Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Anti-SARS-CoV2 mRNA vaccination may result in blunted humoral immune responses with lower peak titers and a different kinetic in patients with rheumatic diseases receiving immunomodulatory therapies compared to healthy controls1.
Vaccine-induced humoral immune responses will elicit IgM and IgA responses and an isotype class switch is required to establish robust IgG responses directed against different viral antigens. We hypothesize that lower peak titers of vaccine-induced anti-S1 result from a delayed isotype switch in RA patients on immunomodulatory treatment
Methods: We seek to analyse the ratio of IgG to IgM and IgG to IgA that may be regarded as a surrogate for a delayed isotype class switching after vaccination with anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-based vaccines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
We prospectively analysed RA patients and HC after receiving mRNA anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Blood sampling was performed before (T0) the first vaccine dose, three weeks (T1) and six weeks (T2) after the first dose, and after 12 (T3) and 24 weeks (T4). Humoral immune responses (IgG, IgA and IgM) to four different SARS-CoV-2 antigens (receptor binding domain (RBD), spike glycoprotein subunits S1 and S2, and nucleocapsid protein (NP) were determined by using the multiplex immunoassay ABCORA.1
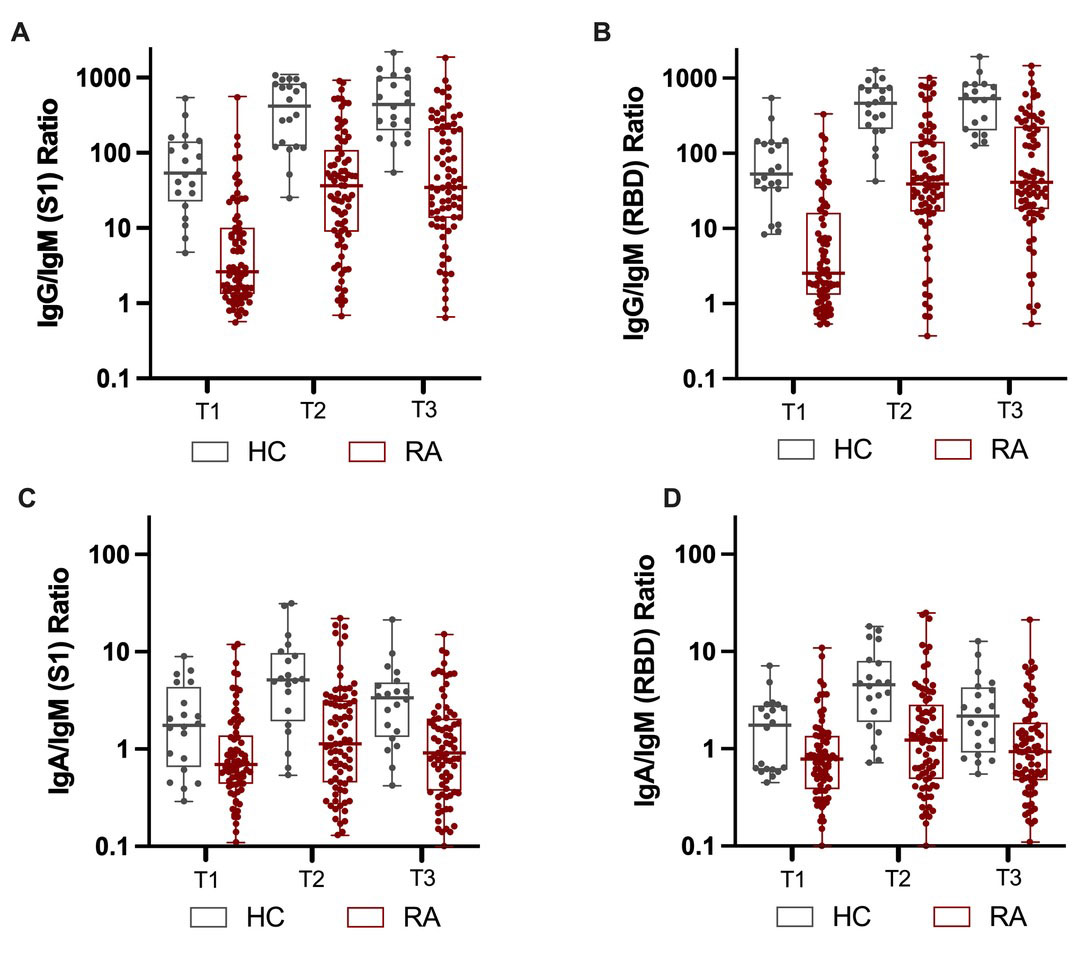
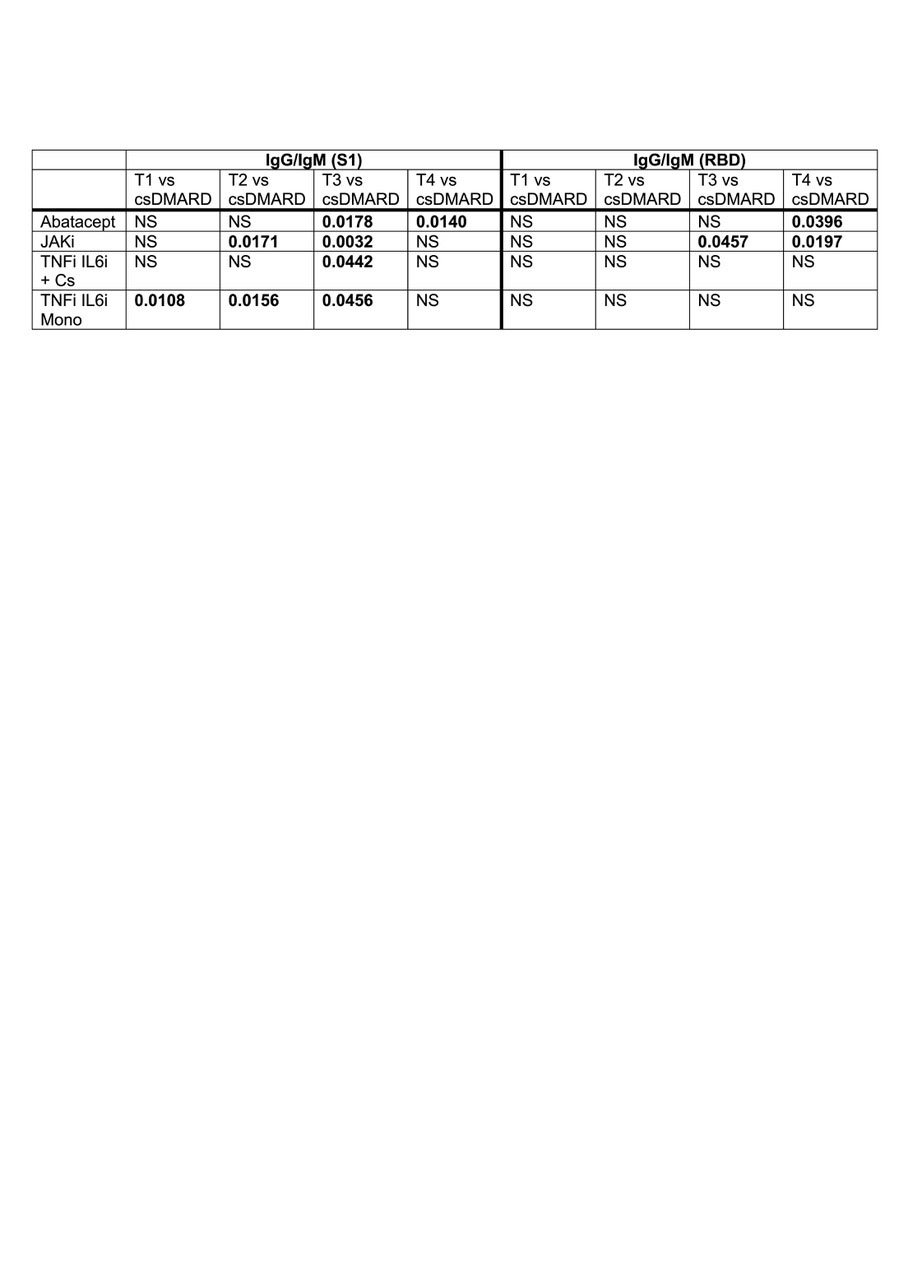
Results: We longitudinally assessed the isotypic humoral immune responses against four SARS-CoV-2 antigens in 21 healthy controls (HC) and 73 RA patients on DMARD therapy following a standard two dose regimen of mRNA based anti-SARS-CoV2 vaccines. HC showed a rapid increase of IgG/IgM ratio two weeks after the second vaccine dose. Overall IgG/IgM and IgG/IgA