Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Treatment: New Agents, Old Agents (1458–1463)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:15PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) disproportionately affects racial and ethnic populations. Contreras reported African-American (AA) and Hispanic patients had worse outcomes as compared to patients of European ancestry. ALMS highlighted different responses finding that AA and Hispanics had better response rates with MMF than with cyclophosphamide (CYC) (p=0.033). Reports from Asian nations describe high response rates especially with MMF regimens. The purpose of our study is to determine response rates in relation to treatment and demographics
Methods: Retrospective review of NYU Lupus registry. Patients met ACR/SLICC criteria for LN, had at least one episode of proteinuria ( >500 mg spot or 24-hour uPCR), and LN flare after 2012 Epic implementation. Demographics, uPCR, Creatinine (Cr), albumin, C3, C4, anti-DNA levels collected at 0, 12, 24, 52, and 104 weeks for de novo episodes and renal flares. De novo episode defined as first episode leading to biopsy followed by change in medication or a clinical note documenting new onset LN accompanied by a change in medication. A renal flare was defined as a prior de novo episode and 1 of 3 conditions: biopsy, episode with change in proteinuria by at least 50%, or a note documenting a renal flare with each scenario required medication change. Responses are complete uPCR ≤ 0.5, satisfactory uPCR ≤ 0.7, or partial uPCR at least < 50% from baseline and in all 3 cases Cr unchanged or increased < 20%. No response uPCR more than 50% from baseline. Treatment regimens included MMF, CYC, MMF/tacrolimus, RTX, or other. Univariate analysis chi-squared test used to assess for differences in responses by treatment. Multivariable logistic regression (MR) analysis used to assess for differences in responses by gender, race, and ethnicity.
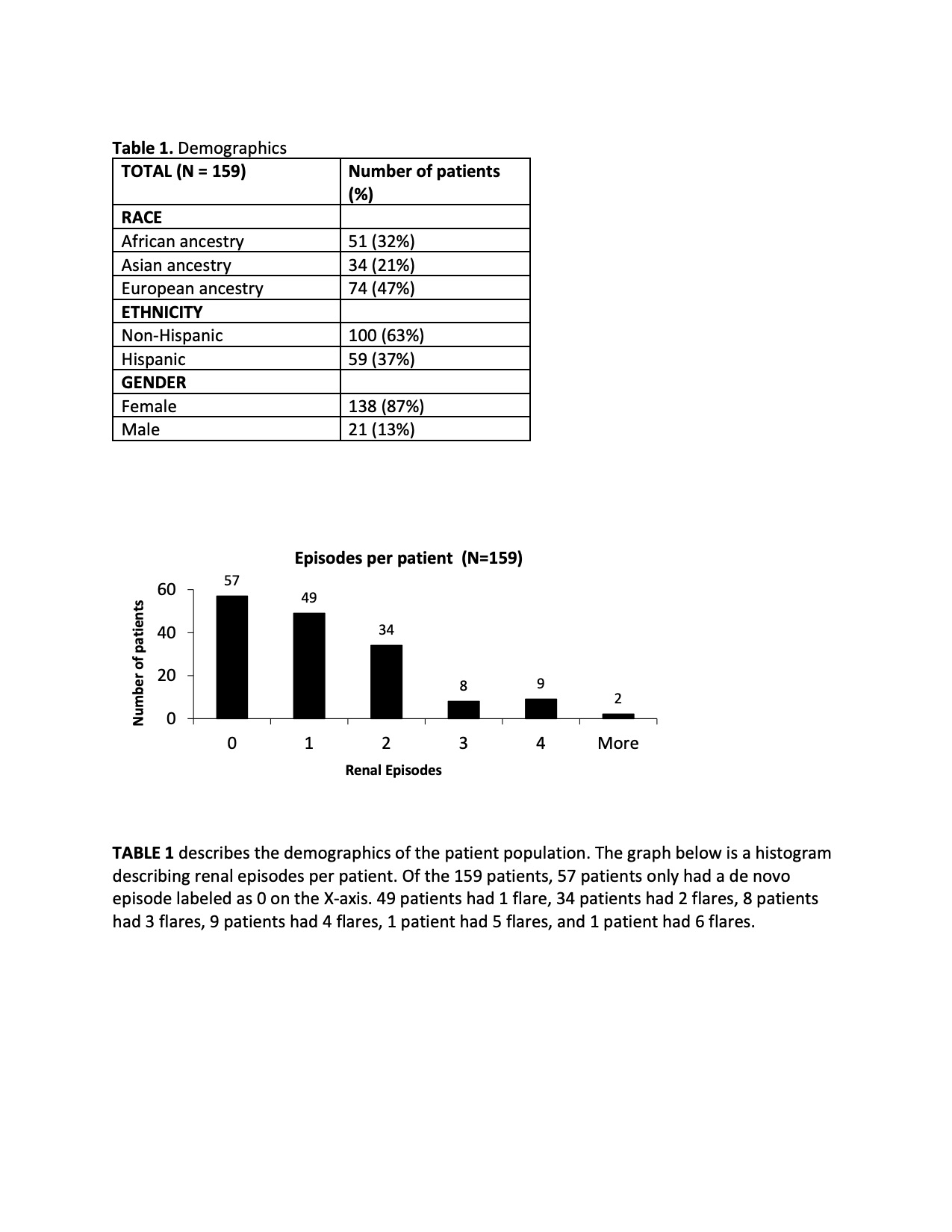
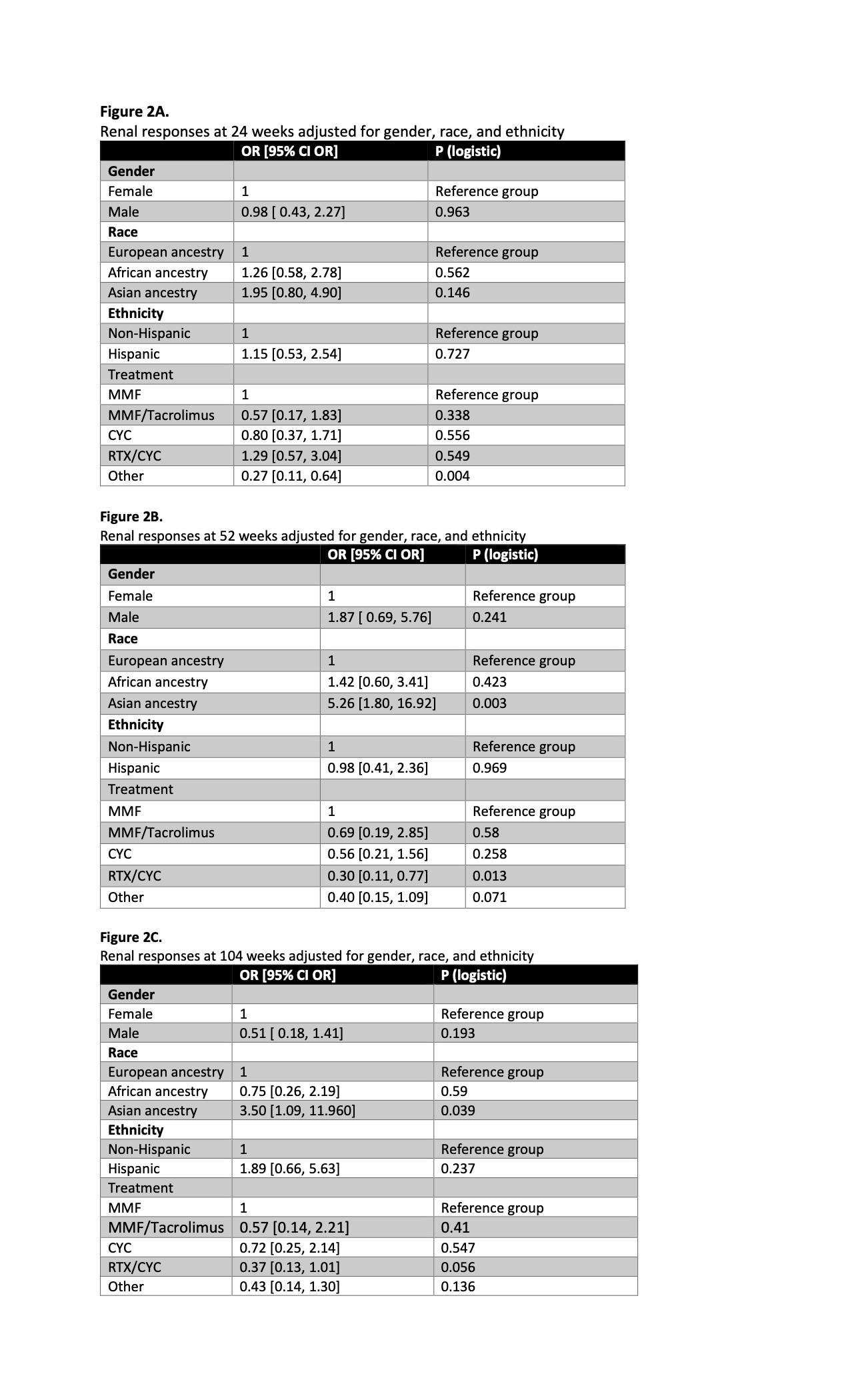
