Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster Session III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We aim to evaluate the
differences and rationale behind the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to
proliferative lupus nephritis (LN) among nephrologists and rheumatologists.
Methods: A de-identified,
multiple-choice survey was distributed to nephrologists and rheumatologists in
the United States. The survey consisted of a demographic questionnaire and two
case vignettes exploring the decision of when to biopsy for the diagnosis of LN,
management of International Society of Nephrology (ISN) Class III LN, and
management of refractory ISN Class IV LN.
Results: There were 38
respondents to the survey: 12 rheumatologists and 26 nephrologists. Work
setting: 81% academic, 19% non-academic. Management of abnormal urinalysis
findings in an asymptomatic lupus patient: 33% of rheumatologists versus 76% of
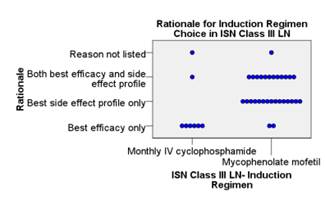
nephrologists chose to biopsy. Induction regimen of ISN Class III LN: 79% of
all providers chose mycophenolate mofetil
(MMF) and 21% chose IV cyclophosphamide.
Choice of Induction Regimen in ISN Class
III LN per Specialty
|
Mycophenolate Mofetil
|
IV Cyclophosphamide |
Total |
|
|
Nephrology |
18 |
8 |
26 |
|
Rheumatology |
12 |
0 |
12 |
|
Total |
30 |
8 |
38 |
Maintenance regimen of ISN Class III LN: all surveyed rheumatologists chose MMF
as a sole maintenance agent compared to 32% of nephrologists who elected the
addition of low-dose corticosteroids to MMF. Choice of an adjunctive agent in
refractory ISN Class IV LN: 68% of all providers chose rituximab, 14% chose tacrolimus, 5% chose abatacept, and
14% elected not to add any agents listed.
Conclusion: The results of this
survey suggest a significant difference among rheumatologists and nephrologists
on the decision to perform initial kidney biopsy and management of ISN Class
III LN. The results suggest that perception of side effect profiles play an
important role in the choice of therapeutics. This study emphasizes the need
for a multi-disciplinary approach toward renal disease in lupus patients. We
continue to recruit subjects to complete this survey.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nandan A, Syed H, Vagts C, Kidd J. Lupus Nephritis: An Exploration of Management Style [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-nephritis-an-exploration-of-management-style/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-nephritis-an-exploration-of-management-style/