Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Filgotinib (FIL) is a preferential Janus kinase 1 inhibitor for the treatment of moderate to severe RA. FINCH 4 (NCT03025308) is an ongoing, open-label, long-term extension study designed to assess the safety and efficacy of FIL in patients with RA who have completed a Phase 3 parent study, FINCH 1, 2 or 3.1–3 This post hoc, interim analysis of FINCH 4 characterizes the long-term efficacy of FIL administered as monotherapy or combination therapy.
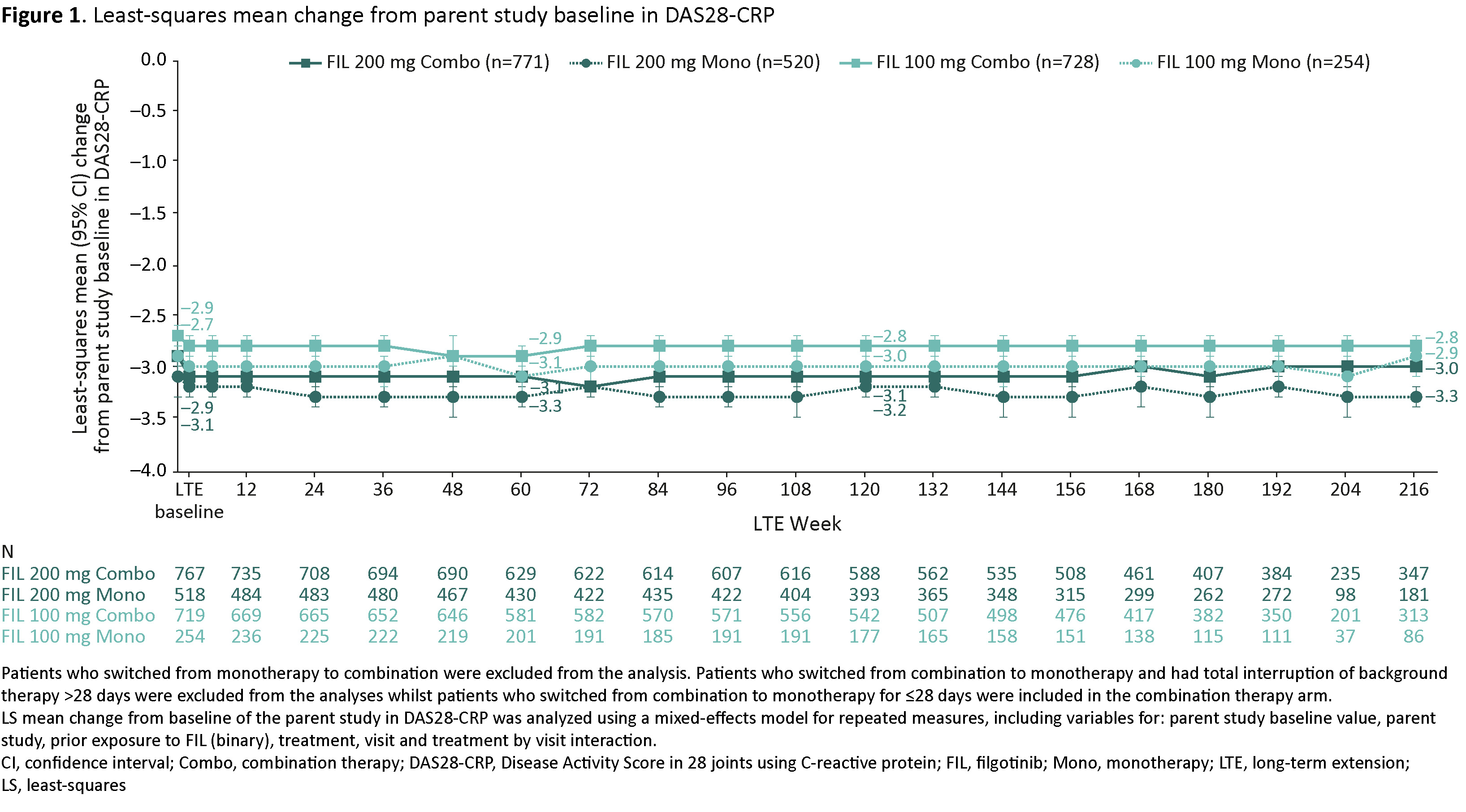
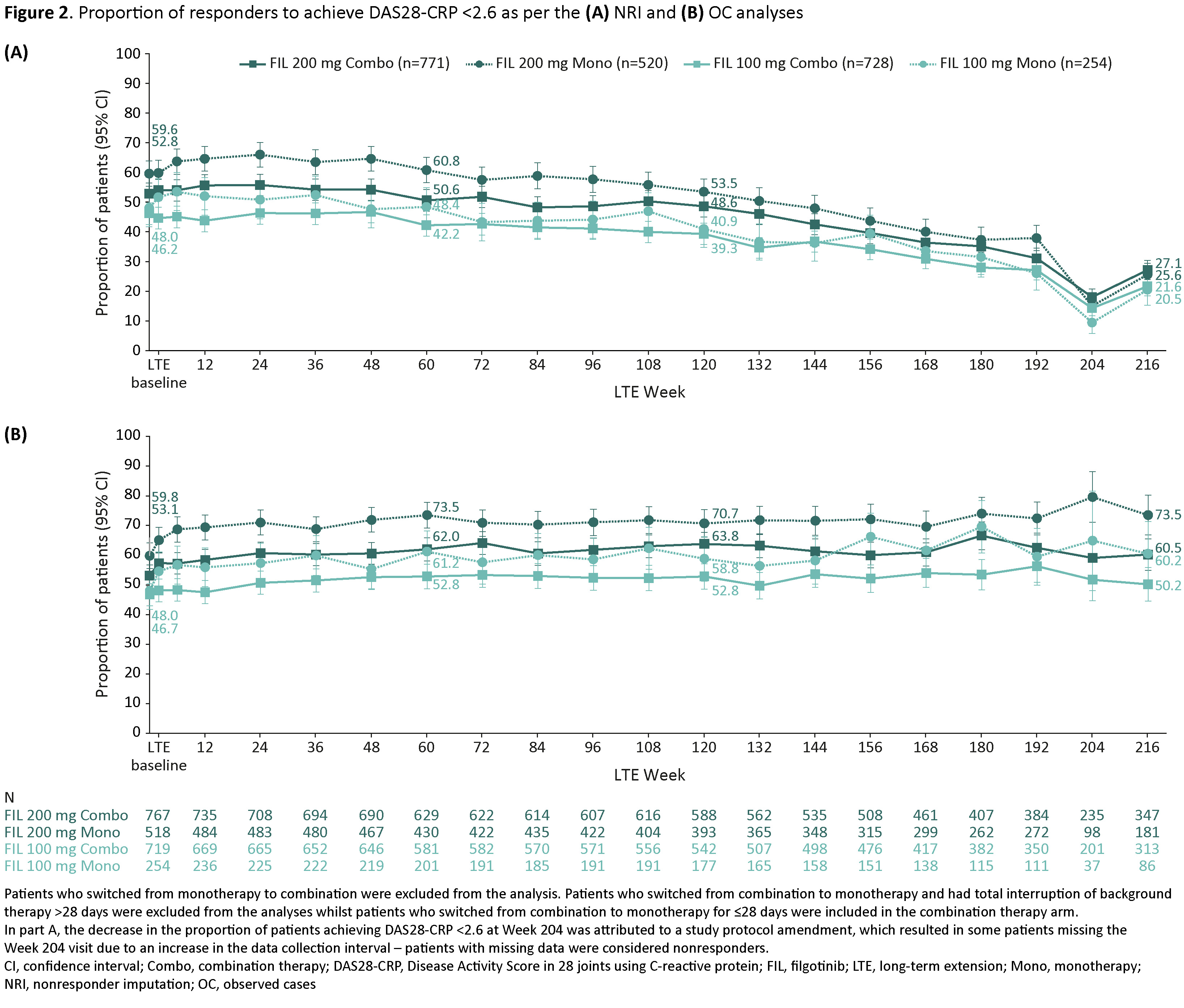
Methods: Patients enrolled in FINCH 4 from FINCH 1, 2 and 3 were assessed according to treatment group: FIL 200 mg (FIL200) or FIL 100 mg (FIL100) administered as monotherapy or combination therapy. Combination therapy and monotherapy were defined as FIL with and without concurrent methotrexate or other conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug from baseline of FINCH 4 for the duration of the study, respectively. Patients who switched from monotherapy to combination were excluded from the analysis as were patients who switched from combination to monotherapy and had a total interruption of background therapy of >28 days. Least-squares (LS) mean change from baseline of the parent study in Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) was assessed. The nonstratified response rates of DAS28-CRP < 2.6 and ≤3.2 were analyzed based on observed cases (OC) and nonresponder imputation (NRI).
Results: Database cutoff was May 8, 2023. A total of 2,273 patients were included in the analyses (771 patients received FIL200 combination therapy, 520 received FIL200 monotherapy, 728 received FIL100 combination therapy and 254 received FIL100 monotherapy). At Week 216, LS mean change (95% confidence interval) from baseline of the parent study in DAS28-CRP was –3.0 (–3.1, –2.9) in the FIL200 combination therapy arm, –3.3 (–3.4, –3.2) in the FIL200 monotherapy arm, –2.8 (–2.9, –2.7) in the FIL100 