Results: 159 patients with de novo episodes, 188 flare episodes:138(87%) female, 74(47%) European, 51(32%) AA, 34(21%) Asian & Hispanic 59(37%) (Table 1A-B). There was a statistical difference (p= 0.003) in responses by treatment for de novo episodes at 104 weeks, favoring MMF or CYC as opposed to MMF/tacrolimus or RTX/CYC (Fig 1A). There were no differences seen in responses by treatment for any flares occurring 24, 52, or 104 weeks (Fig1b-d). MR analysis demonstrated that patients who received “other” treatments had worse outcomes at 24 weeks as compared to MMF (p=0.004) (Fig2A). Patients who received RTX/CYC had worse outcomes when compared to MMF group at 52 and 104 weeks (p =0.013) (Fig2B-C). AA did not have worse responses when compared to Europeans. Asians had better outcomes when compared to Europeans at 52 and 104 weeks (Fig 2B-C).
Conclusion: Renal responses for de novo episodes were superior with MMF or CYC at 104 weeks compared to MMF/tacrolimus or RTX/CYC explained by treatment resistance when first episode appeared on immunosuppression. There were no differences seen in responses by treatment for any flares. Our findings are inconsistent with previous studies demonstrating that AA and Hispanic patients have worse outcomes when compared to Europeans explained by reliance on MMF as first line therapy and use of rescue options including low dose CYC and RTX. Asian residents of NY metropolitan had better outcomes validating high response rates reported from Asian nations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Haj-Ali M, Deonaraine K, Engel A, Qian Y, Saxena A, Izmirly P, Buyon J, Belmont H. Lupus Nephritis Renal Responses in Relation to Treatment and Demographics: Observations from a Multi-racial/ethnic Cohort of 159 Patients in the NYU Lupus Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-nephritis-renal-responses-in-relation-to-treatment-and-demographics-observations-from-a-multi-racial-ethnic-cohort-of-159-patients-in-the-nyu-lupus-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-nephritis-renal-responses-in-relation-to-treatment-and-demographics-observations-from-a-multi-racial-ethnic-cohort-of-159-patients-in-the-nyu-lupus-registry/