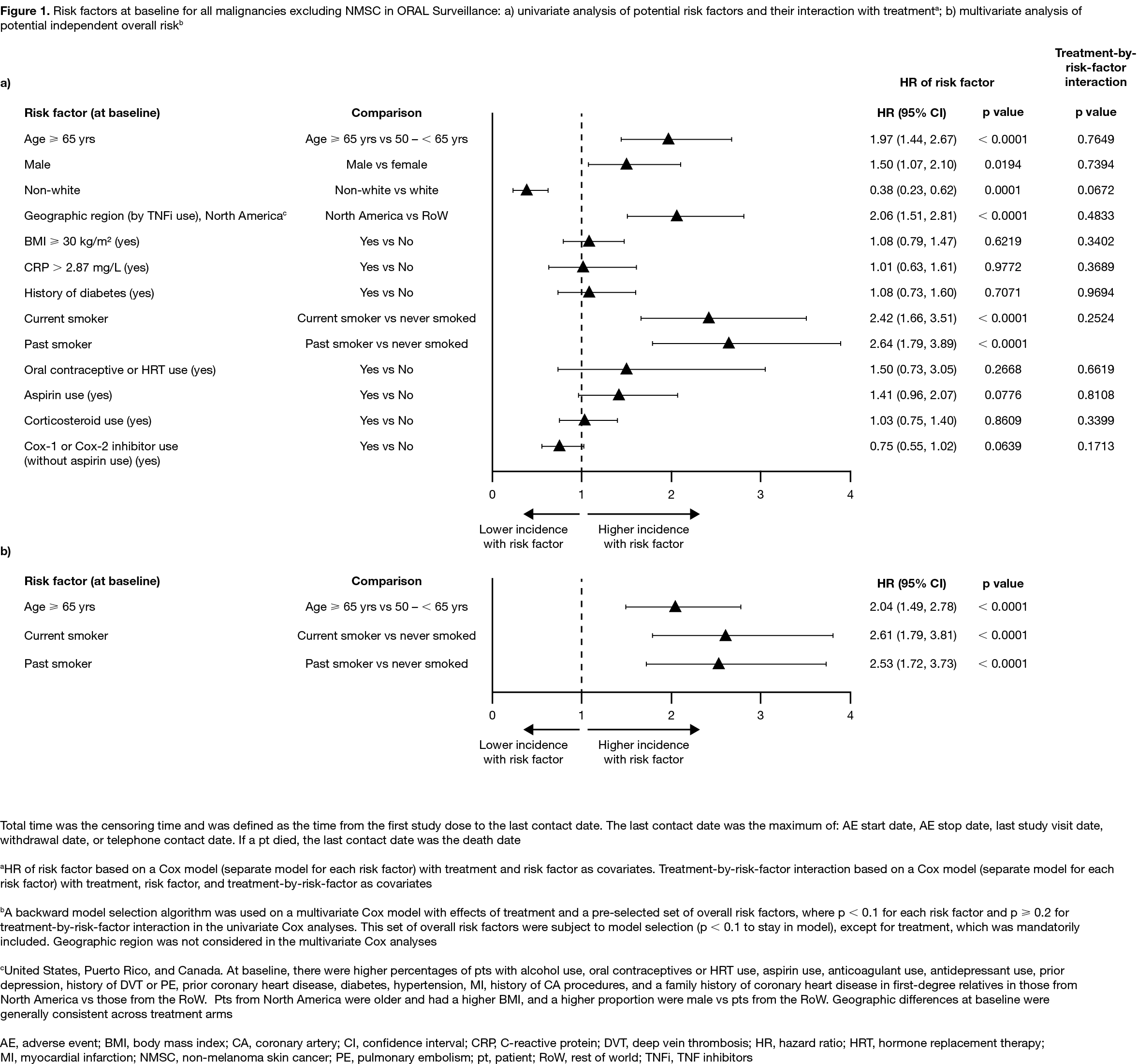
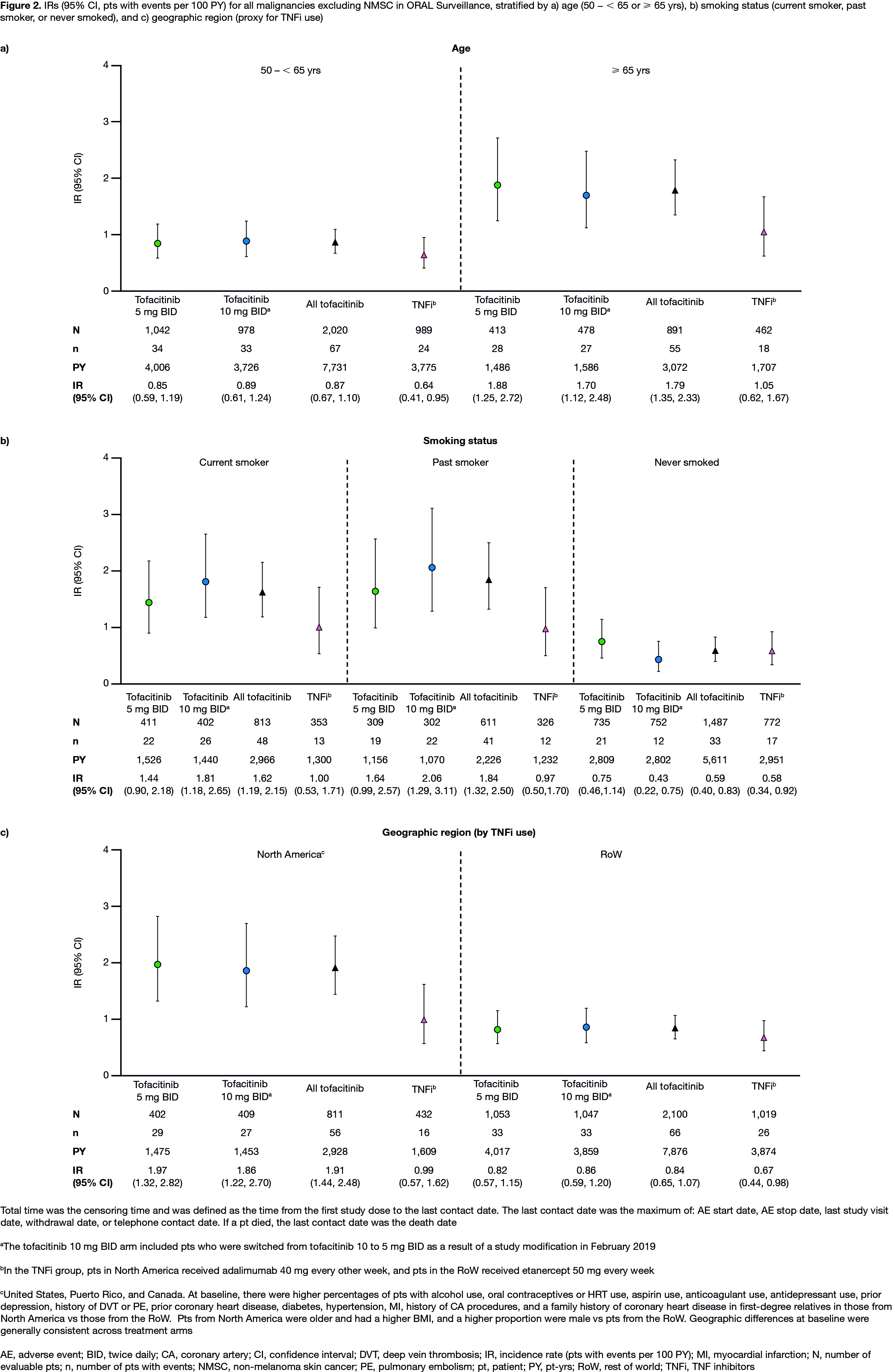
Results: In 4,362 treated pts (tofacitinib 5 mg BID, N=1,455; tofacitinib 10 mg BID, N=1,456; TNFi, N=1,451), mean age was 61.0 yrs, 78% were female, and 49% were current/past smokers. Differences in BL demographics were seen in pts from NA vs RoW (described in Figure 1 and 2 footnotes). IRs for all malignancies excluding NMSC, and for NMSC, were numerically higher with both tofacitinib doses vs TNFi (Table); hazard ratio (tofacitinib vs TNFi) for all malignancies excluding NMSC: 1.48 (95% CI 1.04, 2.09). Excluding NMSC, the most frequently reported cancer subtypes of interest (greatest number of pts with events) were lung cancer (tofacitinib) and breast cancer (TNFi) (Table). There were 10 pts with lymphoma in the tofacitinib arm (both doses) and 1 in the TNFi arm (Table). The NNH for all malignancies excluding NMSC was 276 PY for tofacitinib 5 mg BID vs TNFi, and 275 PY for tofacitinib 10 mg BID vs TNFi. Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses identified age (≥ 65 vs 50 – < 65 yrs) and smoking status (current/past smoker vs never smoked) as independent overall risk factors across treatment arms for all malignancies excluding NMSC (Figure 1a, b). Across treatment arms, IRs for all malignancies excluding NMSC were numerically higher in pts aged ≥ 65 vs 50 – < 65 yrs (Figure 2a), current/past smokers vs pts who had never smoked (Figure 2b), and pts in NA vs RoW (Figure 2c).
Conclusion: In pts with RA in ORAL Surveillance, IRs for malignancies were numerically higher with tofacitinib vs TNFi. Older age (≥ 65 vs 50 – < 65 yrs) and current/past smoking (vs never smoking) were independent risk factors for increasing malignancy rate across treatments.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by S Piggott, CMC Connect, funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis J, Yamaoka K, Chen Y, Gunay L, Sugiyama N, Connell C, Wang C, Wu J, Menon S, Vranic I, Gomez-Reino J. Malignancies in Patients Aged ≥ 50 Years with RA and ≥ 1 Additional Cardiovascular Risk Factor: Results from a Phase 3b/4 Randomized Safety Study of Tofacitinib vs TNF Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/malignancies-in-patients-aged-%e2%89%a5-50-years-with-ra-and-%e2%89%a5-1-additional-cardiovascular-risk-factor-results-from-a-phase-3b-4-randomized-safety-study-of-tofacitinib-vs-tnf-inhibitors/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/malignancies-in-patients-aged-%e2%89%a5-50-years-with-ra-and-%e2%89%a5-1-additional-cardiovascular-risk-factor-results-from-a-phase-3b-4-randomized-safety-study-of-tofacitinib-vs-tnf-inhibitors/