Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although many RA patients attribute their disease onset to recent life events, results from retrospective studies remain unclear. We compared characteristics of newly diagnosed RA patients who did and did not report significant stressful life events (+stress) in year prior to diagnosis at baseline and 12 months.
Methods: Data were from early RA patients (symptoms < 1 year) enrolled in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) from 01-2007 to 03-2017 with ≥ 12 months of follow-up. Patients were asked about major psychological (death, divorce/separation, family, financial, other) and physical (motor vehicle accident, surgery, major illness/infection, other) stressors in previous year. We used independent t-tests and chi square to compare characteristics by sex and stress classification and multivariable regression to examine the impact of stress on disease activity and patient reported outcomes (PROs) at 1 year after adjusting for age, sex, education, and baseline fibromyalgia diagnosis and swollen joint count.
Results: The 1933 adults were mostly female (72%), with a mean (SD) age of 55 (15) years. At baseline, 52% reported one or more stressors in previous year; family (48%), financial stress (36%), death (35%), surgery (28%), and major illness (26%) were the most common stressors. Patients with +stress were more likely to be women, were significantly younger, had more comorbidities, slightly higher mean DAS28, and were more likely to have fibromyalgia (Table 1). Patients with +stress also reported significantly baseline higher pain, fatigue, depression, sleep disturbance, patient global, and HAQ-DI scores.
At 1 year, swollen joint counts and the proportion of patients in DAS28 REM was similar between groups. However, PROs remained higher in those with a history of +stress, with some evidence of a dose-response relationship (Table 2). The greatest impacts were on mood, sleep disturbance, and fatigue.
Conclusion: In this pan-Canadian early RA cohort, stressful life events were common in the year prior to diagnosis and were associated with significantly worse depression, fatigue, sleep disturbance, pain, patient global and disability scores at diagnosis; 1 year later effects on PROs persisted even though disease activity was similar between groups. Newly diagnosed RA patients with a history of recent stressors may benefit from emotional support to optimize how they feel and function.
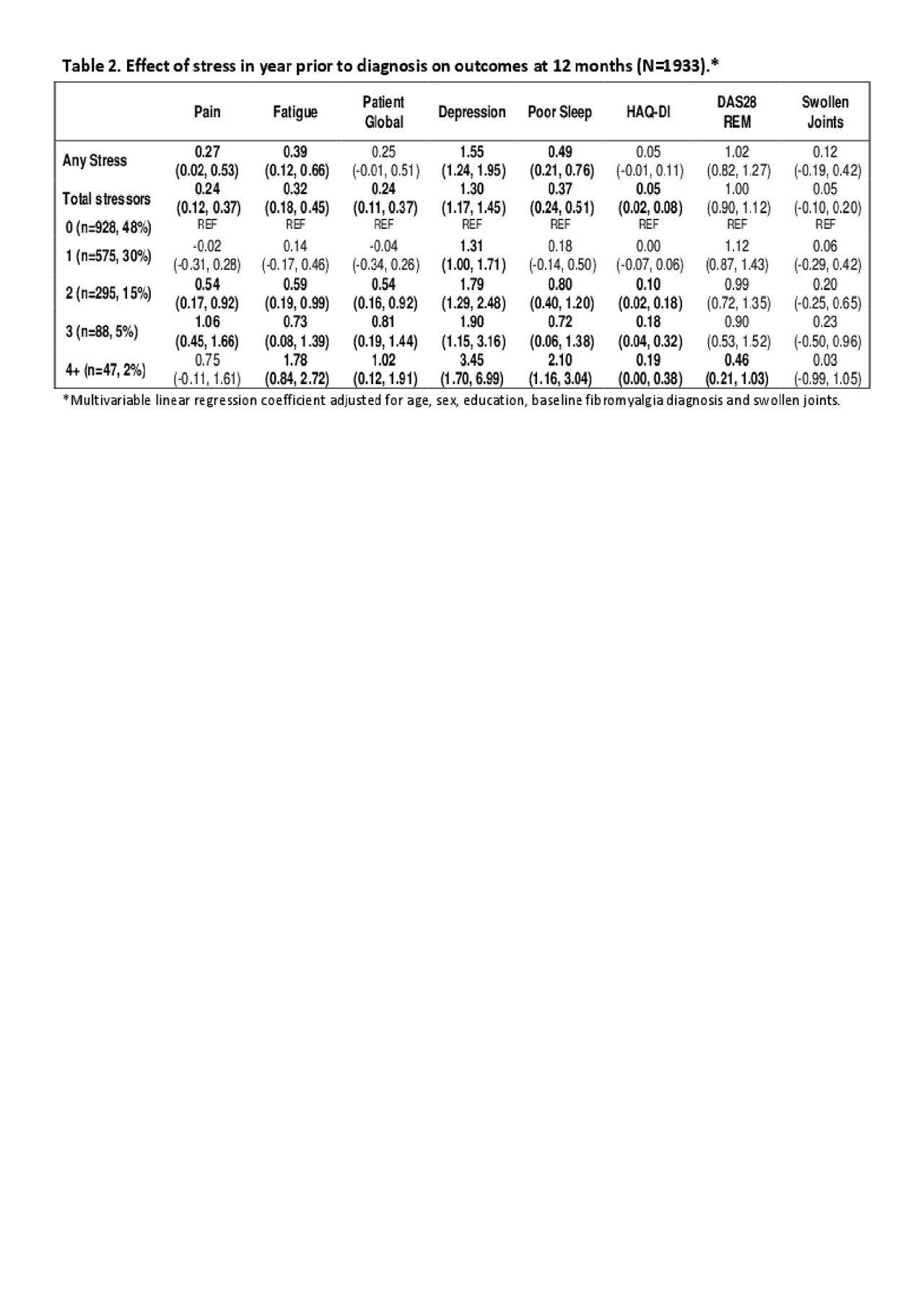
Table 2 ACR2019 Stress Nicole FINAL
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Andersen N, Schieir O, Valois M, Boire G, Pope J, Hazlewood G, Bessette L, Hitchon C, Tin D, Thorne C, Keystone E, Bykerk V, Bartlett S, (CATCH) Investigators C. Major Stressors in the Year Prior to Diagnosis Affects RA Characteristics at Presentation and 1 Year [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/major-stressors-in-the-year-prior-to-diagnosis-affects-ra-characteristics-at-presentation-and-1-year/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/major-stressors-in-the-year-prior-to-diagnosis-affects-ra-characteristics-at-presentation-and-1-year/

