Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab(RTX) has been used for the management of systemic sclerosis(SSc). Its efficacy has been recently confirmed in a phase III clinical trial with extension observation up to 48 weeks, but long term data are limited. We analyzed the real life long-term use of RTX in SSc Italian patients.
Methods: SSc patients treated with RTX and with a follow-up ³36 months were included. Disease features at baseline, 6, 12, 24 months and latest available follow-up were analyzed. Persistence of RTX, reasons for RTX introduction and suspension, immunosuppressive therapy (ISTs) modifications, and RTX-related adverse events (AEs) were recorded.
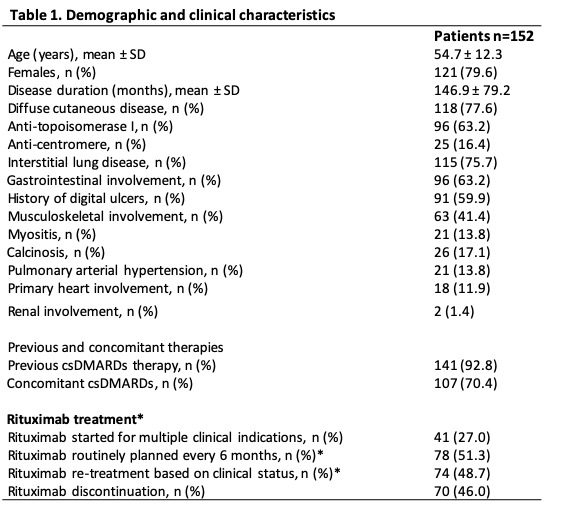
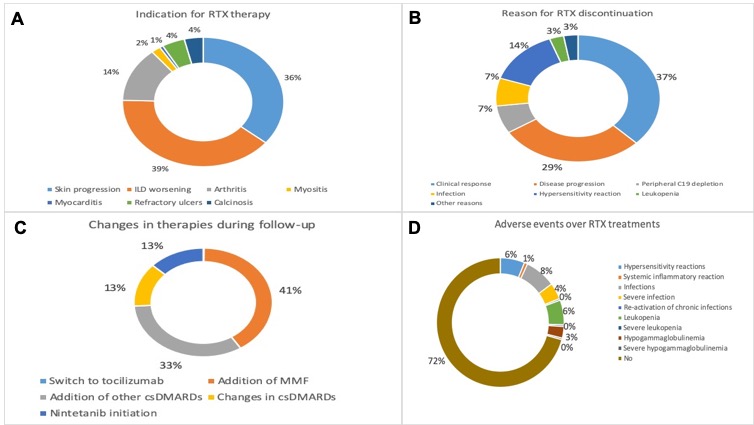
Results: the main characteristics of SSc patients are presented in on Table 1 (median follow-up was 72(52-96) months). RTX was primarily started for lung (38.8%), skin (36.2%), or arthritis (13.8%) worsening (Figure 1A). Patients were treated with RTX for a median of 42.5(26.0-69.7) months: 138 patients(90.8%) were treated with ³1 RTX course. In the entire cohort, mRSS significantly improved both at 6 months and at final follow- (mRSS: 11.9±8.0 and 8.3±7.4 vs 16.5±9.6) and in dcSSc patients with progressive skin involvement (mRSS: 15.6±9.6 and 9.2±7.9 vs 21.0±10.8)(p< 0.001 for all). Mean predicted (%) FVC and DLCO remained stable at 6 months and at final follow-up, both in the entire cohort (FVC: 105.1±84.2 and 87.0±23.5 vs 91.1±49.3; DLCO: 69.4±23.2 and 63.0±26.5 vs 62.1±19.7) and in patients with ILD (FVC: 88.7±38.2 and 82.9±22.5 vs 89.0±54.8; DLCO: 63.8±18.0 and 56.9±18.8 vs 58.7±19.9)(p= ns for all). in 41 patients(27.0%) ILD worsened, defined as a decline in pFVC ≥5% or in pDLCO ≥10% at 12±3 months. During follow-up, in 26 patients (17.1%) RTX was stopped for complete clinical response, especially in dSSc (p< 0.001); median time to discontinuation was 30.0 [24.0-48.0] months. RTX was stopped due to disease progression in 20 patients (13.2%) and due to infections in 5 (3.3%) (Figure 1B-C). AEs were recorded in 42 patients (27.6%)(Figure 1D). Discontinuation for both clinical remission or AEs was not influenced by indication for RTX, disease features or therapeutic scheme (p=ns).
Conclusion: our study shows that in Italian SSc patients, RTX is used as a long-term immunosuppressive drug due to its clinical effectiveness and satisfactory safety profile. The most common reason for RTX suspension was indeed clinical remission, whereas infectious concerns were only marginal.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
De Luca G, Campochiaro C, Cacciapaglia F, Del Papa N, Zanatta E, Airò P, Lazzaroni M, Giuggioli D, De Santis M, Alonzi G, Stano S, Binda M, Moccaldi B, Tonutti A, Iannone F, D'Agostino M, Dagna L, Matucci Cerinic m, Bosello S. Long-term Use of Rituximab in Systemic Sclerosis: A Real-life Italian Multicentre Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-use-of-rituximab-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-real-life-italian-multicentre-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-use-of-rituximab-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-real-life-italian-multicentre-study/