Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Limited information about lupus myocarditis (LM) comes from small case series. The aim of our study is to describe and compare clinical characteristics, cardiac imaging findings and outcomes in patients with LM, non-LM and patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) without myocarditis.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective case-control study in a tertiary care center. We identified all cases of LM from 2005-2021 through electronic data base. Cases: patients with SLE diagnosis according to the 2019 ACR/EULAR criteria who met the criteria for clinically suspected acute myocarditis and a cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) compatible were included. Patients with preexisting cardiac disease were excluded. Control groups: 1. patients with moderate/severe active SLE without history of myocarditis, paired 1:1 with cases according to age, gender and disease duration; 2: patients with diagnosis of acute myocarditis and CMR compatible, with no signs or symptoms suggestive of SLE (non-LM). All patients in LM and non-LM groups had a CMR compatible with myocarditis according to Lake Louise criteria. Patients were follow-up for two years. We compared demographic, clinical and laboratory characteristics, and outcomes in cases and both control groups. Disease activity and damage accrual at inclusion and follow-up was compared in patients with LM and control group 1. Echocardiographic and CMR findings were compared between case group and control group 2.
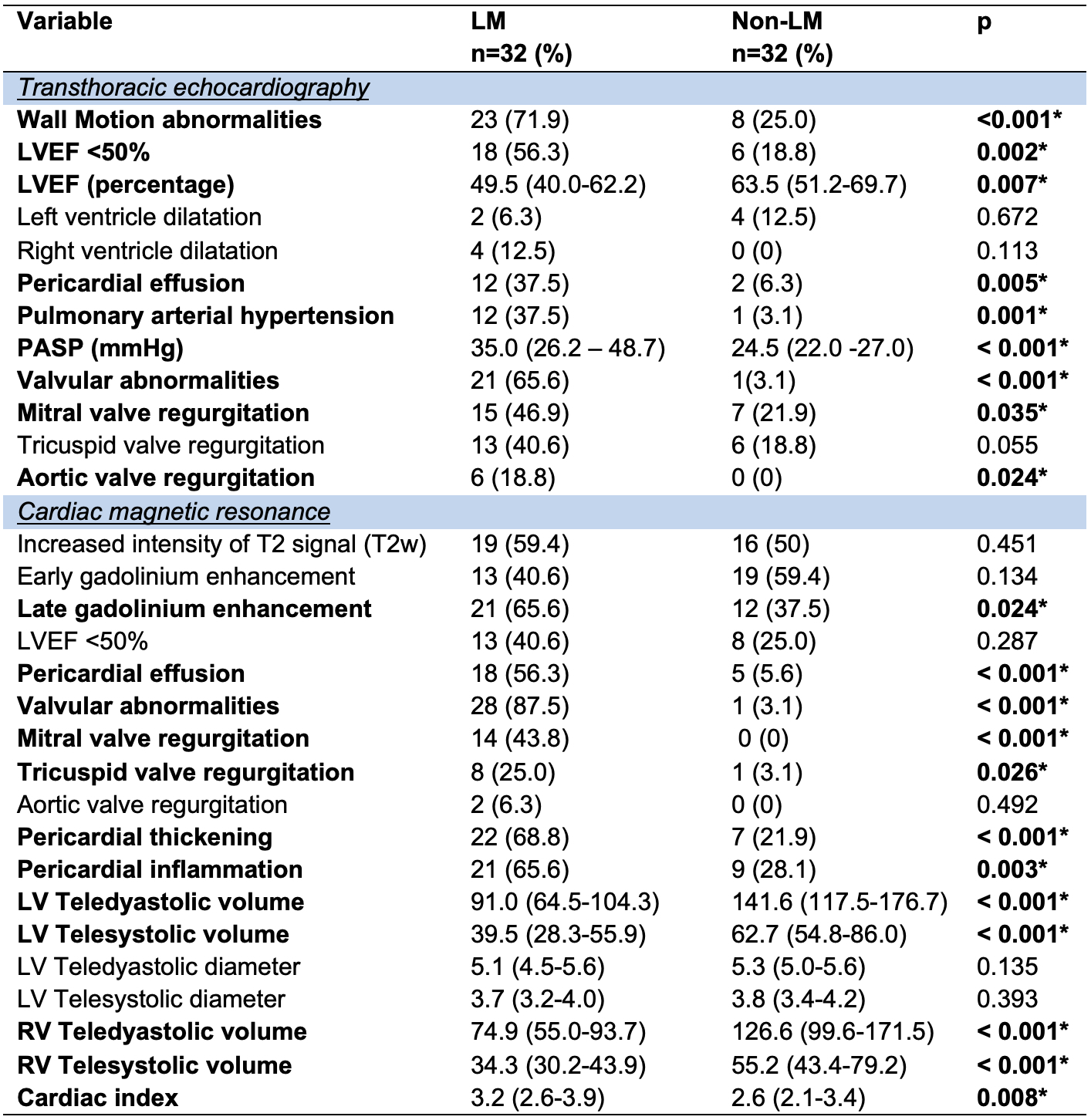
Results: Thirty two patients (31 women), with a median age of 29 years (IQR 22-38.1) were included in LM group. Same number of patients were included in both control groups. No differences in age were found (p=0.3). At inclusion, there were no differences in clinical characteristics among the SLE groups. However, the SLICC/ACR DI was higher in the LM group compared to control group 1. Additionally, no differences were found in clinical and electrocardiographic data between LM and non-LM patients. Reduced LVEF < 50% (56.3% vs 18.8%, p=0.002), wall motion abnormalities (71.9% vs 25%, p< 0.001) and increased pulmonary systolic artery pressure ≥30 mmHg (37.5% vs 3.1%, p< 0.001) were more frequent echocardiographic findings in LM compared to non-LM. Mean LVEF was lower in LM (49.5% vs 63.5%, p=0.007) during acute myocarditis episode. CMR showed increased pericardial effusion (56.3% vs 5.6% p< 0.001), pericardial thickening (68.8% vs 21.9%, p< 0.001), valvular abnormalities (87.5% vs 3.1% p< 0.001) and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) (65.5 vs 37.5, p=0.02) in LM compared to non-LM (Table 1). Outcomes: invasive mechanical ventilation and ICU admission were increased in LM group, compared to both control groups (28.1% vs 3.1% vs 6.3%, p=0.004 and 25% vs 3.1% vs 6.3%, p=0.012, respectively), although no difference in deaths were seen at two years follow-up compared to non-LM (15.6% vs 0 vs 6.3%, p=0.054).
Conclusion: Impaired left ventricular systolic function along with wall motion abnormalities, pericardial involvement, LGE and cardiac valve regurgitation are the main imaging findings in LM. Lupus myocarditis is a severe manifestation in SLE patients associated with increased ICU admissions and invasive mechanical ventilation.
Data are expressed as proportions (percentages) or medians (interquartile ranges). Statistical analysis: Chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests were used for nominal variables, the Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used for numerical variables.
LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction; PAH: Pulmonary arterial hypertension; PASP: Pulmonary artery systolic pressure; LV: left ventricle; T2w: Intensity of T2 signal; RV: right ventricle.
*Statistically significant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zamora-Medina M, Cimé-Aké E, G. Lazarini E, Muñoz-Castañeda W, Fragoso-Loyo H. Lupus Myocarditis: Clinical Characteristics, Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings and Outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-myocarditis-clinical-characteristics-cardiac-magnetic-resonance-imaging-findings-and-outcomes/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-myocarditis-clinical-characteristics-cardiac-magnetic-resonance-imaging-findings-and-outcomes/