Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
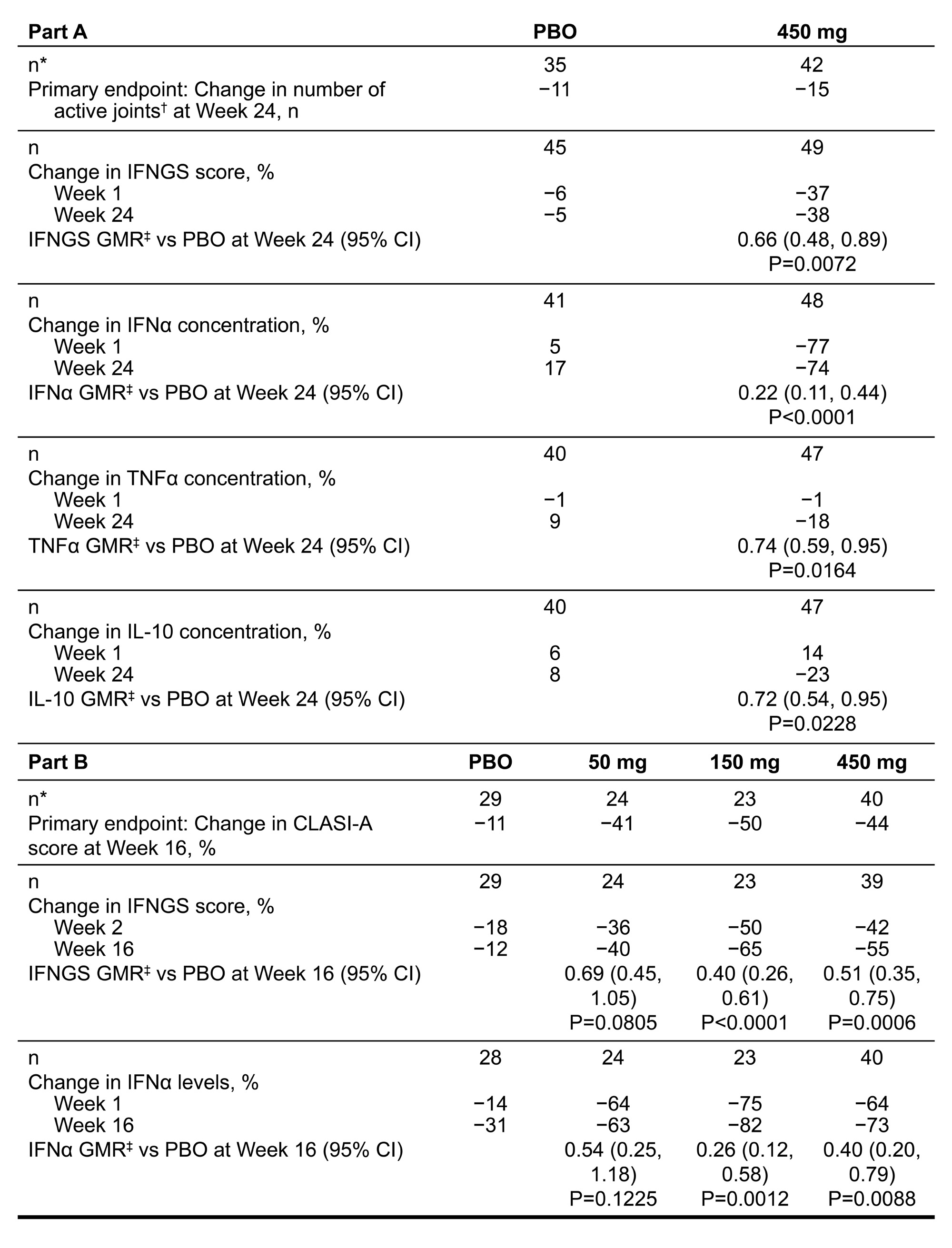
Background/Purpose: Litifilimab is a humanized IgG1 mAb targeting BDCA2, a receptor expressed on plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), that negatively regulates the production of Type I IFN and proinflammatory chemokines and cytokines.1,2 In the Phase 2 LILAC study of litifilimab (NCT02847598), Part A (participants with SLE, active arthritis and rash) and Part B (participants with active CLE, with or without SLE) met their primary endpoints at Weeks (W) 24 and 16, respectively.1,2 We evaluated the effects of litifilimab on IFN gene signature (IFNGS) scores from whole blood samples, serum IFNα concentrations, and other serum cytokine concentrations in LILAC participants.3,4
Methods: Expression of 22-gene panel IFNGS scores and concentrations of IFNα and other cytokines were examined over time in the modified intent-to-treat population (Part A N=120, Part B N=132) with available data at baseline (BL) and ≥1 post-BL visit. Treatment effects were estimated using a mixed model repeated measures approach. In Part A, IFNα concentration changes over time were compared with W24 total active joint counts and CLASI-A scores (Spearman rank correlations) and SLE Responder Index (SRI-4) status. In Part B, Pearson correlations between percent changes in CLASI-A score and IFNGS score were estimated and the dose-response relationship was estimated using a previously described MCP-Mod method.2
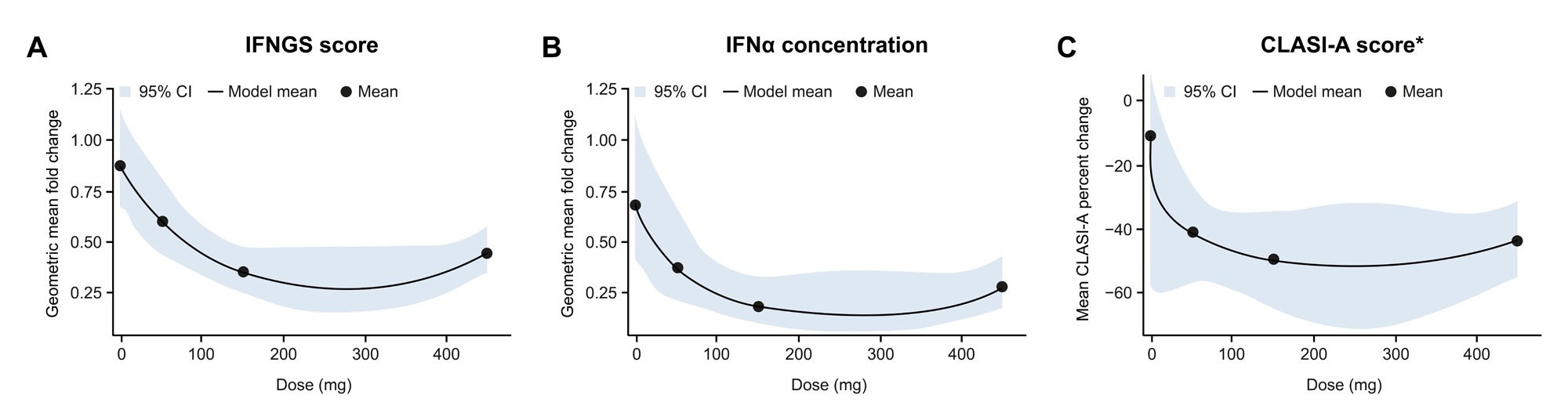
Results: As too few participants were IFNGS-low at BL, only data for the IFNGS-high subgroups are described. Litifilimab induced rapid, substantial, and sustained reductions in 22-gene IFNGS scores and IFNα concentrations that were greater (nominal P< 0.05) vs placebo (PBO) with litifilimab 150 mg (Part B) and 450 mg (Parts A and B) (Table 1 and Figure 1). In Part A, TNFα and IL-10 concentrations were reduced (nominal P< 0.05) with litifilimab 450 mg at W24 (Table 1); no strong evidence of