Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (BARI), an oral selective Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor, is approved for treatment of adults with moderately-to-severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). BARI demonstrated efficacy in patients (pts) with RA who have inadequate response to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD-IR) in a 24-week (wk) phase 3 study, RA-BEACON.1 BARI efficacy was evaluated up to 3 years (yrs) of treatment in a long-term extension (LTE) study, RA-BEYOND.2 This study discloses long-term efficacy of BARI 4 mg and 2 mg in bDMARD-IR pts in the completed study RA-BEYOND.
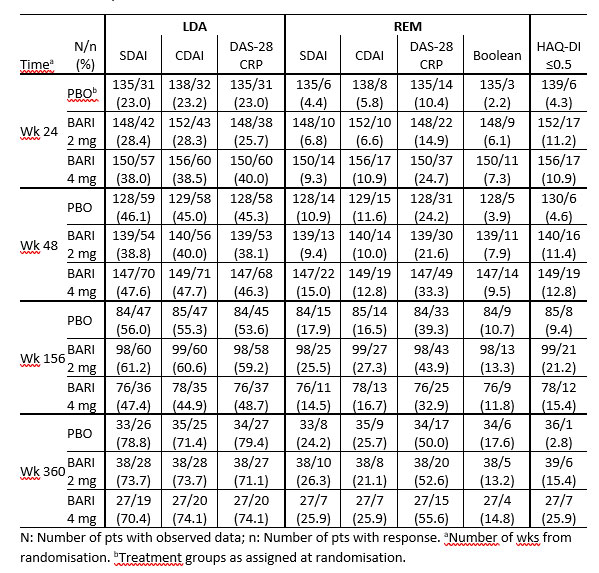
Methods: In RA-BEACON, pts were randomized 1:1:1 to BARI 4 mg, 2 mg, or PBO; pts with no response could be rescued after wk 16. Completers to wk 24 could enter with BARI 4 or 2mg RA-BEYOND for up to 360 wks (6.9 yrs). LTE data were analysed by treatment assigned at baseline in RA-BEACON as observed up to time of stepdown (if applicable), study discontinuation, or study completion, whichever occurred earlier. Efficacy response rates (RR) were assessed as proportions of pts with observed data up to wk 360 for low-disease activity (LDA) (SDAI ≤ 11, DAS28-hsCRP ≤ 3.2, CDAI ≤ 10), remission (REM) (SDAI ≤ 3.3, DAS28-hsCRP < 2.6, CDAI ≤ 2.8, Boolean), and physical functioning (HAQ-DI ≤ 0.5). No formal statistical comparisons were conducted.
Results: 156, 152, and 140 pts entered the LTE (4 mg, 2 mg, and PBO, respectively). Pts in BARI 4 and 2 mg arms had higher LDA and REM RR vs PBO at LTE entry (wk 24) (Table 1). PBO-treated pts achieved comparable RR to pts in the BARI 4 mg arm by wk 48 (24 wks after switch to BARI 4 mg) and up to wk 360. Of pts enrolled to RA-BEYOND, approx. 50% in BARI 4 mg, 65% in 2 mg and 61% in PBO remained active at wk 156; 17%, 26% and 26% at wk 360, respectively. SDAI LDA RR were 47%/70% and 61%/74% for pts treated with BARI 4 mg and 2 mg, at wk 156 (yr 3)/ 360 (yr 6.9), respectively; SDAI REM RR were 15%/26% and 26%/26% for BARI 4 mg and 2 mg, at wk 156/360, respectively (Table 1). SDAI and CDAI had comparable RR. DAS-28CRP LDA RR were similar to SDAI and CDAI, while REM RR were about twice those of SDAI and CDAI. HAQ-DI ≤ 0.5 RR was 15%/26% (BARI 4 mg), 21%/15% (BARI 2mg), and 9%/3% (PBO) at 3/6.9 yrs.
Conclusion: In observed data, BARI maintained efficacy and normative physical function bDMARD-IR population up to 6.9 yrs (360 wks).
References:
1. Genovese MC et al. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374:1243-52
2. Wells AF et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021; 8:987–1001
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Caporali R, Aletaha D, Sanmarti R, Takeuchi T, MO D, Haladyj E, Zaremba-Pechmann L, Taylor P. Long-Term Efficacy of Baricitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Inadequate Response to Bdmards: Results from RA-BEYOND up to 6.9-Years of Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-of-baricitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-inadequate-response-to-bdmards-results-from-ra-beyond-up-to-6-9-years-of-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-of-baricitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-inadequate-response-to-bdmards-results-from-ra-beyond-up-to-6-9-years-of-treatment/