combination therapy arm and –2.9 (–3.1, –2.7) in the FIL100 monotherapy arm (Figure 1). Based on the NRI analysis, DAS28-CRP < 2.6 was achieved by 27.1% in the FIL200 combination therapy arm, 25.6% in the FIL200 monotherapy arm, 21.6% in the FIL100 combination therapy arm and 20.5% in the FIL100 monotherapy arm (Figure 2A). With the OC analysis, the corresponding proportions were 60.2%, 73.5%, 50.2% and 60.5% (Figure 2B). The proportion of patients to achieve DAS28-CRP ≤3.2 in the FIL200 combination therapy, FIL200 monotherapy, FIL100 combination therapy and FIL100 monotherapy arms was 35.4%, 30.4%, 30.9% and 24.8%, respectively, with the NRI analysis, and 78.7%, 87.3%, 71.9% and 73.3%, respectively, with the OC analysis.
Conclusion: Interim results from the FINCH 4 study show that across treatment subgroups, DAS28-CRP < 2.6 was achieved by 20.5–27.1% of patients at Week 216 based on the NRI analysis, and by 50.2–73.5% based on the OC analysis. The latter analysis indicates improvements in DAS28-CRP were maintained over time, regardless of whether FIL was administered as monotherapy or as combination therapy.
References:
1. Combe B, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:848–58; 2. Genovese MC, et al. JAMA 2019;322:315–25; 3. Westhovens R, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:727–38
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Buch M, Verschueren P, Caporali R, Huizinga T, Ekoka Omoruyi E, de Vries D, Ritsema J, De Leonardis F, Aletaha D. Long-term Efficacy of Filgotinib Monotherapy and Combination Therapy: Interim Results from a Post Hoc Analysis of the FINCH 4 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-of-filgotinib-monotherapy-and-combination-therapy-interim-results-from-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-the-finch-4-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-of-filgotinib-monotherapy-and-combination-therapy-interim-results-from-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-the-finch-4-study/