Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Shared epitope smoking interaction does not fully explain MHC association in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). We have previously shown HLA-DQB1*0601 (DQ6.1) to be a susceptibility allele in India1. It has a restricted geographic distribution being common in Japan, India and parts of middle-east while absent in Africa and western Europe (Fig 1 heat map of DQ6.1 distribution). In Pristane induced arthritis, susceptibility is determined by rat ortholog of DQ locus RT1-B. Thus it is possible that HLA-DQ6.1 may have an interaction with hydrocarbons. We therefore planned this study to confirm the association of DQ6.1 with RA and explore interactions with smoking and household fuel use.
Methods: Patients with RA (ACR 2010 criteria) and healthy controls of similar ethnic background were included. Data on environmental exposure like tobacco use, active and passive smoking and exposure to household smoke during cooking including biomass fuels (wood, coal, cow-dung cake) and hydrocarbon fuels LPG and kerosene was collected. Patients sex, age of onset, duration of exposure, birth year, RF , anti-CCP were also recorded. HLA-DQB1*0601, DQB1*0603 and DQA1*0103 were typed using Sequence specific PCR. The association of Chi-squared test was used to test the strength of association. Gene environment interaction was studied using Cox regression after stratifying by genotype.
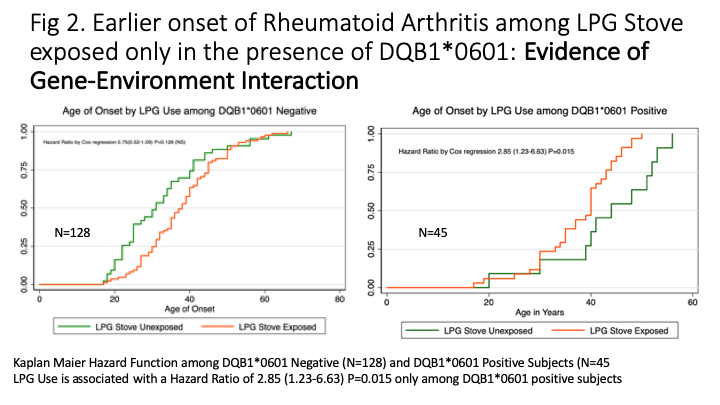
Results: 175 patients (21 males) and 263 healthy controls were included. The median age of onset of RA was 37(range 17-67 years) and median duration of disease was 9 years(range 2mo to 35 years). Of these 138/172 (80%) were RF positive and 104/126 (82.5%) were anti-CCP positive. Overall 165 were seropositive and 7 seronegative. Among patients DQB1*0601 was present in 45/175 (25.7%) while DQB1*0603 in 27/175(15.4%) and DQA1*0103 in 35/175(20%). Among controls, DQB1*0601 was present in 47/263 (17.9%) while DQB1*0603 was present in 31/263(11.8%) and DQA1*0103 in 42/263(16%). The putative risk allele DQB1*0601 was significantly associated with RA with an Odds Ratio of 1.59 (P< 0.005) confirming the association. There was no significant association between serological status with presence of DQ6.1. Smoking was rare among Females (4/154 versus 9/21 in males). 116/175 had exposure to biomass fuels (wood 107, cow-dung cake 72) while LPG stove was used by 121/175 subjects. Exposure to LPG was associated with earlier age of onset of RA (median 40 years versus 44 years) in the presence of DQ6.1 with a hazard ratio of 2.5 (CI 1.2-5, P=0.014, Figure 2) but not in DQ6.1 negative patients.
Conclusion: This replication study confirms the association of DQB1*0601 with RA. Smoking is rare among Indian women with RA. There is signal of gene-environment interaction between DQ6.1 and exposure to LPG stoves.
Lawrence A, Prakash S, Bharadwaj U, Aggarwal A, Misra R, Agrawal S. Major Histocompatibility Antigen HLA-DQ6.1 (DQA1*0103/DQB1*0601) Increases Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Independent of Shared Epitope Among Indians [abstract].Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). [ACR Annual Congress, 11-16 Nov 2016, Washington DC abstract no 1573]
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lawrence A, Dhar A, Prakash S, Arya S, Aggarwal A, Agrawal S. Major Histocompatibility Antigen HLA-DQB1*0601 Is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Among Indians in a Replication Study: Evidence of Gene-Environment Interaction with LPG Stove Use [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/major-histocompatibility-antigen-hla-dqb10601-is-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-among-indians-in-a-replication-study-evidence-of-gene-environment-interaction-with-lpg-stove-use/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/major-histocompatibility-antigen-hla-dqb10601-is-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-among-indians-in-a-replication-study-evidence-of-gene-environment-interaction-with-lpg-stove-use/