Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2257–2325) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The SDI is a robust instrument, but is limited by incomplete items, restricted applicability in paediatric patients, and outdated item definitions1. The SLICC, ACR and LFA have embarked on a data- and expert/patient-driven project to develop a revised SDI. Our objective was to report the item generation and reduction phases of a five-phase process for developing a revised SDI.
Methods: Item generation and reduction involved a thorough literature review, a three-round Delphi exercise, and a subsequent revision by a 14-member steering committee. A group of lupus experts conducted a literature review to identify items that reflect the construct of damage in SLE and grouped the items into organ domains. A large international group of expert lupus clinicians was established by snow-ball sampling amongst SLICC members. Patient and caregiver partners were nominated through the LFA, Lupus UK, Lupus Europe, and Lupus Canada.
Participants generated and rated candidate items based on their appropriateness for inclusion in a revised SDI using a Delphi exercise. The 14-member steering committee then reviewed the items for further refinement.
Results: We assembled a diverse group of 146 individuals (mean age 50.6, ranging from 28 to 79 years; 60.3% females; 58.9% white; clinical experience ranging from 1 to 51 years) from 35 countries, representing the lupus research and patient community extensively. There were 135 medical doctors, 2 allied health professionals and 9 patients.
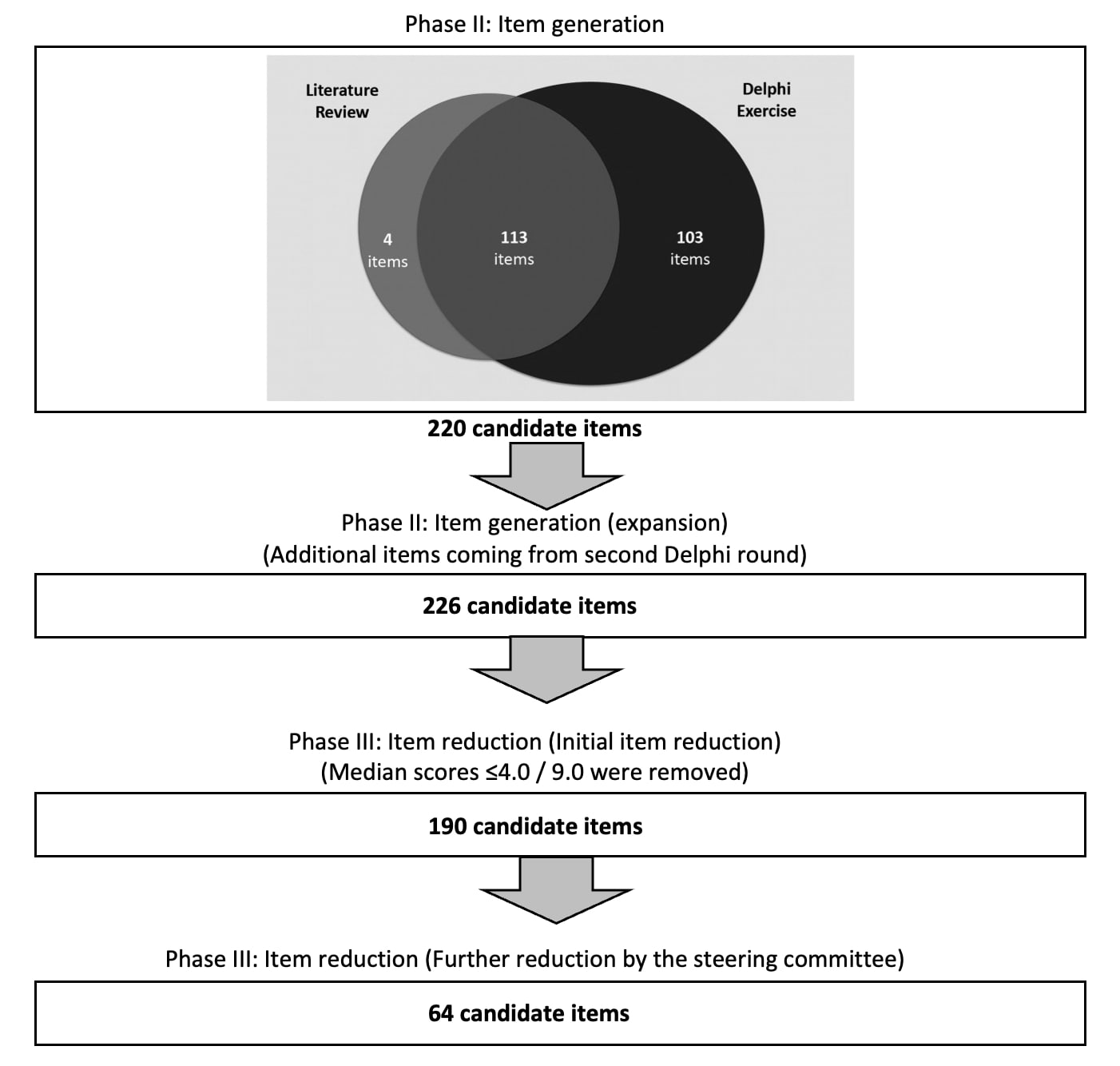
Item generation resulted in a total of 220 items across 14 organ systems. The literature review identified 4 unique items (1.8%), while 103 unique items (46.8%) were derived from the Delphi exercise alone, and 113 items (51.4%) appeared in both exercises. In the second round of the Delphi exercise, participants suggested an additional 6 unique items. Overall, 226 items were subjected to re-rating for appropriateness for inclusion in the revised SDI. Completion rates for the first, second, and third Delphi rounds were 97.9%, 95.0%, and 91.7%, respectively. Thirty-six items received a median score of 4 out of 9 and these were removed. All original 1996 SDI items were retained with median appropriateness scores of 7, 8, and 9, except for upper gastrointestinal tract surgery (median appropriateness score 5) and osteomyelitis (median appropriateness score 5). The steering committee further eliminated 126 items due to redundancy, limited availability or feasibility for assessment, overlap, lack of reflection of damage construct or association with lupus disease activity, and rarity. Figure 1 shows the number of candidate items identified at different stages during revised SDI development.
Conclusion: Using a combined data-driven and expert/patient-based approach, items and domains that comprise damage in SLE have been expanded. The item generation and reduction phase resulted in 64 candidate items for consideration. All original SDI items were retained in this step. Further steps are now underway to agree upon definitions for those items, including extent and duration of item presence, based on the best current evidence and internationally accepted norms.
1) Barber M, et al. Evolving concepts in SLE damage assessment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(6):307-8
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kundakci B, Barber M, Clarke A, Johnson S, Bruce I, organ damage index (SDI) collaborators O. Lupus Damage Index Revision – Item Generation and Reduction Phase [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-damage-index-revision-item-generation-and-reduction-phase/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-damage-index-revision-item-generation-and-reduction-phase/