Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab (RTX) is an effective and safe treatment for patients with RA, but is associated with an increased risk for reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Therefore, it is recommended by (inter)national guidelines to screen for HBV prior to start of RTX treatment [1]. However, HBV reactivation risk is expected to be lower in RA patients compared to lymphoproliferative diseases, although exact incidences are not known. Together with the low incidence of unknown HBV in RA patients from non-endemic areas, also thanks to extensive monitoring for liver abnormalities prior to RTX, the value of routine HBV serological screening prior to RTX in non-endemic countries is doubtful. Indeed, screening adherence in practice is varying and suboptimal [2]. The aim of this study is to determine the protocol adherence and yield of routine serological screening for HBV in RA patients starting with RTX treatment in the eastern part of the Netherlands.
Methods: All patients with a clinical diagnosis of RA who intended to start with RTX from April 2012 until April 2024 were included in this retrospective single-centre cohort study. Data on patient and disease characteristics as well as HBV screening results were collected. Protocol adherence to HBV testing and proportion of positive test results, defined as hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) positive (active or chronic infection) and/or hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) positive (resolved infection), were assessed.
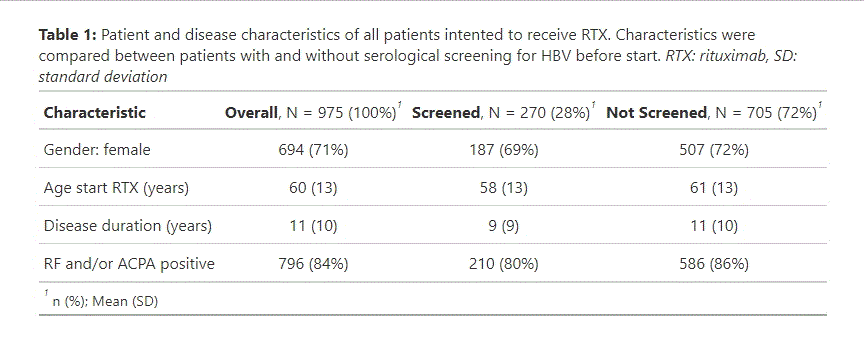
Results: Of 975 patients who intended to start with RTX (1x1000mg or 2×500 mg per cycle) from April 2012 until April 2024, 270 (28%) were serologically screened for HBV (Table 1). Six patients (2.2%) had a positive screening result (1 HbsAg+, 5 HbsAg-/anti-HBc+), three of whom eventually did not start RTX. The HbsAg+ patient and one of the HbsAg-/anti-HBc+ patients had a known history of HBV. From the other patients, three were born in an endemic country. No patient from either screened or unscreened group had an active HBV infection within one year after start of RTX.
Conclusion: Adherence to routine serological screening was low, similar to what is known from literature [2], and screening for HBV prior to start of RTX treatment never revealed previously unknown or unsuspected relevant HBV infections. Also no patient developed an RTX related HBV reactivation. Routine serological screening for HBV therefore seems redundant in a low-risk population, and HBV testing should be reserved for patients with known risk factors.
Reference
[1] Fragoulis, G.E., et al., Ann Rheum Dis, 2023. 82(6): p. 742-753.
[2] Brakenhoff, S.M., et al., Eur J Intern Med, 2023. 108: p. 68-73.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bovens P, Wientjes M, den Broeder N, Ten Cate D, Van der maas A, den Broeder A. Low Yield of Routine Serological Screening for Hepatitis B in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Starting Rituximab Therapy in a Non-Endemic Country [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-yield-of-routine-serological-screening-for-hepatitis-b-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-starting-rituximab-therapy-in-a-non-endemic-country/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-yield-of-routine-serological-screening-for-hepatitis-b-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-starting-rituximab-therapy-in-a-non-endemic-country/