Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), an IL-23p19-subunit inhibitor, is efficacious in treating patients (pts) with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). In the Phase 3, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled DISCOVER-2 study, GUS 100mg given every 4 or 8 weeks (Q4W or Q8W) significantly improved joint and skin symptoms; GUS-treated pts had smaller mean changes in radiographic progression vs. placebo (PBO) at W24.1 Clinical response rates and a favorable safety profile were durable through W100.2, 3 We now report details of radiographic assessments comprising the third reading session through W100 of DISCOVER-2, including relationships between radiographic changes and measures of clinical outcomes.
Methods: Biologic-naïve adults with active PsA (≥5 swollen joint count + ≥5 tender joint count; CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL) were randomized (1:1:1) to GUS 100mg Q4W; GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or PBO with crossover to GUS 100 mg Q4W (PBO→Q4W) at W24, all through W100. Radiographic Reading Session 3 included assessments at W0, W24, W52, and W100 (or at discontinuation after W52) from pts continuing study treatment at W52; readers were blinded to treatment group and timepoint. Observed mean changes in total PsA-modified van der Heijde-Sharp (vdH-S), joint space narrowing (JSN), and erosion scores are reported. Changes in total vdH-S scores from W0-100 were determined in pts who did and did not achieve clinical response at W100, assessed by ACR20/50/70, low disease activity (LDA) based on Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis score (DAPSA; ≤14) or Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score (PASDAS; ≤3.2), minimal disease activity (MDA), and normalized HAQ-DI score (< 0.5).
Results: Of 739 enrolled and treated pts, 664 had evaluable data from Reading Session 3; 629 pts had evaluable data from W52-100. Mean total baseline vdH-S scores were 28.0 (Q4W), 23.9 (Q8W), and 25.6 (PBOàQ4W). Mean progression of joint damage from W0-24 was numerically lower in GUS- than PBO-treated pts for erosion, JSN, and total vdH-S scores (Table), consistent with the results from Reading Session 1.1 Mean changes in radiographic scores from W52-100 indicated low rates of radiographic progression across GUS groups. Among GUS-randomized pts, mean changes in vdH-S score from W0-100 were numerically lower for pts achieving clinical response assessed using a variety of outcome measures (ACR20/50/70, DAPSA LDA, PASDAS LDA, MDA, and HAQ-DI < 0.5) when compared with pts not achieving response at W100 (Figure).
Conclusion: In a population of biologic-naïve pts with active PsA enriched for greater risk of radiographic progression, GUS 100 mg (Q4W or Q8W) was associated with low rates of radiographic progression through 2 years. Pts achieving clinical response across several global measures of disease activity or normalized physical function at W100 had lower mean changes in total PsA-modified vdH-S scores compared with nonresponders.
References
1. Mease PJ. Lancet. 2020 Apr 4;395(10230):1126-1136.
2. McInnes IB. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73: 604-616.
3. McInnes IB. Innovations in Dermatology. Presentation: March 16-20, 2021.
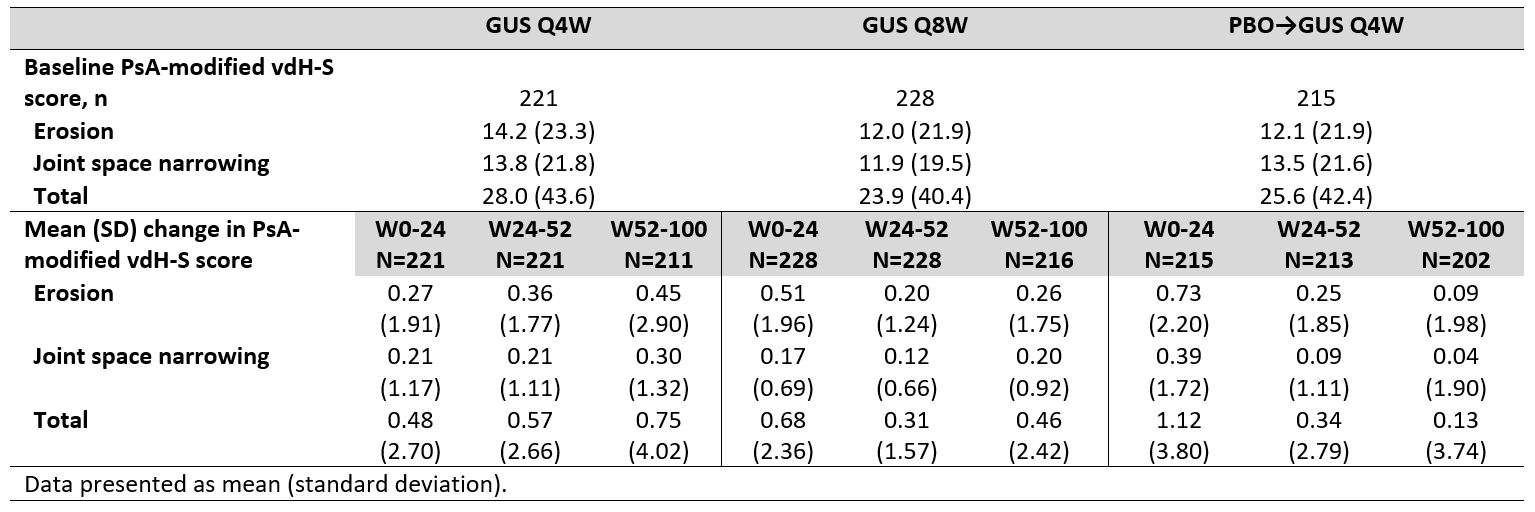 Table. Observed erosion, joint space narrowing, and total PsA-modified vdH-S scores through W100 of DISCOVER_2.
