Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In severe, early progressive systemic sclerosis (SSc), autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) allows significant improvements in overall and event free survival. The objectives of this study were to quantify the magnitude, domains and duration of improvement in HRQoL in SSc subjects treated with AHSCT compared to standard of care in the setting of routine clinical care.
Methods: We compared SSc patients treated with AHSCT to SSc patients who fulfilled ASTIS eligibility criteria for AHSCT but who were treated with standard of care. Outcomes of interest were the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) and its disease-specific visual analogue scales (VAS), and the Short Form Health Survey-36 (SF-36) Physical Component Summary (PCS) and Mental Component Summary (MCS) scores. Differences in HAQ, VAS and SF-36 scores were compared using linear models, adjusting for baseline scores and inverse probability of treatment weights (iptw), calculated as 1/propensity score (ps) for the AHSCT subjects and 1/(1-ps) for the standard of care subjects. Propensity scores were estimated using logistic regression including the following covariates: female, age, disease duration, and other variables with a p-value < 0.10 in univariate comparisons. In addition, to account for the potential informative censoring between baseline and follow-up visits, the inverse probability of censoring weights (ipcw) was estimated by logistic regression, using the same covariates as in the propensity score model. The outcome model was a marginal linear model including only AHSCT, weighted by the product of the iptw and ipcw.
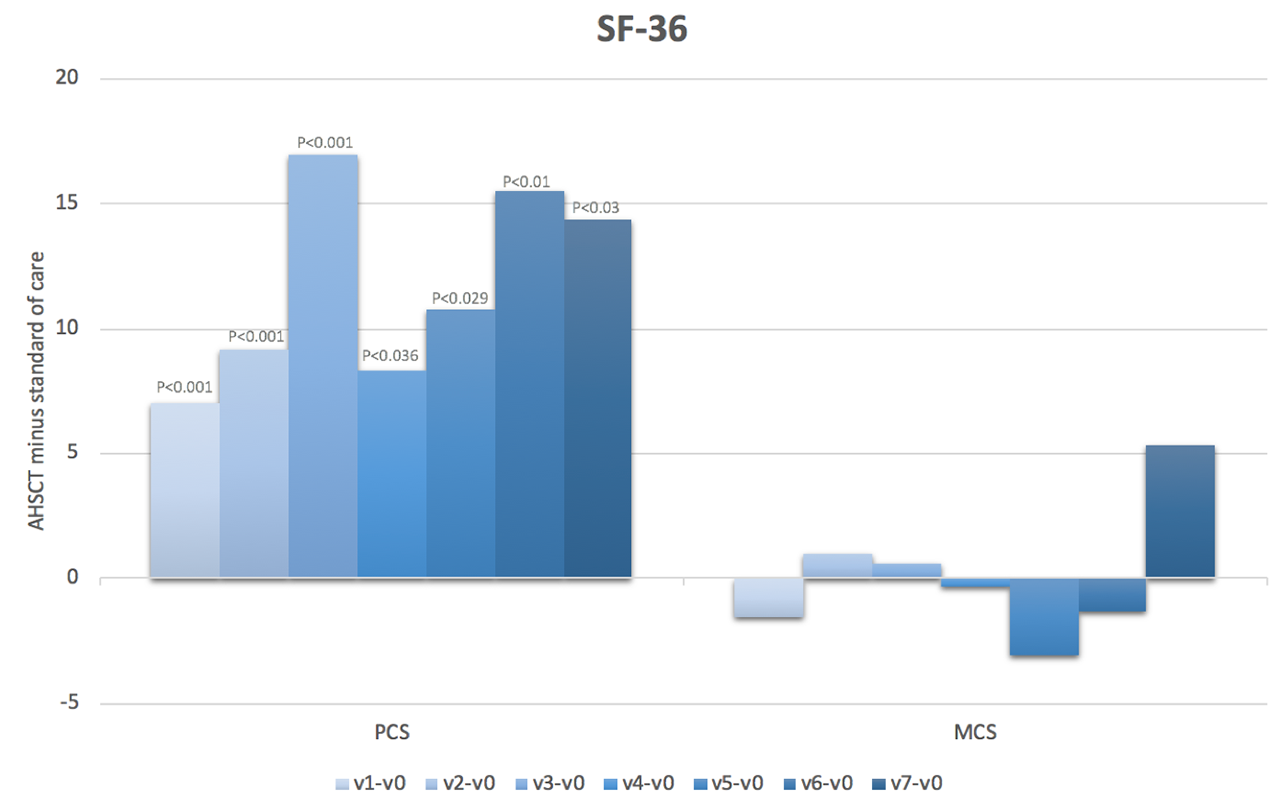
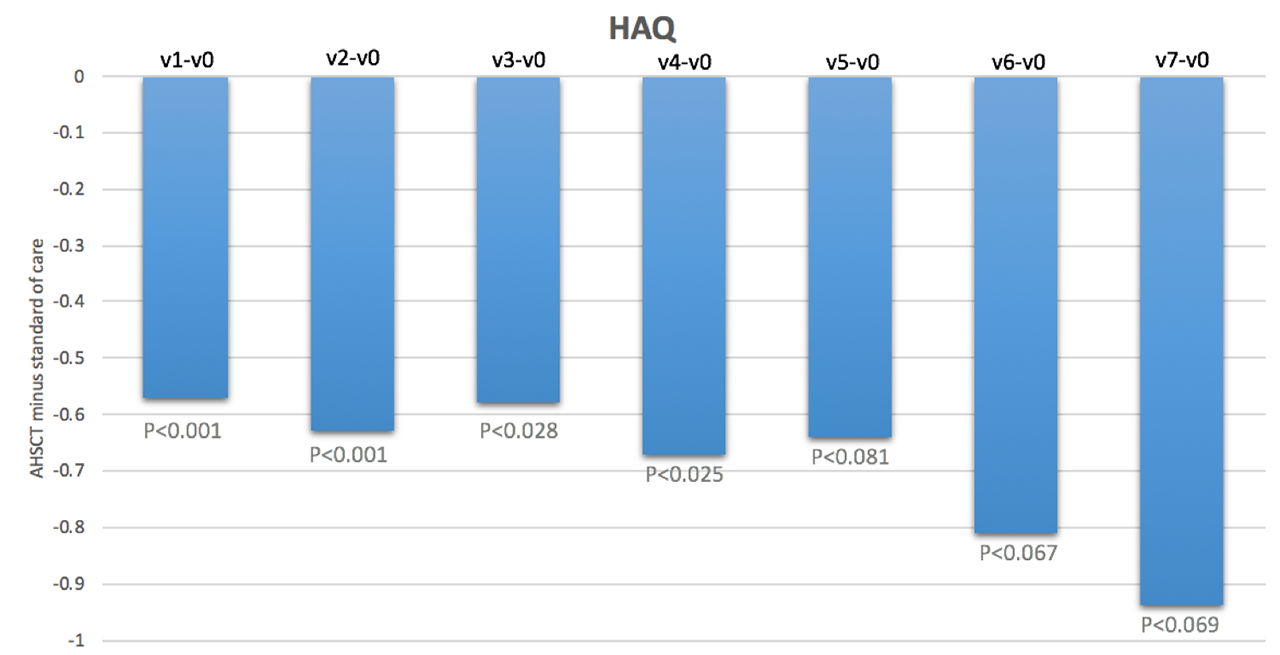
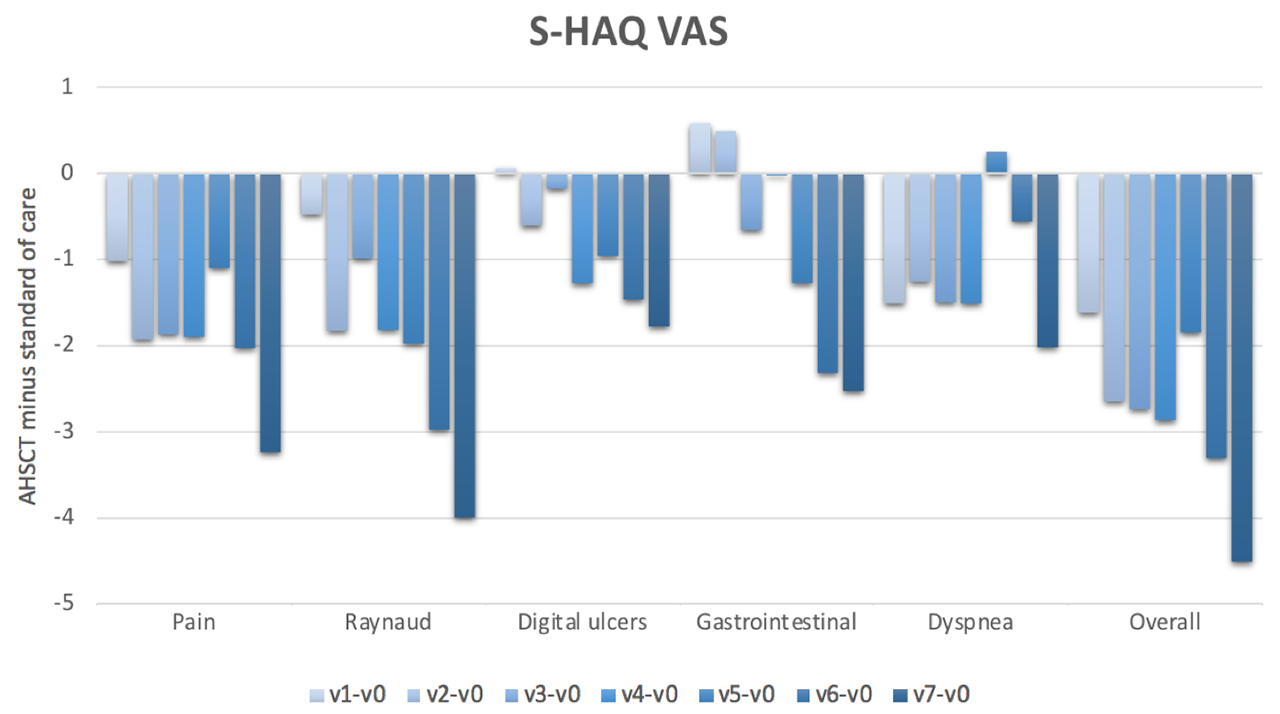
Results: We included 41 subjects who underwent AHSCT (66% female, mean age 44.7 years, mean disease duration 2.6 years, mean modified Rodnan skin score (mRss) 25, interstitial lung disease (ILD) present in 93%, FVC %predicted 79% and DLCO %predicted 55%) and 69 subjects treated with standard of care (78% female, mean age 53.9 years, mean disease duration 1.5 years, mean mRss 27, ILD 47%, FVC %predicted 84% and DLCO %predicted 64%). Baseline HAQ scores were 1.4+0.7 in both groups. Baseline SF-36 PCS and MCS scores were 33.4 and 30.1, and 41.8 and 46.2, respectively, in the AHSCT and standard of care subjects. At baseline, the most severely affected VAS scale was that of general health. On a scale of 0-10, the mean was 4.9 in the AHSCT subjects and 5.1 in the standard of care subjects. In marginal linear weighted models, HAQ, VAS and SF-36 PCS scores were significantly better in subjects treated with AHSCT compared to standard of care, and the differences largely surpassed minimal clinically important differences (Figures 1-3). These differences also increased over time. However, there were no differences in SF-36 MCS scores in subjects treated with AHSCT compared to standard of care.
Conclusion: AHSCT was associated with marked improvement in physical HRQoL compared to standard of care, and the improvement was sustained and increased over time. This adds considerable complementary data to traditional biomedical outcome measures to support the role of AHSCT in severe SSc. Further research will be needed to understand why there is no difference in mental HRQoL after AHSCT compared to standard of care.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maltez N, Puyade M, Lansiaux P, Wang M, Baron M, Colmegna I, Farge D, Hudson M. Longitudinal Changes in Health-related Quality of Life in Systemic Sclerosis Treated with Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Compared to Standard of Care [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-changes-in-health-related-quality-of-life-in-systemic-sclerosis-treated-with-autologous-hematopoietic-stem-cell-transplant-compared-to-standard-of-care/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-changes-in-health-related-quality-of-life-in-systemic-sclerosis-treated-with-autologous-hematopoietic-stem-cell-transplant-compared-to-standard-of-care/