Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Miscellaneous Aspects of RA (0786–0812)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The use of treat-to-target (T2T) strategy in managing early rheumatoid arthritis (ERA) had been highly advocated in the past decades. Various international guideline utilized a stepwise approach starting with conventional synthetic disease modification anti-rheumatic drug (csDMARDs), and eventually escalate to biologic/targeted synthetic DMARDs (b/tsDMARDs) when the target is not met. The response rate to csDMARDs varies among individuals. Currently, there are limited biomarker data in predicting csDMARDs response. If certain biomarker could predict non-response towards csDMARDs, would early initiation of b/tsDMARDs improve disease prognosis remained uncertain.
Methods: This is a 6-month pilot prospective discovery cohort in patients with ERA. Patients received T2T treatment according to a standardized protocol with every 3-monthly follow up. Patients who achieved simplified disease activity index (SDAI) remission at month 6 is defined as csDMARDs responder. Serum blood sample was collected at baseline and 48 cytokines and chemokines Bio-Rad Bioplex assay was performed.
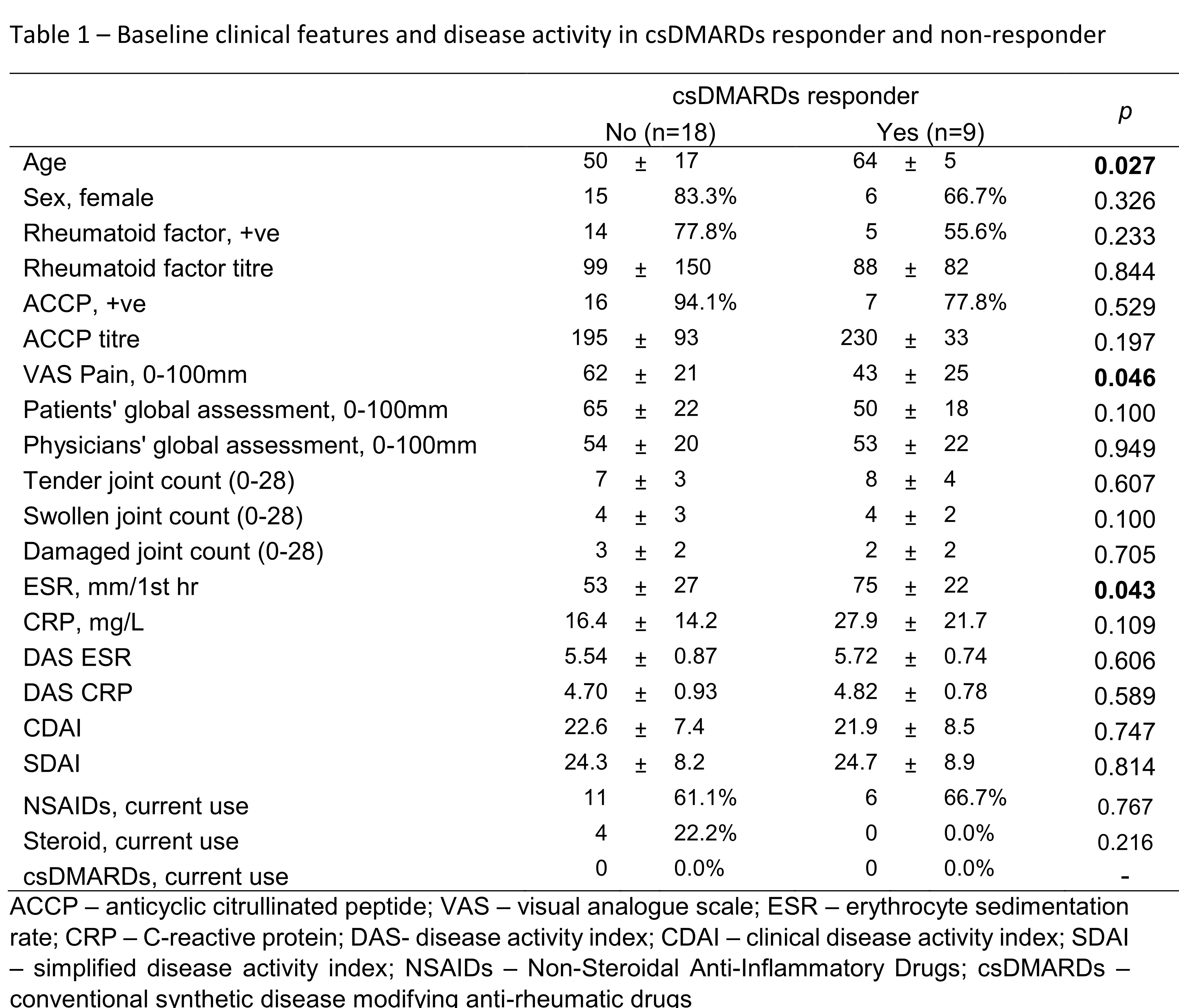
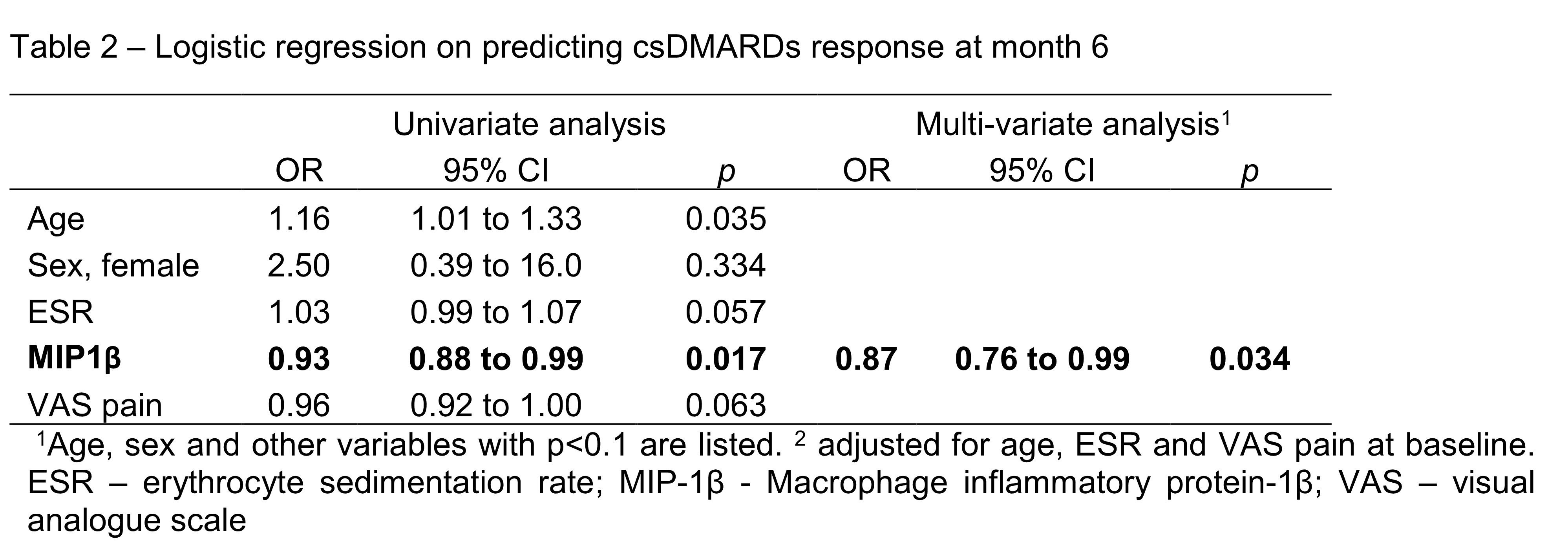
Results: Twenty-seven patients (age: 55±15 years; female: 21(78%)) who had completed month 6 follow up were included in the current analysis. All patient received csDMARDs treatment. After 6 months, significant improvement in disease activity was observed (SDAI: 24.4±8.3 at baseline vs 8.0±6.5 at month 6, p< 0.001). One third of them (9/27, 33%) achieved SDAI remission at month 6 and were regarded as csDMARDs responder (DR). Patients in DR+ group were older, had lower pain score and higher Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (Table 1). There were no statistically difference between the use of drugs across the two groups during study period. