Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Peficitinib, a novel oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, demonstrated efficacy and an acceptable safety profile in a Phase 2b study (RAJ1 study, NCT01649999) and in Phase 3 studies (RAJ3 study [inadequate response to DMARDs], NCT02308163, and RAJ4 study [inadequate response to MTX], NCT02305849). In this long-term interim extension study (NCT01638013), we report the safety and efficacy data for peficitinib (mean treatment exposure, 22.7 months) in patients who previously completed these Phase 2b and 3 studies.
Methods: This multicenter, open-label extension study was conducted in Japan, Korea and Taiwan. All patients had RA previously diagnosed according to 1987 ACR criteria or 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria (RAJ1 study followed 1987 ACR criteria exclusively). Patients received oral peficitinib (50 mg, 100 mg or 150 mg) once daily. The starting dose was 100 mg (RAJ3/4) or 50 mg (RAJ1). Doses could be increased to 150 mg/day or reduced (from 100 mg/day or 150 mg/day) to 50 mg/day according to clinical response and safety assessment, as judged by the investigator. Prior and concomitant administration of study-specific non-biological DMARDs was dependent upon the preceding study. For patients in the RAJ1 study and RAJ3 monotherapy study with peficitinib, administration of DMARDs was prohibited from the end of the assessments to the initiation of administration of peficitinib in this extension study. For the RAJ3/RAJ4 peficitinib combination studies, with DMARDs (including MTX) and MTX, respectively, subjects received the concomitant drug concerned from the termination of study to the initiation of administration of peficitinib and throughout the treatment period in this extension study. Discontinuation of the concomitant drug or alteration of the dose was permitted within the range not exceeding or falling below the baseline dose in the previous study. Efficacy outcomes were assessed in the total patient population and grouped according to their preceding study.
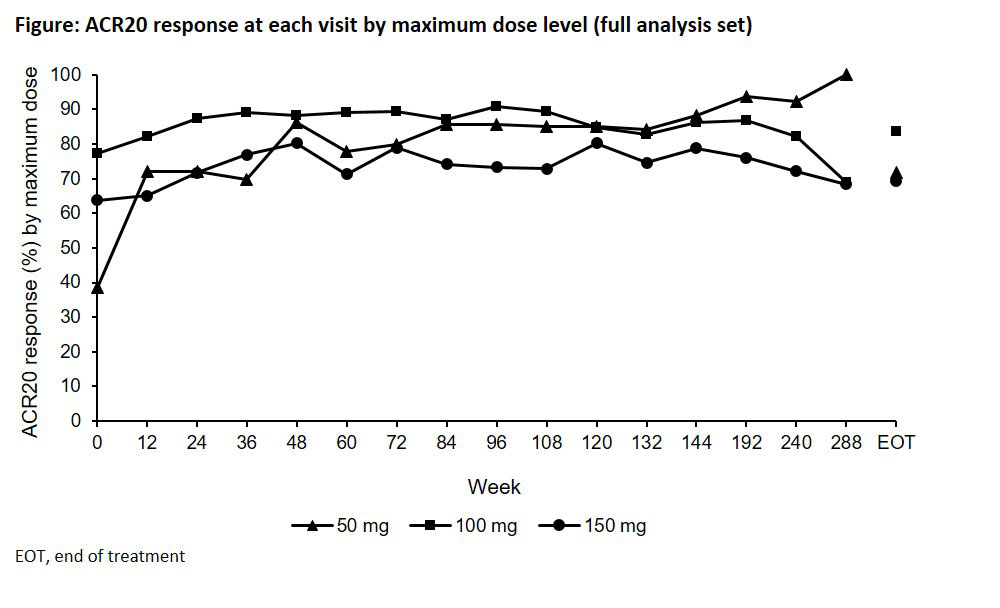
Results: In total, 843 patients received peficitinib: RAJ1, n=201; RAJ3, n=225; RAJ4, n=417. During long-term treatment, ACR20 responses were maintained from baseline for patients receiving maximum doses of 100/150 mg/day, and were improved then maintained in patients receiving maximum doses of 50 mg/day (Figure). ACR components and DAS28-CRP also demonstrated continuous improvements from the baselines of preceding studies. Treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) were reported in 757 (89.8%) patients (Table), primarily grade 1/2 in severity; the most common were nasopharyngitis, RA and herpes zoster. Rates of AEs of special interest (serious infections, herpes zoster-related disease and malignancies) were greater for patients from RAJ3/4 than RAJ1. There was no evidence to support a trend towards increasing incidence rate/100 patient years with treatment duration. One death during and one death after the study were considered probably and possibly related to study drug, respectively (Table).
Conclusion: This interim analysis after 22.7 months mean treatment exposure demonstrated no additional safety concerns were observed with longer term administration of peficitinib in RA patients, and efficacy was maintained for the study duration.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Takeuchi T, Tanaka Y, Tanaka S, Kawakami A, Song Y, Chen Y, Rokuda M, Izutsu H, Ushijima S, Kaneko Y, Nakashima Y, Shiomi T, Yamada E. Longer Term Safety and Efficacy of Peficitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis After 22.7 Months Mean Treatment Exposure: Interim Data from a Long-Term, Open-Label Extension Study in Japan, Korea and Taiwan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longer-term-safety-and-efficacy-of-peficitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-after-22-7-months-mean-treatment-exposure-interim-data-from-a-long-term-open-label-extension-study-in-japan-kore/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longer-term-safety-and-efficacy-of-peficitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-after-22-7-months-mean-treatment-exposure-interim-data-from-a-long-term-open-label-extension-study-in-japan-kore/