Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstract Poster Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although EULAR/ACR guidelines suggest tapering biologics following sustained remission in patients (pts) with RA, specific de-escalation (DE) regimens are not fully defined. The Phase IIIb Assessing Very Early Rheumatoid arthritis Treatment (AVERT)-2 trial (NCT02504268) is evaluating SC abatacept (ABA) + MTX versus ABA placebo (PBO) + MTX in ACPA-positive pts with early (ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria; disease duration ≤6 mths), active RA (SDAI >11). AVERT-2 was designed to investigate achievement of SDAI remission and a clinically meaningful dose DE strategy among pts in sustained remission who completed induction with ABA + MTX. We report results on the maintenance of remission during the DE period of AVERT-2.
Methods: Pts were randomized 3:2 to blinded SC ABA (125 mg once wkly [QW]) + MTX or ABA PBO + MTX induction treatment for 56 wks. Pts who completed induction with ABA + MTX and had sustained SDAI remission (≤3.3 at Wks 40 and 52) were re-randomized 1:1:1 to ABA QW + MTX for 48 wks, ABA every other wk (EOW) + MTX for 24 wks followed by ABA PBO + MTX for 24 wks, or ABA QW + MTX PBO for 48 wks in the DE period. MTX and oral corticosteroid doses in DE were stable. Pts with sustained SDAI remission who received ABA PBO + MTX during induction were not re-randomized and continued this treatment in the DE period in a blinded fashion; no comparisons between this arm and ABA arms were made. Endpoints: proportion of pts in SDAI remission, adjusted mean change from DE Day (D) 1 in SDAI score and safety to DE Wk 48; radiographic progression at DE Wk 48.
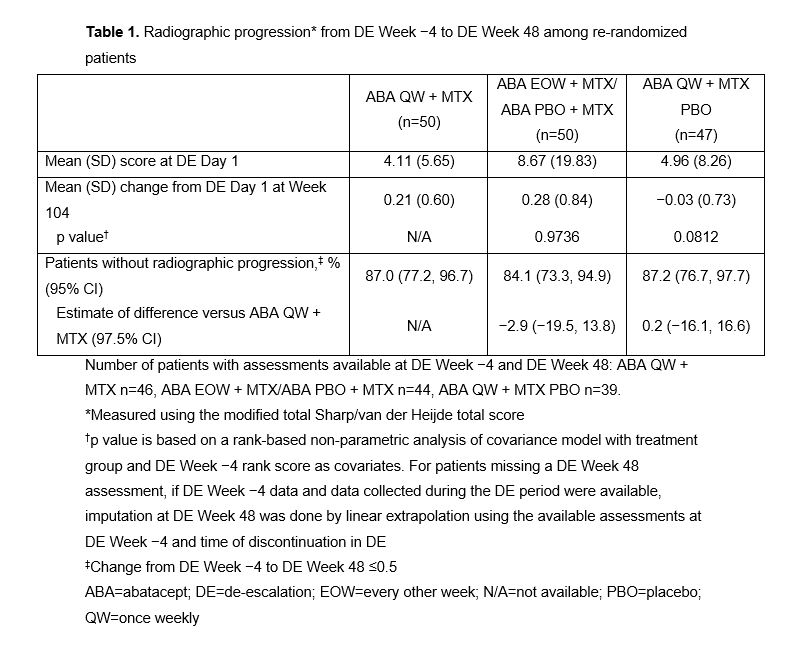
Results: 147 ABA + MTX–treated pts were re-randomized in the DE period (ABA QW + MTX, n=50; ABA EOW + MTX, n=50; ABA QW + MTX PBO, n=47); 37 pts with sustained remission who received ABA PBO + MTX during induction continued in DE period. Across the re-randomized arms, mean DAS28 (CRP), SDAI and HAQ-DI scores ranged from 1.63–1.79, 1.87–2.52 and 0.18–0.30, respectively, at DE D1. 74% of pts receiving ABA QW + MTX maintained remission at DE Wk 48 (Fig 1). Withdrawal of MTX (ABA QW + MTX PBO) led to an initial drop in remission rates to 64%, with stabilization from DE Wk 12. After halving ABA dose to ABA EOW + MTX upon entry to the DE period, remission decreased from 88% at DE Wk 0 to 74% at DE Wk 24, and then further decreased to 48% at DE Wk 48 after ABA was fully withdrawn at DE Wk 24. At DE Wk 48, 59% of pts who received ABA PBO + MTX during induction maintained remission with this treatment. Adjusted mean change in SDAI score in the ABA arms in the DE period was numerically low, but varied between arms and increased following ABA withdrawal from the ABA EOW + MTX arm at DE Wk 24 (Fig 2). Sustained inhibition of structural damage was seen in all ABA arms (Table 1). Safety was similar across treatments with no new signals.
Conclusion: In the DE period of AVERT-2, combination therapy (abatacept + MTX) resulted in the best maintenance of remission and inhibition of structural damage progression in early seropositive pts with RA and sustained SDAI remission following abatacept + MTX treatment. Tapering of abatacept EOW + MTX to MTX only was associated with the greatest loss of remission. Abatacept-containing DE regimens should be investigated further as a viable option in clinical practice.
Writing support: Lola Parfitt, Caudex; funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Emery P, Tanaka Y, Bykerk V, Huizinga T, Citera G, Bingham C, Banerjee S, Soule B, Nys M, Connolly S, Wong R, Huang K, Fleischmann R. Maintenance of Remission Following Dose De-Escalation of Abatacept in Early, MTX-Naïve, ACPA-Positive Patients with RA: Results from a Randomized Phase IIIb Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/maintenance-of-remission-following-dose-de-escalation-of-abatacept-in-early-mtx-naive-acpa-positive-patients-with-ra-results-from-a-randomized-phase-iiib-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/maintenance-of-remission-following-dose-de-escalation-of-abatacept-in-early-mtx-naive-acpa-positive-patients-with-ra-results-from-a-randomized-phase-iiib-study/

.jpg)
.jpg)