Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) is a clinical evaluation score of the extent of cutaneous fibrosis in systemic sclerosis (SSc). mRSS has been associated with morbi-mortality in several studies. This study aimed to delineate different trajectories of mRSS changes overtime in a large database of patients and to compare patients’ characteristics in clusters of patients identified. In this report, the results for non-treated patients are presented.
Methods: From a large French multi-center database of 2098 SSc patients, we included patients fulfilling the 1980 ACR criteria with at least two available records of mRSS. Treatment status was defined as steroids or immunosuppressive intake. Group-based modelling was used to cluster similar mRSS patterns into trajectories. Then variables of clusters obtained were compared using the SAS software.
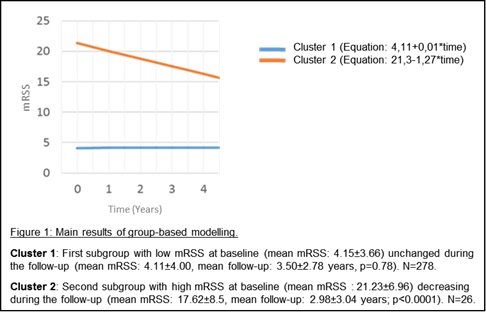
Results: 818 patients were included: 306 had never received treatment, 403 had been treated and treatment status was unavailable for 109. Treated patients were more severe than non-treated patients with a higher frequency of diffuse cutaneous (dc) SSc, anti-topoisomerase I antibodies, muscular and joint involvements, interstitial lung disease (p<0.0001), and mortality (p=0.003). Two subgroups of similar trajectory among untreated patients were identified (p<0.001, figure 1). The analysis of tendencies showed that patients in cluster 1 had a low baseline mRSS (mean mRSS: 4.15±3.66) that did not change significantly during the follow-up (mean mRSS: 4.11±4.00, mean follow-up: 3.50±2.78 years; p=0.78). Patients in cluster 2 had a higher mRSS at baseline (mean mRSS: 21.23±6.96) with a significant decrease during the follow-up (mean mRSS: 17.62±8.5, mean follow-up: 2.98±3.04 years; p<0.0001). Patients in cluster 2 had a higher frequency of dcSSc (77% vs. 7%, p<0.0001), anti-topoisomerase I antibodies (52% vs. 17%, p<0.0001), muscle involvements (23% vs. 6%, p=0.008), digital ulcers (56% vs. 34%, p=0.026), gastrointestinal tract involvements (42% vs. 20%, p=0.0079) and interstitial lung disease (25% vs. 1%, p<0.0001). There was no significant difference between the two clusters concerning heart involvement, pulmonary arterial hypertension and mortality.
Conclusion: This work led to the identification of two different clusters among non-treated patients from a French multicenter database, based on similar mRSS trajectories. Interestingly, mRSS of cluster 2 significantly decreased overtime whereas the patients received no immunosuppressive treatment. Nevertheless, they remained exposed to more severe complications than cluster 1. The analysis of the entire database and comparisons between treated and untreated patients might provide new insights into the natural history of this disease. EL and VS have contributed equally to this work.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ledoult E, Sobanski V, Mouthon L, Béhal H, Agard C, Lega JC, Jego P, Frances YM, Kaplanski G, Harle JR, Berthier S, Bienvenu B, Fain O, Mekinian A, Diot E, Dhote R, Le Quellec A, Amoura Z, Le Gouellec N, Kahn JE, Magy N, Balquet MH, Pugnet G, Papo T, Kieffer P, Queyrel V, Gaultier JB, Wahl D, Maurier F, Chatelus E, Pennaforte JL, Aumaître O, Lidove O, Belizna C, Boulon C, Truchetet ME, Pouchot J, Auxenfants E, Fauchais AL, Imbert B, Hachulla E, Launay D. Longitudinal Analysis of Modified Rodnan Skin Score in Systemic Sclerosis Using Group-Based Trajectory Modelling [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-analysis-of-modified-rodnan-skin-score-in-systemic-sclerosis-using-group-based-trajectory-modelling/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-analysis-of-modified-rodnan-skin-score-in-systemic-sclerosis-using-group-based-trajectory-modelling/