Table. Observed erosion, joint space narrowing, and total PsA-modified vdH-S scores through W100 of DISCOVER_2.
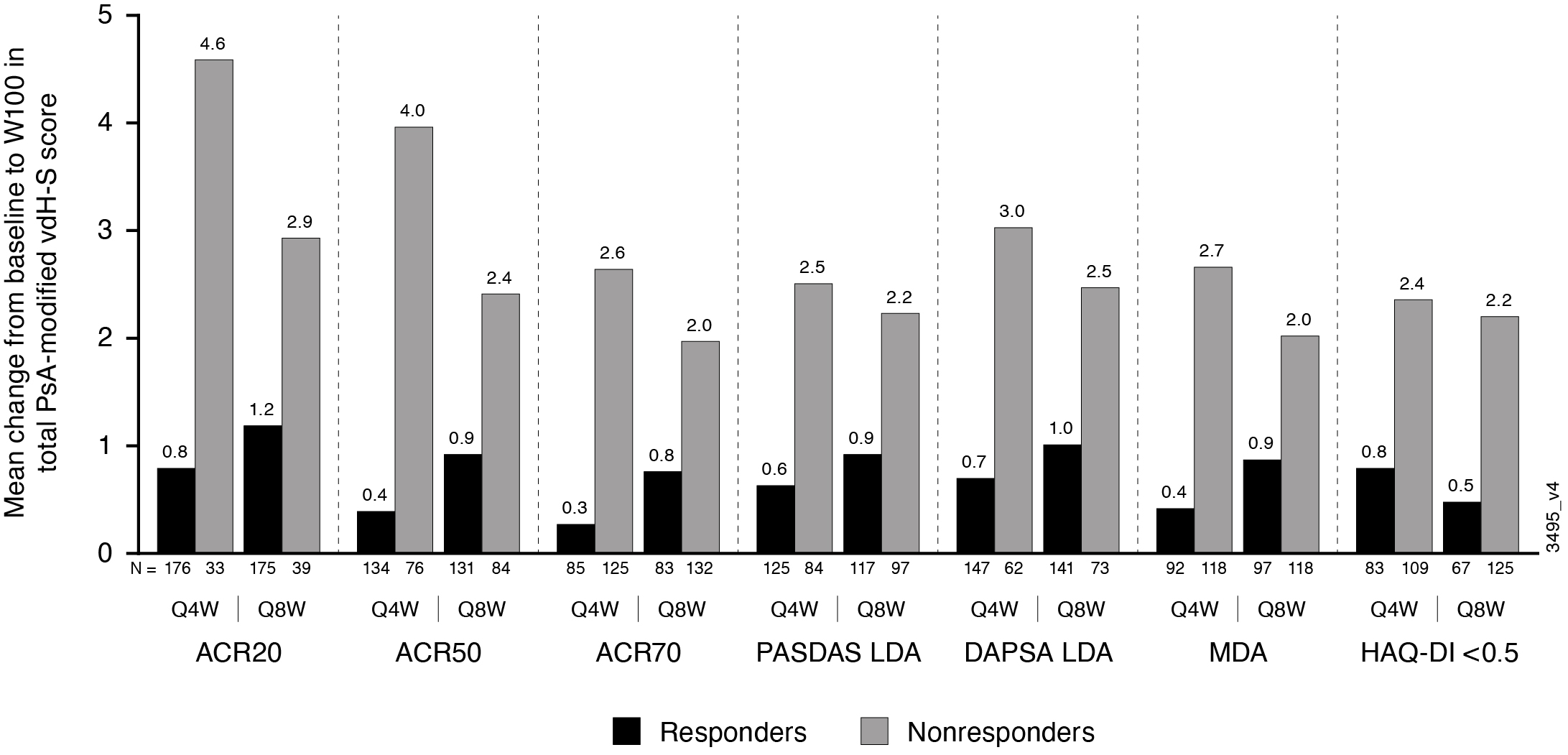 Figure. Mean changes in PsA-modified total vdH-S score from W0_100 for patients who did and did not achieve select clinical responses at W100.
Figure. Mean changes in PsA-modified total vdH-S score from W0_100 for patients who did and did not achieve select clinical responses at W100.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Gottlieb A, McInnes I, Rahman P, Kollmeier A, Xu X, Jiang Y, Sheng S, Shawi M, Chakravarty S, Lavie F, van der Heijde D. Low Rates of Radiographic Progression with 2 Years of Guselkumab (TREMFYA®), a Selective Inhibitor of the Interleukin-23p19 Subunit: Results from a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study of Biologic-naïve Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-rates-of-radiographic-progression-with-2-years-of-guselkumab-tremfya-a-selective-inhibitor-of-the-interleukin-23p19-subunit-results-from-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-cont/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-rates-of-radiographic-progression-with-2-years-of-guselkumab-tremfya-a-selective-inhibitor-of-the-interleukin-23p19-subunit-results-from-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-cont/