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1β (MIP-1β) is a proinflammatory chemokine produced by macrophages. Baseline serum level of MIP-1β were dateable in all patients, and the level was significantly lower in DR (DR: 393±21 ng/ml vs non-DR: 437 ±46 ng/ml, p=0.012). Using multivariate logistic regression, lower MCP-1 was significantly associated with csDMARDs response (OR=0.87, 95%CI: 0.77 to 0.99, p=0.034) after adjustment of age, ESR and pain score at baseline. MIP-1β were also positively correlated with rheumatoid factor (r=0.559, p=0.02) at baseline and SDAI at month 6 (r=0.412, p=0.012).
Conclusion: Lower serum level of MIP-1β was associated with csDMARDs response in patients with ERA. Further validation will testify current findings.
ACCP – anticyclic citrullinated peptide; VAS – visual analogue scale; ESR – erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP – C-reactive protein; DAS- disease activity index; CDAI – clinical disease activity index; SDAI – simplified disease activity index; NSAIDs – Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs; csDMARDs – conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs
1Age, sex and other variables with p<0.1 are listed. 2 adjusted for age, ESR and VAS pain at baseline. ESR – erythrocyte sedimentation rate; MIP_1β - Macrophage inflammatory protein_1β; VAS – visual analogue scale
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheng I, So H, Li M, Chow E, Wong C, Tam L. Lower Serum MIP-1β Level Is Associated with CsDMARDs Response in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lower-serum-mip-1%ce%b2-level-is-associated-with-csdmards-response-in-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lower-serum-mip-1%ce%b2-level-is-associated-with-csdmards-response-in-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/