this was seen in Part B. Change in IFNα concentration and change in total active joint count with litifilimab 450 mg in Part A were correlated (Spearman correlation estimates: PBO −0.15 [95% CI: −0.41, 0.16]; 450 mg 0.34 [0.07, 0.55]), as were changes in IFNα concentration and CLASI-A score (PBO −0.01 [−0.34, 0.31]; 450 mg 0.35 [0.10, 0.58]) at W24. A trend of greater median IFNα concentration reduction in W24 SRI-4 responders relative to non-responders was seen with litifilimab 450 mg. Confirmation of these findings in larger sample sizes is warranted. In Part B, the dose-response relationship was similar to that observed with the clinical responses (Figure 2) and percent change in CLASI-A score was correlated with percent change in IFNGS score in all treatment groups.
Conclusion: Litifilimab induced a rapid, substantial, and sustained reduction in 22-gene IFNGS scores and IFNα concentrations, and reductions in some biomarkers correlated with clinical responses. These results further support the mechanism of action for litifilimab and the role of Type I IFN and pDCs in SLE and CLE.5,6
1Furie R et al. N Engl J Med 2022;387:894–904
2Werth V et al. N Engl J Med 2022;387:321–331
3Werth V et al. J Invest Dermatol 2023;143(5 Supp):S101
4Furie R et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82(1 Supp):1453–1454
5Fetter T et al. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022;9:915828
6Rönnblom L, Leonard D. Lupus Sci Med 2019;6:e000270
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furie R, Werth V, Milliman E, Ferber K, Casey F, Brown R, Raitcheva D, Zoghbi J, Graham D, Kong G, Lahoud Y, Franchimont N, Barbey C. Litifilimab Modulates Type I IFN Biomarkers in Patients with SLE or CLE in the Phase 2 LILAC Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/litifilimab-modulates-type-i-ifn-biomarkers-in-patients-with-sle-or-cle-in-the-phase-2-lilac-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/litifilimab-modulates-type-i-ifn-biomarkers-in-patients-with-sle-or-cle-in-the-phase-2-lilac-study/