ratios were significantly lower in RA patients and involving immune responses to S1 and RBD (Fig.1). Patients treated with abatacept, JAK inhibitors and anti-cytokine (TNFa, IL-6, IL-1) biologics in combination with csDMARDs were more likely to develop a delayed IgM/IgG isotype switch that resulted in a delayed and decreased IgG response (Table 1).
Conclusion: This study provides insights into the attenuated immune response following an mRNA based anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with RA. The decreased immune response after the first dose of an mRNA based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine with an enhanced immune response to subsequent doses is in line with the assumption of a delayed isotype class switch from IgM to IgG.
References 1. Abela IA. 2021. Nat Commun 12: 6703
Boxplots showing antibodies IgG/IgM ratio for S1 (A, C) and RBD (B, D) isotype as determined by Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV_2 (S) assay at 3, 6 and 12 weeks following the first vaccine dose in HC and RA patients. T0=baseline, T1=3 weeks after 1st vaccination, T2=2 weeks after 2nd vaccination, T3=12 weeks after 1st vaccination, T4= 24 weeks after 1st vaccination.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schmiedeberg K, Abela I, Vuilleumier N, von Kempis J, Rubbert-Roth A. Lower mRNA-anti SARS-Cov2 Induced IgG Antibody Responses to S1, S2 and RBD May Result from a Delayed IgA and IgM Class Switch in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lower-mrna-anti-sars-cov2-induced-igg-antibody-responses-to-s1-s2-and-rbd-may-result-from-a-delayed-iga-and-igm-class-switch-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lower-mrna-anti-sars-cov2-induced-igg-antibody-responses-to-s1-s2-and-rbd-may-result-from-a-delayed-iga-and-igm-class-switch-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/